Nodes are Entire System Server nuclei or Entire System Server/UNIX servers and refer to machines or CPUs on which requests to the operating system are executed. They are distinguished by numerical identifiers in the same way as database IDs distinguish between different Adabas databases.
If you are using Entire Operations in a multi-CPU environment, you must define node numbers for machines. Networks and jobs can thus be defined to run under Entire Operations control on different nodes.
Within Entire Operations, each UNIX and Windows server is assigned a node number. More than one operating system server node can reside in one physical machine. The machines identified by node IDs can run different target operating systems.
Entire Operations recognizes the operating system, thus allowing cross-operating-system job control. Communication paths between otherwise isolated nodes are provided by the Software AG products Entire Net-work and EntireX Broker, which allow a transparent connection of nodes, irrespective of how they are physically linked.
This document covers the following topics:
Logging on and off an Operating System Server Node in the User's Guide
 To list all available functions for a Node metanode
To list all available functions for a Node metanode
In the object workspace, select the Node metanode and open the context menu.
The following functions are available:
| Function | Shortcut | Description |
|---|---|---|
| List | F8 | See Listing all Nodes. |
| New | CTRL+N | See Adding a Node Definition. |
| Refresh | F5 | See Refreshing Object Lists in the User's Guide. |
| Filter | F3 | See Filtering Objects in the User's Guide. |
| Logoff | -- | Log off from all Entire System Server nodes to which you are currently connected. |
| Show Connection Status | --- | See Monitoring the Node Connection Status in the User's Guide. |
| Export | --- | Open the Export Objects window to export all items of the Node metanode: see Exporting Objects in the Import/Export Functions documentation. |
| Set Drag And Drop Function | -- | See Drag & Drop in the User's Guide. |
 To list all available functions for a Node instance
To list all available functions for a Node instance
In the object workspace, select a Node instance and open the context menu.
The following functions are available:
| Function | Shortcut | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Open | CTRL+O | See Displaying or Modifying a Node Definition. |
| Display | CTRL+D | See Displaying or Modifying a Node Definition. |
| Delete | DELETE | See Deleting a Node Definition. |
| List Active Jobs | --- | See Listing Active Jobs. |
| Logon | CTRL+ALT+L | Explicitly log on to an Entire
System Server node.
For details, see Logging on to an Operating System Server Node in the User's Guide. |
| Logoff | --- | Explicitly log off from an Entire System Server node. |
| Add to Connection Status | --- | See Monitoring the Node Connection Status in the User's Guide. |
| Trace Level | -- | See Trace Levels for UNIX and Windows Nodes. |
| Export | --- | Open the Export Objects window to export a node: see Exporting Objects in the Import/Export Functions documentation. |
| Add to Workplan | --- | See Add to Workplan in the User's Guide. |
This section covers the following topic:
The Trace Level function only applies to UNIX and Windows nodes.
It is used to specify whether a trace is written to the log file and to determine the trace level (complexity) of the trace if written to the file. Valid input values:
| Trace Level | Description |
|---|---|
0 |
No trace is written to the log file. |
1 - 99999
|
A trace is written to the log file
with different complexity levels from 1 (low) to
99999 (high).
|
 To list all nodes defined to Entire Operations
To list all nodes defined to Entire Operations
In the object workspace, select the Node metanode and choose from the context menu, or press F8.
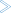
A Node List window similar to the example below opens:
The list is sorted by the Number column (default) in ascending order.
You can click on the column by which you want to sort the list. A triangle in the column indicates the column by which a list is sorted (in the example above, the Number column).
All columns are shown by default.
The columns are explained in Columns: Operating System Server Table.
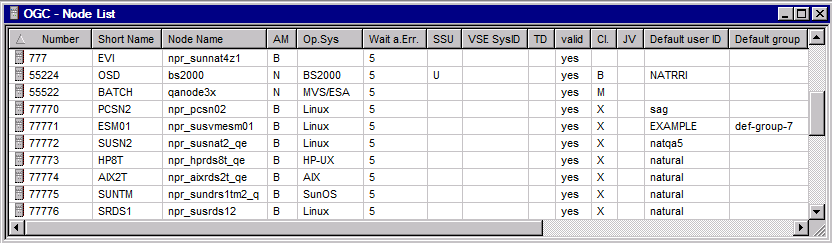
If you want to reorder columns or reduce the number of columns shown in the Node List window, choose Columns from the context menu:
Uncheck the column(s) you want to hide from the list and choose Hide.
