This document provides general information on code coverage of Natural applications.
In general, code coverage measures the degree to which the source code of a program is executed. It is often used for systematic software testing. The higher the code coverage percentage is, the lower is the chance that the code contains undetected software bugs in code that is not executed.
The Natural code coverage is used to monitor the executed statements of a Natural application. It collects the coverage data while the application is executed and provides tools to analyze the collected data afterwards.
The Code Coverage view of NaturalONE (Software AG’s Eclipse-based development environment) and the Program Coverage table of the Profiler utility show - expressed as a percentage - how many of the statements of the Natural objects have been executed. The Natural Coverage Plugin for Jenkins visualizes the outcome of a Natural coverage cycle directly in the Jenkins job result pages.
In the NaturalONE editor and in the Statement Coverage table of the Profiler utility you can see, which individual statement lines of a Natural object have been executed. Here you can also see the statement lines which have been missed or have only been partly covered.
If a statement source uses multiple lines, only the line in which the statement begins is mentioned in the coverage reports.
You can export the coverage data with the Profiler utility output in text or table (CSV) format. The CSV table can be analyzed with a spreadsheet software such as Microsoft Excel.
If a Natural source contains INCLUDE statements, the
corresponding copycode is included in the generated object (the
GP). For the coverage, we can monitor two statement counts:
The number of the statements in the GP which includes all copycodes recursively (a copycode can include further copycodes).
The number of the statements in the source which does not include the copycodes.
The GP coverage reflects the percentage of the covered statements in the GP including copycodes; whereas the source coverage reflects the percentage of the covered statements in the source not including copycodes.
This section briefly describes the steps required for performing the code coverage of a Natural batch applications and viewing the results. The instructions provided here may serve as a guideline when starting to use Natural code coverage. Detailed information regarding the steps is provided in the remainder of this chapter.
The steps to take depend on the evaluation you want to perform for your application as illustrated in the following graphic:
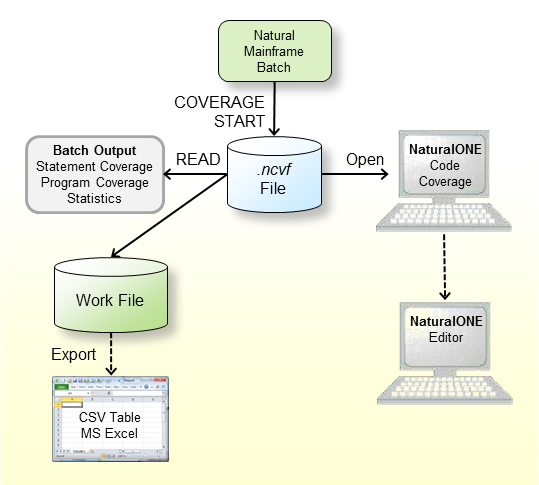
Check that the prerequisites are met.
Add the Profiler utility COVERAGE and START functions to
the Natural batch job to start the code coverage data collection.
In the following example for z/OS, the Natural program TESTCOVP in library COVDEMO is covered.
//CMSYNIN DD * PROFILER FUNCTION=COVERAGE /* Initialize coverage RESOURCE-NAME='ResNam' /* Resource name REPLACE=YES /* Replace the resource RESOURCE-LIB=RESLIB /* Resource library FUNCTION=START /* Start data collection END-PROFILER /* End Profiler input LOGON COVDEMO TESTCOVP FIN
In the example above, the Profiler coverage data is written to a resource file with
the name ResNam.ncvf in the library RESLIB. See also
Initializing Code
Coverage and Starting and Pausing Data Collection.
Open the NCVF resource in NaturalONE to obtain the Code Coverage view.
From the NaturalONE Code Coverage view, you can directly edit the source. The editor shows all lines containing covered statements with a green background.
Submit a Natural batch job with the Profiler utility READ function to print the
program and statement coverage and the Profiler statistics.
Example:
FUNCTION=READ /* Read Profiler data RESOURCE-LIB=RESLIB /* Resource library RESOURCE-TYPE=NCVF /* Use resource type EVENT=ON /* Print statement co PROGRAM=ON /* Print program cove STATISTICS=ON /* Print statistics EXPORT=ON /* write to work 7 FORMAT=C /* Semicolon/Comma/Text
If the EXPORT keyword of the Profiler utility READ
function is switched on, the output is written to Work File 7. If FORMAT
is specified as C or S, the result is written as
comma-separated values (CSV) where a comma or a semicolon is used as a separator,
respectively.
Export the data of Work File 7 with any tool (such as FTP) as a CSV-formatted file to a Windows environment if you want to process it further in Microsoft Excel.
