The EntireX Micro Focus COBOL RPC Server allows standard RPC clients to communicate with COBOL servers written with Micro Focus COBOL. It works together with the COBOL Wrapper and the IDL Extractor for COBOL.
This document covers the following topics:
This section covers the following topics:
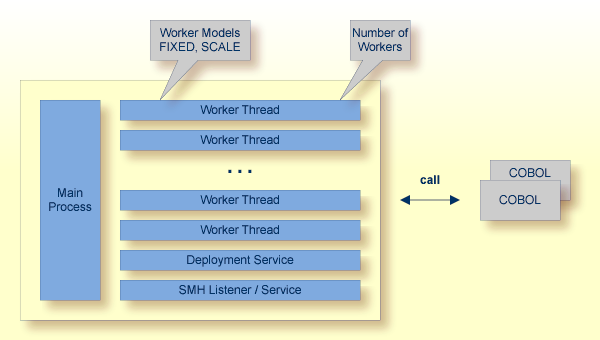
RPC requests are worked off inside the RPC server in worker threads, which are controlled by a main thread. Every RPC request occupies during its processing a worker thread. If you are using RPC conversations, each RPC conversation requires its own thread during the lifetime of the conversation. The Micro Focus RPC Server provides two worker models:
FIXED
The fixed model creates a fixed number of worker threads.
The number of worker threads does not increase or decrease during the lifetime of an RPC server instance.
SCALE
The scale model creates worker threads depending on the incoming load of RPC requests.
Micro Focus RPC Server provides the following services for ease-of-use:
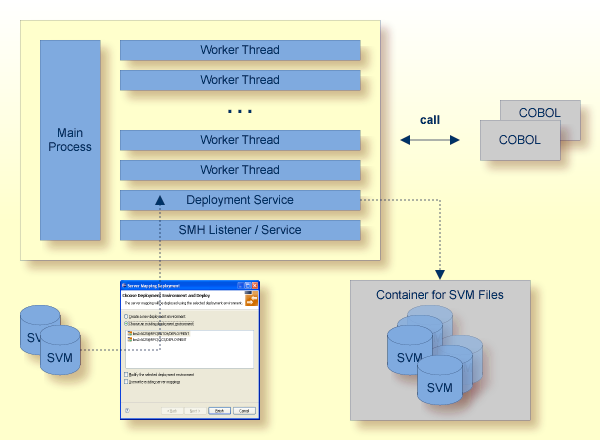
The Deployment Service allows you to deploy server mapping files (SVM files) interactively using the Deployment Wizard (see Server Mapping Deployment). On the RPC server side, the SVM files are stored in a directory as the container. See Deployment Service with Micro Focus RPC Server for configuration information.
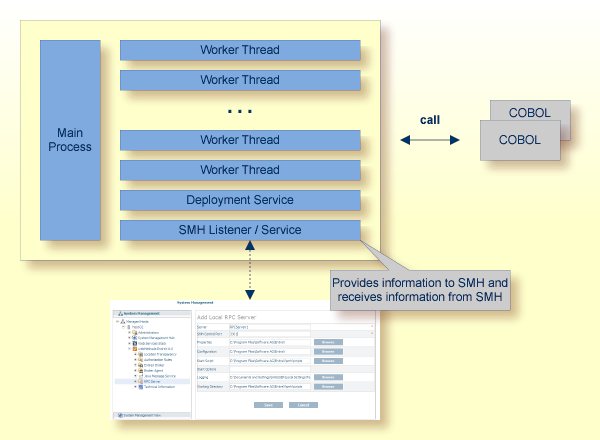
With the SMH Listener Service you use the System Management Hub to monitor the RPC server. See Administering the EntireX RPC Servers using System Management Hub under UNIX | Windows.
The Micro Focus RPC Server is optimized to call COBOL servers originally written with Micro Focus COBOL, and servers ported from other environments (e.g. z/OS), to Micro Focus. For this purpose, the RPC server requires in many situations a server mapping file (SVM).
SVM files contain COBOL-specific mapping information that is not included in the IDL file and therefore not sent by an EntireX RPC client to the RPC server. See also When is an SVM File Required? under Handling SVM Files.
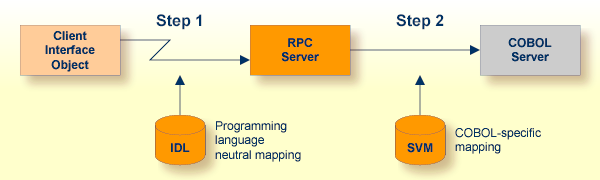
The RPC server marshalls the data in a two-step process: the RPC request coming from the RPC client (Step 1) is completed with COBOL-specific mapping information taken from the SVM file (Step 2). In this way the COBOL server can be called as expected.
The SVM files are retrieved as a result of the IDL Extractor for COBOL extraction process and the COBOL Wrapper if a COBOL server is generated.
You can customize the usage of the SVM file using parameter
svm. See Configuring the RPC Server.
Note:
SVM files are used for COBOL only.
![]() To call an existing COBOL server
To call an existing COBOL server
Use the IDL Extractor for COBOL to extract the Software AG IDL and, depending on the complexity of the extraction, also an SVM file.
Build an EntireX RPC client using any EntireX wrapper. See EntireX Wrappers. For a quick test you can:
use the IDL Tester; see EntireX IDL Tester in the EntireX Workbench documentation
generate an XML mapping file (XMM) and use the XML Tester for verification; see EntireX XML Tester
See Client and Server Examples for Micro Focus (UNIX and Windows) for COBOL RPC Server examples.
![]() To write a new COBOL server
To write a new COBOL server
Use the COBOL Wrapper to generate a COBOL server skeleton and, depending on the complexity of the extraction, also an SVM file. Write your COBOL server and proceed as described under Using the COBOL Wrapper for the Server Side.
Build an EntireX RPC client using any EntireX wrapper. See EntireX Wrappers. For a quick test you can:
use the IDL Tester; see EntireX IDL Tester in the EntireX Workbench documentation
generate an XML mapping file (XMM) and use the XML Tester for verification; see EntireX XML Tester
See Client and Server Examples for Micro Focus (UNIX and Windows) for COBOL RPC Server examples.