Or:
Select the column you want to shift and choose
Move Up or Move Down to move the
selected column left or right in the list.
You cannot move or hide the Number column.
When you are finished, choose OK to save and apply your changes.
Or:
Choose Cancel to undo all changes.
Any column changes are persistent and retained for future sessions.
If required, choose to restore the default settings for the columns.
This section covers the following topics:
The columns contained in the Node List window are explained in the following table.
| Column | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Number | Entire System Server or UNIX node number. | |
| Short Name | Short node name. | |
| Node Name | User-defined (long) node name. | |
| AM | Access mode: | |
N
|
Use Entire Net-Work for Mainframe nodes. | |
B
|
Use EntireX Broker for UNIX and Windows nodes. | |
L
|
Local node (invoked directly on the machine where Entire Operations is running; for Entire Operations on UNIX and Windows only). | |
| Op. Sys. | Operating
system under which the node is running as received from the last
SYSTEM-INFO call to Entire System Server or UNIX/Windows system
information.
|
|
| Wait a.Err. | Wait after error.
Time in minutes to wait until the next node access after a temporary error. |
|
| SSU | Submit Security User
Type: see Fields: Monitor Defaults - General.
If empty, the system-wide default is in effect for this node. |
|
| VSE SysID | The SYSID defined for a z/VSE node is added to the job cards of jobs submitted on this node. | |
| TD | Time difference between local time and GMT in hours if the node is in a different time zone. | |
| Valid | Possible values: | |
yes
|
Node can be used. | |
no
|
Node has been disabled. | |
| Cl. | Operating system class: | |
B |
BS2000 | |
M |
z/OS | |
V |
z/VSE | |
W |
Windows | |
X |
UNIX, Linux | |
| JV | Applies to BS2000 nodes
only.
Indicates whether a BS2000 job variable is supported. Possible values: |
|
Y |
Variable is supported. | |
| empty column | Variable is not supported. | |
|
The value is returned by Entire System Server for each BS2000 node defined in your environment. Note: |
||
| Default user ID | UNIX or Windows user ID the Monitor uses for operations that are independent of a specific network or job. | |
| Default group | UNIX: If this column is
empty, the default group name as defined in /etc/passwd is used.
Otherwise, this column contains the name displayed when you issue the UNIX
command groups.
Windows: The domain name used to log on to the server. |
|
| Broker ID | Attributes
of the EntireX Broker service definition for the node.
See also Node - Broker in Modifying a Node Definition. |
|
| Server Name | ||
| Service | ||
| User ID | ||
This section covers the following topics:
 To display or modify a node definition
To display or modify a node definition
In the object workspace, select a Node instance.
If you want to display a node definition, choose from the context menu or press CTRL+D.
Or:
If you want to modify a node definition, choose
from the context menu or press
CTRL+O.
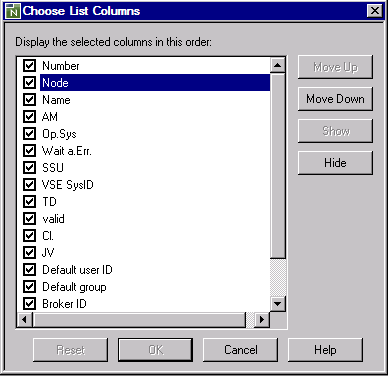
A Display Node or Maintenance Node window (respectively) with an open General page similar to the example below opens:
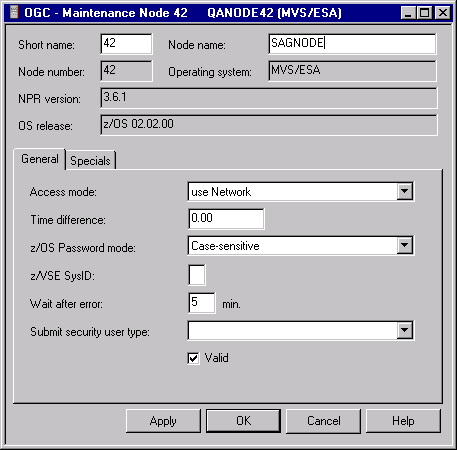
Now you can change the definitions for the selected node.
The fields in the upper section of the window and on the tabbed page General are used to specify general definitions for the node. They are explained in Fields: Node Definition - General.
The fields on the other tabbed pages available are explained in the following section.
