This section explains the use of logical printers and how to define them. It covers the following topics:
Logical printers are used to print reports or bundles. A logical printer refers to printing on a physical printer such as a VTAM printer, a system printer or a DASD sequential data set by applying a set of printing characteristics, such as FORM, CHARS, FCB, etc.
Different logical printers can print on the same physical printer but with different characteristics.
The following figure illustrates the relation between logical printers and physical printers:
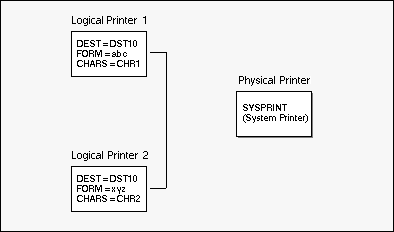
In this example, two logical printers with different parameters are assigned to the same physical printer: SYSPRINT, the system printer.
To define logical printers, you must first have defined at least one physical printer, as described under Physical Printers in the System Administration documentation.
| Field | Explanation | |
|---|---|---|
| Name | If you are adding a logical printer, you must enter its ID before proceeding. This ID must be unique. If you are modifying an existing printer, this field is write-protected. | |
| Description | Enter a short description for the logical printer. | |
| Physical Printer | Name |
Use the list box to select the ID for the physical printer where reports are to be printed. |
| Location | The location of the selected physical printer is displayed here when a printer has been selected. | |
| Restrict usage to administrators and authorized users |
By default, a general user may select any logical printer for which the user or PUBLIC is authorized (even if all authorization options are set to "No"). Also, when printing an active report, the user may select any printer defined in the master report definition. If you select this option, only administrators and users with at least one authorization option set to "Yes" may select this printer. |
|
| Copies | Enter the number of copies to be printed. | |
| Priority | Enter the print priority. This is passed to the spooling system when using system printers, or used internally when referring to VTAM printers. | |
| Printer Exit | Member |
Use the list box to select the name of the exit to be executed for each line before it is printed. |
| Library | This field displays the name of the library where the printer exit is located. | |
| Enter the jobcards to be used
when printing in batch mode.
SERIAL - If a jobcard contains the keyword SERIAL, Entire Output Management checks if the desired printer is already in use by another printer task. If so, the printout processing is delayed until the printer completes. This is useful if, instead of a printer spooler, a printer is addressed directly which cannot spool itself. SERIAL only applies to NATUNIX and UNIXLP printers. SKIP - The keyword "SKIP nnnnnn" is interpreted as SKIP nnnnnn pages and will suppress the output for nnnnnn pages. However, if a printout is resumed that begins with the line after an error occurred, SKIP will also suppress nnnnnn pages - which might not be intended. In this case the SKIP parameter has to be omitted. The SKIP function is not exact, it will start the printing shortly before the desired page, because the print data are passed to the print program with internal blocking (for performance reasons). Other parameters of the jobcard fields are not affected. SKIP can be used for any printer type where jobcards are allowed. WAIT-PRINTER - If this keyword is contained in a jobcard of the
printout queue or of the logical printer, it will be checked whether the
physical printer name of the special printer attributes contains a pipe to the
UNIX command EXTERNAL-OK – If this keyword is contained in one of the jobcard
fields, a printer task will print the output completely, but instead of status
"D" (printed successfully) status "X" (wait for external confirmation) will be
set. To change this status to "D", you execute a batch job which calls the
Natural program NOMEXOK printout-id1 message-number1 message1 printout-id2 message-number2 message2 printout-id3 message-number3 message3 ... printout-id-n message-number-n message-n END or FIN printout-id is the printout ID of the output; message-number is any user error number; message is any text to be written to the monitor log and to the status field of the printout. If the message-number is 0, the
printout status will be set to "D". If it is greater than 0, the printout
status will remain set to "X", and the
message-number and
message will be returned. If it is a negative value,
the printout status will be set to "E" (error) with
message-number and
message being returned. If processing is not
successful, If you specify no jobcards here, the specifications made for the Monitor Standard Definitions will be used. |
||
Depending on the type of the physical printer, as determined by the Physical Printer specifications under General Attributes (see above), you can set special attributes for a logical printer. They are the same as the special attributes of the corresponding physical printer type, which are described under Attributes of Physical Printers in the System Administration documentation.
