These tasks would typically be carried out by an experiened SOA Gateway user.
Typically when you install SOA Gateway on Windows, the Control Centre and the SOA Gateway server are on the same machine. If you wish to install SOA Gateway on a remote Windows here are the steps involved.
Transfer win32Build.msi to the target machine.
The msi can be located at ../eclipse/features/com.SOAGateway.feature.install.x86.windows_2.6.1.NN
where ../eclipse is the folder from which your Control Centre is launched.
Transfer the SOA Gateway license to the target machine.
Logon to the target machine and run:
msiexec /I c:\temp\win32Build.msi /L*v c:\temp\installLog.txt SERVERPORT=56000 LICENSESRC=c:\temp\LIC.xml
Assuming that:
The msi and your license are in c:\temp\
You want the server to run on port 56000
Your license is named LIC.xml
The server prerequisites have already been installed. Check here for these.
This section outlines the steps required to run multiple instances of SOA Gateway, either of the same, or different versions, on a single operating system image.
The simplest way for setting up multiple SOA Gateway servers on z/OS is to execute the Deployment Wizard once for every server, specifying distinct HLQs (High Level Qualifiers) for the datasets, TCP/IP port numbers etc., then execute the setup jobs.
This will also create multiple copies of the SOA Gateway load library, which is not required, so the start job / procedure for the various instances of the server can be modified to all use the same loadlib in its STEPLIB.
This step-by-step guide assumes good knowledge of the Apache webserver on a Linux platform.
The following steps outline how to copy the existing SOA Gateway installation, and then bring up both the existing and new installations using the same Apache webserver.
If running, stop SOA Gateway. See here on how to do this.
Make a duplicate of the current installations files and directories. For example, if installed in /home/bre/soaGateway, then
mkdir /home/bre/soaGatewayNew
cp -R /home/bre/soaGateway/* /home/bre/portusNew
In the new installation, change the Apache Listen directive, specifying a yet unused port number. This directive can be found in the httpd.conf file in the apache2/conf directory.
Again, edit the new httpd.conf file and change the Include directive on the last line to pick up the new installation.
Edit new adabas_soa_gw.conf file in the new installation. Modify required directives to pick up the new files and directories in the new installation.
Add a fully qualified PidFile directive to the new httpd.conf (if one is not already present ). This pid file should point into the new installation.
For example
<IfModule !mpm_netware.c>
PidFile /home/bre/portusNew/apache2/logs/httpd.pid
</IfModule>Modify the new xmiddleEnv.sh file , updating its contents to use the new installation.
Edit the new envvars file, updating its contents to use the new installation.
In the current installation (not the one you have just created) copy the apachectl control script. For example
cp /home/bre/portus/apache2/bin/apachectl /home/bre/portus/apache2/bin/apachectl_new
Modify the new file to pick up the new httpd.conf and new envvars file.
Note:
You do not need to change the path to the httpd binary.
Note:
Therefore you may remove the new Apache libraries and binaries. For
example, these are located under
/home/bre/portus/apache2/lib and
/home/bre/portus/apache2/bin/. Do not remove the
apache2/bin/envvars file.
Use the 2 apachectls scripts to start SOA Gateway
Verify that the SOA Gateway start-up messages (found in the Apache logs) refer to the new SOA Gateway configuration file.
IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) is the latest revision of the Internet Protocol (IP), the primary communications protocol upon which the entire Internet is built. It is intended to replace the older IPv4, which is still employed for the vast majority of Internet traffic as of 2012. IPv6 was developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) to deal with the long-anticipated problem of IPv4 running out of addresses.
IPv6 SOA Gateway is supported on all non-Windows platforms. The underlying hosting infrastructure of SOA Gateway is provided by an Apache web server, therefore IPv6 configuration changes take place in the Apache configuration.
Further information can be found here
To make SOA Gateway listen on the IPv6 interface, provide the IPv6 address of the host machine on the Listen directive in the Apache configuration file. This file is [INSTALL_DIR]/apache2/conf/httpd.conf or [INSTALL_DS].CONF(HT$CONF) depending on your system.
E.g.
Listen on port 56001 on this machine : Listen [2607:f0d0:1002:11::4]:56001
Listen on port 56001 for ONLY local IPv6 connections: Listen [::1]:56001
More than one Listen directive can be applied, but the ports must be unique
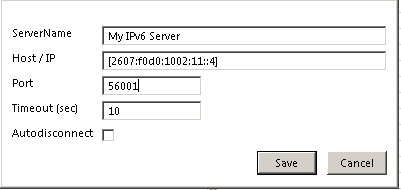
To connect to this server from the SOA Gateway Control Centre, add a new server connection with the IPv6 address surrounded by [ and ] and the port number of your server
When SOA Gateway handles a request it builds XML structures internally to hold the response payload. This data can become very large, and on systems where memory is limited, unexpected results can occur. To resolve this, SOA Gateway has the ability to stream back data as it is retrieved from the database. The SOA Gateway streaming uses HTTP chunked transfer encoding as a transfer mechanism. This is only available in HTTP clients that understand HTTP 1.1 or above. When data is streamed back to the client, SOA Gateway does not have to build large internal strutures to handle the payload, therefore the memory footprint is considerably less.
When streaming is enabled, it only applies when the client issues a LIST request, with all keys wildcarded. E.g. a REST request with LIST&ID=*
Important:
SOA Gateway may use extra CPU resources when streaming is enabled.
Streaming can be enabled by adding the following line in the Apache configuration
SoaGatewayStreaming on
And stopping and starting the server
This directive can also be applied to specific services using the <Location /SERVICENAME > directive
Important:
Not all clients understand HTTP 1.1 or indeed support the chunked transfer encoding.