The tabbed page Specials specifies user- and group-specific information for the node as shown in the example below:
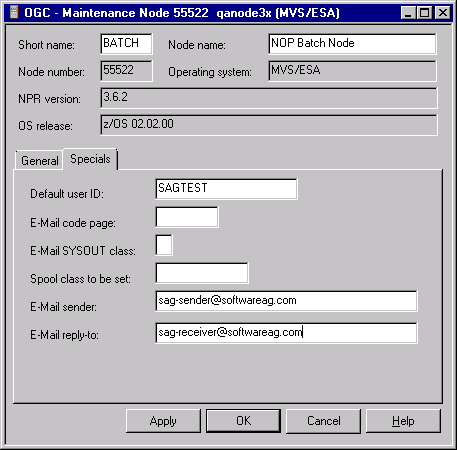
The fields available on the Specials page are described in
If is specified as the access mode, the additional tab Broker is displayed which contains EntireX Broker details for UNIX and Windows nodes.
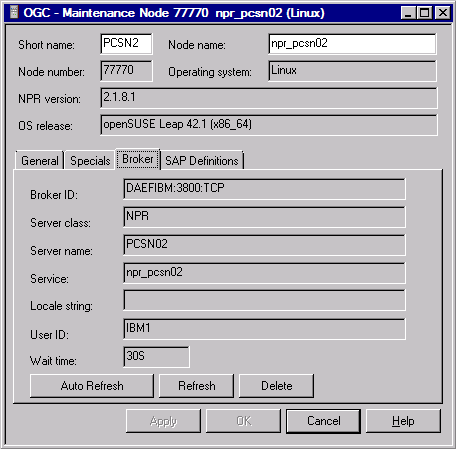
The fields contain the current attributes of the EntireX Broker service definition for the node.
The EntireX Broker service definition can only be modified in the SATSRV text object in the Natural SYSSATU system library on the server. If you change the service definition, choose Refresh to force a re-read of the service definition from SATSRV/SYSSATU into Entire Operations.
Choose Delete if you want to delete all fields of an EntireX Broker service definition in Entire Operations at once.
Note:
This does not delete any entries in
SATSRV/SYSSATU.
If is specified as the access mode, the additional tab SAP Definitions is displayed which contains SAP settings for UNIX and Windows nodes.
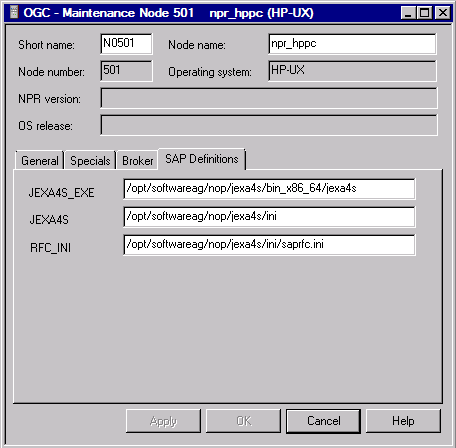
The fields on the tabbed page are explained in Fields: Node - SAP Definitions.
Choose .
Your changes are saved.
 To add a node definition
To add a node definition
In the object workspace, select the Node metanode and choose from the context menu, or press CTRL+N.
A Create new Node window opens.
The input fields and tabbed pages available in the window correspond to the fields and tabbed pages in the Maintenance Node window:
The fields in the upper section of the window and on the tabbed page General are explained in Fields: Node Definition - General.
The fields on the tabbed page Specials are explained in Fields: Node Definition - Specials (Mainframe) and Fields: Node Definition - Specials (UNIX and Windows).
The fields on the tabbed pages Broker and SAP Definitions (if available) are explained in Node - Broker and Node - SAP Definitions.
Enter the required values and choose to save the new node definition.
The fields in the upper section of a Create new Node or Maintenance Node window and on the tabbed page General are explained in the following table:
| Field | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Node Number | Node number.
Valid range: 1 to 99900. |
|
| Short Name | Mnemonic short name for
the node.
The mnemonic short name can be used instead of the node number in various locations. This can be set in the Other Settings of the user profile. |
|
| Node Name | Unique, user-defined
node name.
For nodes with access mode Use Network: Enter a short description to help the user select an appropriate node for a network or job run. For nodes with access mode Use Broker: Enter the name of a UNIX or Windows node (server) as it appears in System Automation Tools and EntireX Broker definitions in the SATSRV text object contained in the Natural SYSSATU library. This field is case-sensitive. |
|
| NPR Version | (Information field
only.)