Notes:
READ function
of the Profiler utility, the NCVF resource created last in the library is used.
While a Natural application is executed, coverage data can be collected and written to a NCVF resource file.
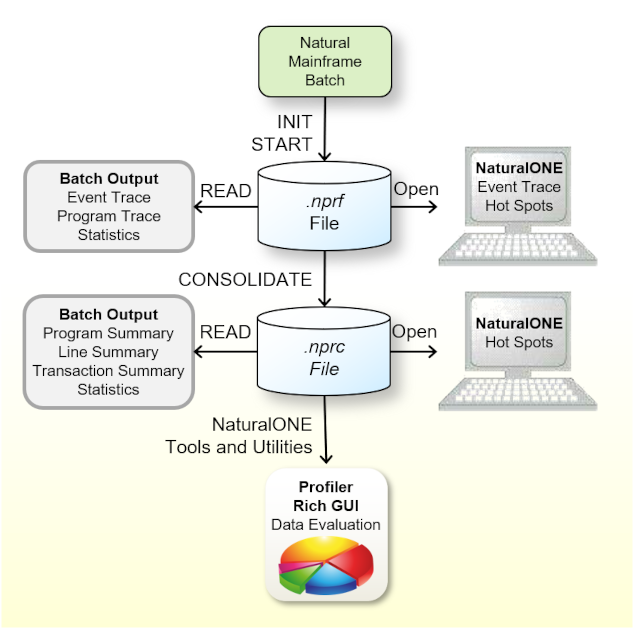
On the mainframe, the data collection is performed by the Profiler utility in batch mode. Therefore, code coverage of mainframe applications is only available if the Profiler utility in batch mode can be started. This is true for mainframe batch applications but also for mainframe interactive applications remotely executed from Natural Studio or RPC if the corresponding setting have been done.
On Windows and UNIX, the data collection is performed by Natural if the
COVERAGE parameter is specified. Therefore, code coverage is always
possible.
Unlike profiling, there is no direct code coverage under NaturalONE in which the coverage is triggered and immediately processed by NaturalONE.
If NaturalONE runs against a Windows or Unix Natural, the code coverage data
collection to an NCVF resource file can be initiated by setting the Natural
COVERAGE parameter.
NaturalONE processes the coverage data of an NCVF resource file and shows the results in the Natural Code Coverage view and in the Natural Source editor.
The Profiler utility in batch mode processes the coverage data of an NCVF resource file and provides statement and program coverage results. The data can also be written in CSV (comma-separated values) format to a file which can be further analyzed with a spreadsheet software (like Microsoft Excel).
You can perform the Natural code coverage on Linux, Windows, and mainframe platforms. How to proceed depends on the platform and the application processing mode used:
Code coverage of mainframe interactive applications remotely executed from Natural Studio or RPC is performed using the Profiler utility in batch mode.
Code coverage of mainframe batch applications is performed using the Profiler utility in batch mode.
Note
Code coverage is not available for mainframe interactive applications running
locally on a mainframe or remote from NaturalONE.
Code coverage of Linux and Windows interactive applications is performed with the NaturalONE code coverage or the Natural code coverage for Linux and Windows, respectively.
Code coverage of Linux and Windows batch applications is performed with Natural code coverage for Linux and Windows, respectively.
This section summarizes the key features of the Natural profiling tools:
Reads and analyzes Natural code coverage resource files containing coverage data collected by the mainframe Profiler utility in batch mode or by the Natural code coverage for Linux or Windows.
Interactive Natural applications from Linux or Windows can be covered by activating the Natural code coverage for Linux or Windows and reading the corresponding Natural code coverage resource file.
The Natural code coverage view shows which percentage of the statements of the Natural objects have been executed.
From the Natural code coverage view the involved Natural objects can be edited. The NaturalONE editor displays all covered lines with a green background.
Note
Interactive code coverage of Natural applications from mainframe platforms is
currently not supported.
Code coverage of interactive or Natural batch applications from Linux or Windows platforms.
Provides features for big data handling:
automatic event filter,
automatic data consolidation.
Saves the code coverage data as a Natural code coverage resource file.
Code coverage of Natural batch applications from mainframe platforms.
Code coverage of mainframe interactive applications remotely executed from Natural Studio or against a Natural RPC server.
Provides features for big data handling:
program, count and time filters,
automatic event filter,
automatic data consolidation.
Saves code coverage data as a Natural code coverage resource file.
Reads and analyzes Natural code coverage resource files.
Lists the Program Coverage table for all accessed Natural objects with
percentage of the covered statements,
number of covered statements,
number of missed (not covered) statements and
total number of statements of the object.
The Statement Coverage lists the source of each accessed Natural objects and shows for each line the percentage of the covered statements.
