The following tutorial demonstrates how SOA Gateway can be used with Adabas transactions. It is assumed you are already familiar with the following
soapUi ( see here )
Creating SOA Gateway web services from Adabas ( see here )
Familar with SOAP Header usage concepts ( see here )
For this tutorial, we will use the Employees demo file (usually file number 11) that comes with Adabas, and the adabas_employees_mini_view data view. It is assumed you have already created a web service for your Adabas file.
Important:
By default, SOA Gateway will time-out and kill existing
Conversations after a period of time. This is can be configured using the
Control Centre. with a maximum value of 3600 (10 minutes). See
here for more
information.
Import the WSDL into soapUi.
Choose the request for the add operation,
and in the XML set the ConversationState to
"New" and the
TransactionState to "New".
Also remove the other Header values. Send the request to SOA Gateway
E.g
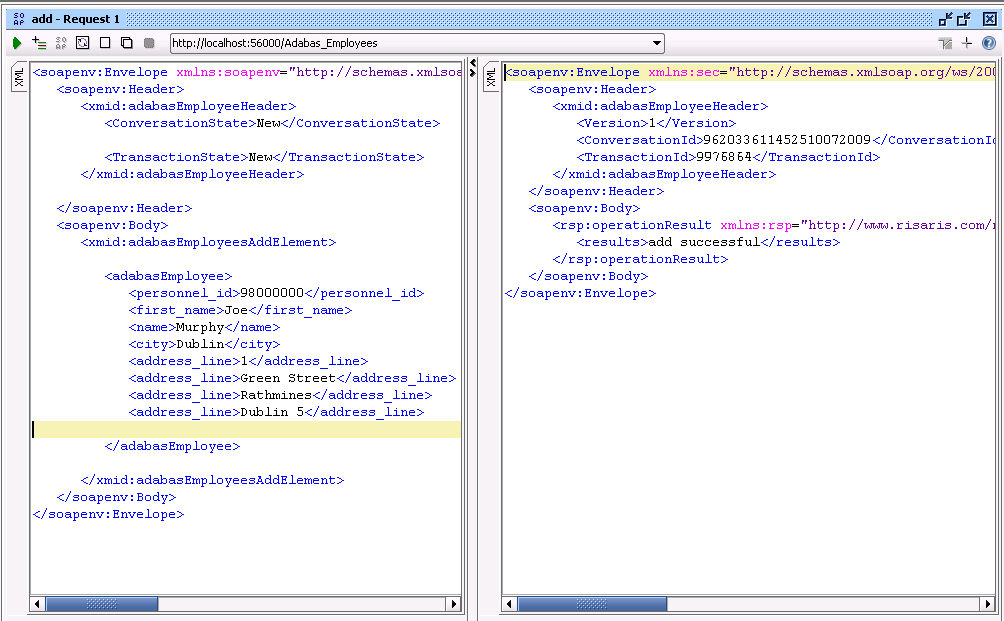
SOA Gateway has now created a new Conversation and a new Transaction for this request. The IDs for each of these are returned.
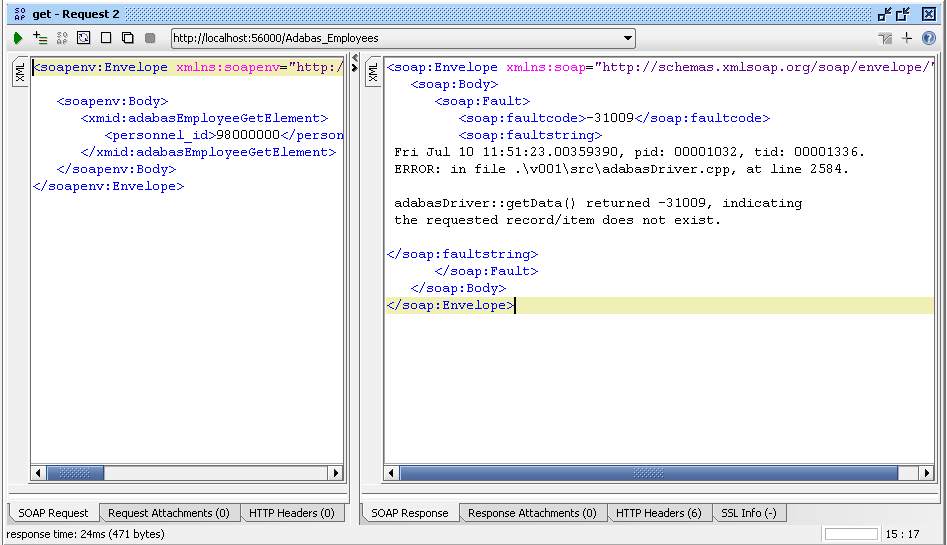
Verify that the record has been added successfully, (but not yet committed).