Version of the Entire System Server (NPR) currently installed. |
|
| Operating System | (Information field
only.)
Operating system that hosts the server node. |
|
| OS Release | (Information field
only.)
Detailed information (where available) on the operating system installed. |
|
| Access Mode | Possible selection options: | |
| use Network | Use Entire Net-Work for mainframe nodes. | |
| use Broker | Use EntireX Broker. | |
| local node | Use the local node (invoked directly on the machine where Entire Operations is running; for Entire Operations on UNIX and Windows only). | |
| Time Difference | Difference between
local time and GMT in hours if the node is in a different time zone. Input
format: xn, where:
|
|
| z/OS Password Mode | This setting is
evaluated for nodes on z/OS only.
Conversion mode to be used for password entries. Possible selection options: |
|
| Upper case | Passwords are converted to upper case (default for mainframe nodes). | |
| Case-sensitive | Passwords in lower or mixed case are not converted to upper case (default for UNIX and Windows nodes). | |
| z/VSE SysID | ID
added to the job cards of jobs submitted on a z/VSE node.
Valid range: 1 to 9. |
|
| Wait after Error | Time in minutes to wait
until the next node access after a temporary error.
Default: 5 minutes. |
|
| Submit Security User Type | Submit security user
type can be set individually for each node.
If this field is blank, the global default applies to this node: see the field described in Monitor Defaults for possible values of this field. |
|
| Valid | Allow or disallow use
of the node.
Possible check box settings: |
|
| checked | Allow use. | |
| unchecked | Disallow use. | |
UNIX and Windows nodes (i.e. on Entire System Server) must be defined in the following locations as well:
SATSRV/SYSSATU (see the section Definitions for Entire System Server in the Installation documentation of System Automation Tools.)
EntireX Broker parameters. You can omit these definitions for the Monitor node if this node is accessed in local mode.
Entire System Server/UNIX or Windows initialization file npr.ini (see Customize the NPR Server in the section Completing the Installation in the Entire System Server documentation).
Note:
For each combination of UNIX or Windows node and user ID,
at least one successful login (by
LOGON
NODE) must have been made, before this combination can
be used within the Entire Operations Monitor. These LOGON
NODE commands must be repeated after a password modification on a
UNIX or Windows system.
The fields available on the tabbed page Specials of the Maintenance Node window depend on the access mode selected on the General page and the operating system of the server node.
Possible fields for a mainframe node are described in the following section.
| Field | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Default User ID | User ID used by the Monitor for actions for which no specific user ID is available on the job or network level. |
| Spool Class to be set | Spool class to be set after job completion.
You can enter any valid z/OS or z/VSE spool class to which the job spool class will be set after job completion. Usage precedence:
Note: |
| E-Mail Code Page | E-mail host code page (z/OS and BS2000).
The host code page to be used for e-mail sending. Refer to the description of the field
|
| E-Mail SYSOUT Class | (z/OS and older Entire System Server versions only.)
SYSOUT class to be used for e-mail messages, which are sent from z/OS via SMTP. |
| E-Mail Sender | Default sender name for e-mails which are sent via
this node.
The commercial at sign ( |
| E-Mail Reply-To | Return address for e-mails which are sent via this
node.
The commercial at sign ( The name specified in E-Mail Sender is used by default. |
The fields available on the tabbed page Specials of the Maintenance Node window depend on the access mode selected on the General page and the operating system of the server node.
Possible fields for a UNIX or Windows node are described in the following section.
Jobs of the type SAP require SAP-specific default
values to set environment variables using jexa4S. All definitions are mandatory
to run jobs of the type SAP.
The fields on the tabbed page SAP Definitions of a Node definition window are explained in the following section:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| JEXA4S_EXE | Full path name of the jexa4s
executable.
Example:
|
| JEXA4S | This path will be set as the JEXA4S
environment variable prior to the invocation of jexa4s.
Example:
|
| RFC_INI | This path will be set as the RFC_INI
environment variable prior to the invocation of jexa4s.
Example:
|
Before you delete a node, consider the impact on master or active objects using this node:
When a node definition is deleted, this node is no longer available for new objects like network or job definitions.
A deleted node is not invalidated in existing objects.
A node status list can still show a deleted node as active.
Various node access errors can occur if a deleted node is still referenced, for example, during network activation or job submission.
 To delete a node definition
To delete a node definition
From the Node metanode in the object workspace, select the node you want to delete and choose Delete from the context menu, or press DELETE.
A dialog opens where you have to confirm the deletion.