Exports Natural code coverage data in CSV (comma-separated values) format which can be further analyzed with a spreadsheet software (e.g. Microsoft Excel).
Collects and displays Profiler and code coverage properties and statistics.
Note
On the mainframe, there is no one-to-one relationship between a Natural source code
statement and the corresponding object code in the cataloged object. The Natural code
coverage on the mainframe monitors the object code rather than the Natural source code.
Therefore, multiple Natural statements can be merged into one coverage entry and
conversely, one Natural statement can cover multiple coverage entries.
Reads and analyzes Natural code coverage resource files.
Lists the Program Coverage table for all accessed Natural objects with
percentage of the covered statements,
number of covered statements,
number of missed (not covered) statements and
total number of statements of the object.
The Statement Coverage lists the source of each accessed Natural objects and shows for each line the percentage of the covered statements.
Exports Natural code coverage data in CSV (comma-separated values) format which can be further analyzed with a spreadsheet software (e.g. Microsoft Excel).
Note
On Windows and Linux, missed statements are not collected. Therefore the Statement
Coverage can only mark lines containing covered statements and the coverage of these
lines is always 100%.
Template for coloring the Natural code coverage data exported in CSV (comma-separated values) format by the Natural Profiler utility.
Program and copycode coverage with source and GP counters for
percentage of the covered statements,
number of covered statements,
number of missed (not covered) statements and
total number of statements of the object.
Statement Coverage of the object source whereby the lines are colored in
green – if all statements of the line are covered,
yellow – if the statements of the line are partly covered,
red – if all statements of the line are missed,
gray – if the line is empty or contains only comments.
Profiler and code coverage properties and statistics (for mainframe data).
Note
A Microsoft Excel spreadsheet template for Natural code coverage is available as a
resource in the Natural Profiler library SYSPRFLR on Linux and
Windows.
This section describes the evaluations provided by the Natural code coverage tools:
The program coverage provides you with an overview of the programs executed and the amount of the code that has been covered by the application.
The Program Coverage report of the Profiler utility shows the coverage (in percentage of the total number of statements) of each Natural object executed. It shows for each object how many statements have been covered or missed and the total number of statements. In addition, it summarizes the values for all objects in a library and the totals over all libraries.
If the output is written in text format, only the GP coverage is provided. If the data is exported in CSV (comma-separated values) format, the source coverage is given as well. Additionally, the counters for all included copycodes are printed.
The following is an example for text format:
Program Coverage ---------------- Library Object Ty Coverage% Covered Missed Total COVDEMO TESTCOVN N 84.0% 37 7 44 COVDEMO TESTCOVP P 69.2% 9 4 13 COVDEMO -------- -- 80.7% 46 11 57 Totals -------- -- 80.7% 46 11 57
In the Program Coverage example above, 69.2% of 13 statements in
the TESTCOVP program were covered, corresponding to 9 covered and 4
missed statements. 80.7% of the statements of the accessed objects in the library
COVDEMO were covered, which is also the total value for the whole
application run.
The Code Coverage view of NaturalONE shows the coverage (in
percentage of the total number of statements) of each Natural object executed. It
shows for each object how many statements have been covered or missed and the total
number of statements. If copycodes are included, the object node can be opened to view
the coverage of the copycode. In general, the counters reflect the GP coverage
(copycodes included). The source coverage (copycodes not included) is displayed in the
line where the object name is enclosed in the << >>
brackets.
From any line you can directly navigate to the corresponding source code to view the statement coverage.
Example:
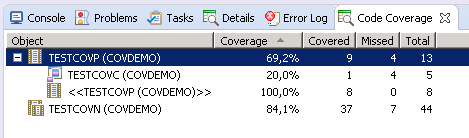
In the example above, the TESTCOVP program has a GP coverage of 69.2
percent whereby in the program itself all 8 statements are covered (100% source
coverage) and in the included copycode TESTCOVC only 1 of 5 statements
was covered.
The statement coverage shows which lines of the program have been executed. For mainframe data, the Profiler utility also indicates which lines containing statements have not been executed or are only executed partly.
The Statement Coverage report of the Profiler utility shows for each source line the coverage of the statements in the line. If the data is exported in CSV (comma-separated values) format, the number of covered or missed statements and the total number of statements in the line are printed as well. The Microsoft Excel spreadsheet template delivered with Natural on Linux and Windows, can be used to color the lines according to the coverage.
If a source contains an INCLUDE statement, the
corresponding copycode source is included in the report right after the
INCLUDE statement.