Choose a get request, remote the
soapenv:Header element, and enter get the record.
E.g.
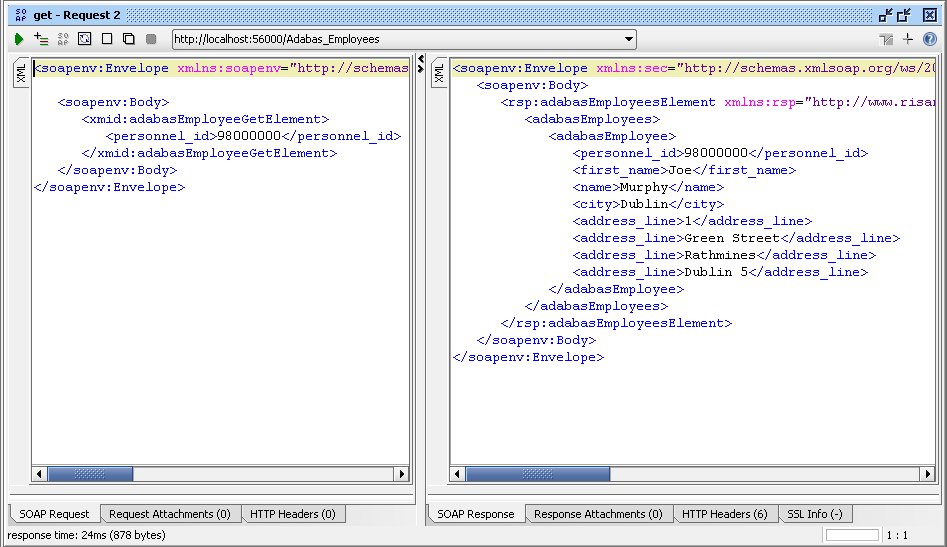
The record has been added, but not yet committed. Because Adabas' isolation level is "Read Uncommitted" (also known as "dirty read"), a request from a non-conversational request will still return the added, but-yet-uncommitted, record.
Now backout the transaction.
Choose a get request, and enter the
following:
ConversationState to
"End"
ConversationID to the value returned in
the add response
TransactionState to
"Backout"
TransactionID to the value returned in
the add response
E.g
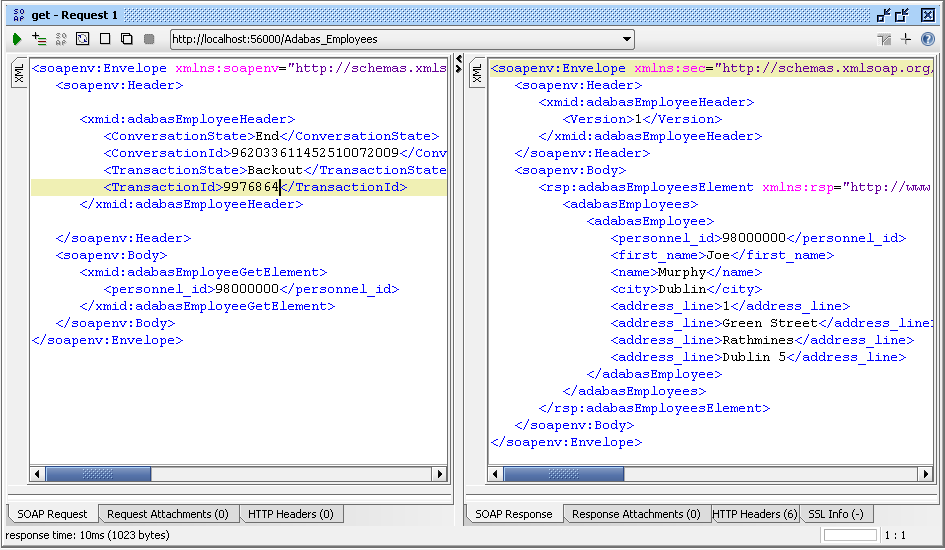
Now, if you re-run the request from Step 3, the item does not exist as the previous add has been backed out.
E.g.