![]() To list all available commands for logical printers:
To list all available commands for logical printers:
In the object workspace, expand the Printers folder.
Select a printer and invoke the context menu.
A list of available commands is displayed.
These are:
| Command | Shortcut | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Authorization | F9 | Authorize other users to process the logical printer. |
| Copy | Ctrl+C | Copy a logical printer. (*) |
| Delete | Del | Delete a logical printer. (*) |
| Display | Ctrl+D | Display a logical printer. |
| Display Log | F10 | Display log information about maintenance activity on this printer. |
| Filter | F3 | List selected logical printers. |
| List | F8 | List all logical printers. |
| New | Ctrl+N | Add a new logical printer. |
| Open | Ctrl+O | Modify a logical printer. |
| Rename | F2 | Rename a logical printer. (*) |
(*) These commands cannot be used for DEFAULT printers.
![]() To list all defined logical printers:
To list all defined logical printers:
In the object workspace, select the folder.
Invoke the context menu and choose .
All defined logical printers are listed in the content pane.
For each printer, the following information is displayed:
| Field | Explanation | |
|---|---|---|
| Printer | Name of the logical printer. | |
| Authorization | Authorization used to access the
logical printer. Possible values:
|
|
| Description | Short description of the logical printer. | |
| Physical | The name of the physical printer. | |
| Status | The status of the physical printer: S = printer stopped; blank = printer started and active for printing. | |
| Location | The location of the physical printer. | |
![]() To list defined logical printers according to selection
criteria:
To list defined logical printers according to selection
criteria:
In the object workspace or in the printer list, select the Printers folder.
Invoke the context menu and choose .
The Filter Printers window is displayed.
Enter your selection criteria, and choose .
Now only defined logical printers which satisfy the selection criteria appear in the expanded Printers folder in the object workspace.
![]() To define a new logical printer:
To define a new logical printer:
Select the folder in the object workspace and invoke the context menu.
Choose .
The New Logical Printer window is displayed in the content pane.
You can define and . To do so, select the appropriate tab.
The corresponding window is displayed, and you enter your data. The fields are described under Attributes of a Logical Printer.
Choose to save your data.
![]() To copy a logical printer:
To copy a logical printer:
In the object workspace or in the printer list, select the desired printer.
Invoke the context menu and choose .
The Copy window is displayed.
Enter the name of the target logical printer in the field provided and choose .
The new logical printer appears in the printers list.
Note:
DEFAULT printers cannot be copied.
![]() To modify a logical printer:
To modify a logical printer:
In the object workspace or in the printer list, select the desired printer.
Invoke the context menu and choose .
The logical printer definition is displayed, and you can change it. The fields are described under Attributes of a Logical Printer.
Choose to save your changes.
![]() To rename a logical printer:
To rename a logical printer:
In the object workspace or in the printer list, select the desired printer.
Invoke the context menu and choose .
Change the name of the selected printer, and press ENTER.
Note:
DEFAULT printers cannot be renamed.
![]() To delete a logical printer:
To delete a logical printer:
In the object workspace or in the printer list, select the desired printer.
Invoke the context menu and choose .
A window is displayed, asking you to confirm the deletion.
Choose to delete the printer, or to cancel the operation.
Note:
DEFAULT printers cannot be deleted.
![]() To display a logical printer:
To display a logical printer:
In the object workspace or in the printer list, select the desired printer.
Invoke the context menu and choose .
The definition of the logical printer is displayed. The fields are described under Attributes of a Logical Printer.
![]() To display log information for a logical printer:
To display log information for a logical printer:
In the object workspace or in the printer list, select the desired printer.
Invoke the context menu and choose .
The Log Information window for the printer is displayed.
To display more detailed log information, select an entry from the Log Information window.
Invoke the context menu and choose .
A detailed log message for the selected entry is displayed.
![]() To authorize user access to a logical printer:
To authorize user access to a logical printer:
In the object workspace or in the printer list, select the desired printer.
Invoke the context menu and choose .
The Authorization List for the printer is displayed. It lists all users and user groups on distribution lists who are authorized for the printer, and their authorization levels.
Invoke the context menu for the dialog and select .
The Authorization Definition is displayed.
Enter the data for the authorization. The fields are described under Authorization Options.
Choose to save your data.