The following is an example for an export in CSV format colored using a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet:
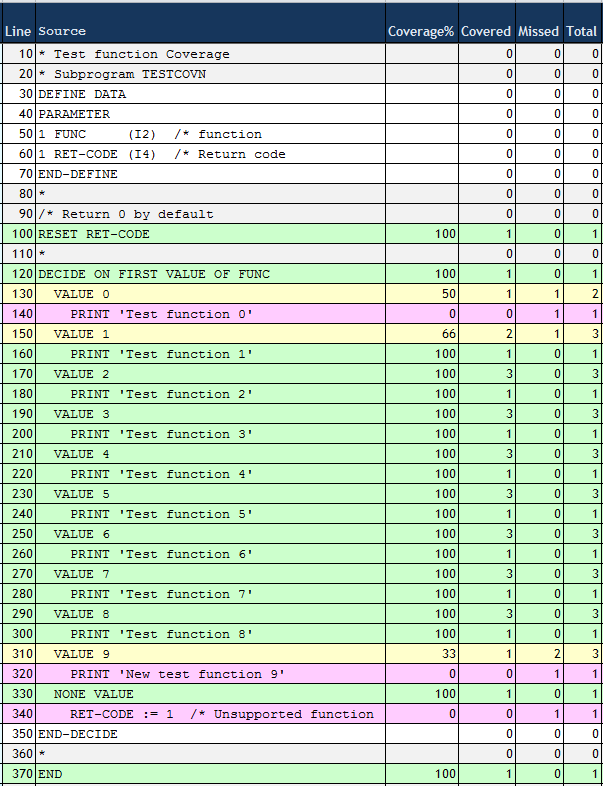
The three red lines of the subprogram TESTCOVN have not been executed.
Thus, the test run does not cover the new test function 9. It also
neither covers the (old) function 0 nor the case when the subprogram is
called with an unsupported function.
The data originates from the mainframe. Therefore, the counts refer object code
statements rather than Natural statements. A Natural VALUE
statement can correspond up to 3 object code statements. The yellow lines refer to
VALUE statements where some of the object code has been
covered and some not.
If the source editor is opened from the Code Coverage view in NaturalONE, the source is colored according to code coverage. Every line in which one or more statements are covered, is colored with a green background.
Example:
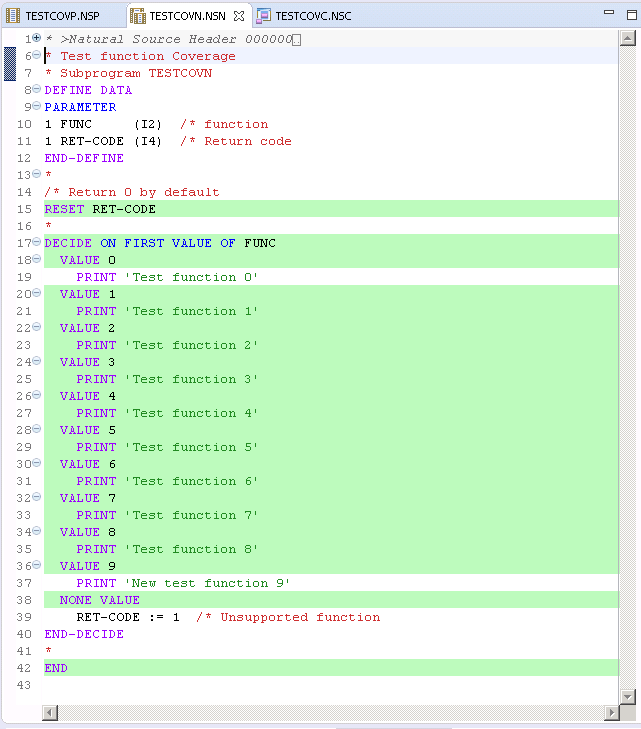
The source editor shows all lines in which at least one statement has been executed
with a green background. Therefore, all lines except line 19, 37 and 39 of the
DECIDE statement have been executed.
The Profiler properties and statistics is provided by the Natural Profiler utility and the Profiler Rich GUI. It lists Profiler properties such as the Profiler revision. It additionally displays statistics of the monitored application, for example, the total CPU time and the elapsed time. For a code coverage run, it shows the coverage statistics.
*************************************************************************** * 13:30:48 ***** NATURAL PROFILER UTILITY ***** 2017-09-04 * User SAG - Statistics - COVREAD * * General Info * Machine class ...................... MAINFRAME * Environment ........................ Batch ... * Coverage * Coverage ........................... ON * Missed statements recorded ......... ON * Coverage records ................... 60 * Program information records ........ 3 * Coverage records/block ............. 60 * Bytes/coverage record .............. 10.3 * Programs covered ................... 2 * Statement coverage (percent) ....... 80.7 * Statements covered ................. 46 * Statements missed .................. 11 * Statements total ................... 57