The batch interface is standard for SMH.
Note:
You must have a valid admin user to run batch commands.
This document covers the following topic:
The batch interface is a distributed console-based application. You must have at least one Software AG Runtime instance installed on your Intranet in order to perform batch-based management of a Software AG product.
The SMH installation procedure installs all of the generic components used by the batch interface. The specific product installation adds all product-specific components such as batch agents and templates.
Notes:
>argbatch) must be run from the same directory on
which the SMH software is installed: Software
AG_directory\InstanceManager\bin.
From the batch interface you can query for supported commands, command syntax, etc. Usage of the batch interface is identical on every supported platform.
Notes:
![]() To display the batch interface screen
To display the batch interface screen
From the system console enter
>argbatch. Remember that the batch interface must
be started from the same directory on which SMH software is installed.
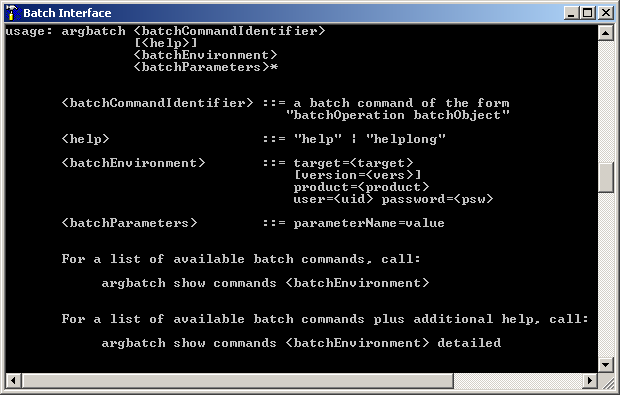
A screen similar to the following is displayed. Note that the actual screen contains much more information than this screen capture.
To uniquely address a proper agent in a batch command, you must provide information about the target node, the product and the version. The batch environment is specified in the format:
target=abc version=def product=ghi user=jkl password=mnopq
The following specific commands are available for the batch environment:
show environment set environment clear environment
With the set environment command, the user can preset the values for target, version, product, user and password to avoid having to enter this information for every subsequent command. These settings remain valid until a new set environment or clear environment command has been submitted. If the clear environment command is submitted without additional parameters, all the current settings are cleared. The show environment command lists the current settings.
An environment parameter specified directly in a batch command takes top priority. If no environment is specified in a batch command, the pre-settings are taken (if they exist). Otherwise, an error message is displayed.
Every batch command must begin with the string
argbatch. The individual elements of batch commands
must be separated either by blank spaces or tabs. The basic elements of a batch
command are:
argbatch <batchCommandIdentifier> <batchEnvironment> <batchParameters>* <batchHelp>
Note:argbatch relies on tokenization of the
underlying shell. For this reason, always use double backslashes in parameter
values (for example, for pathnames) to specify a single backslash.
A command identifier consists of a
<commandOperation> and a
<commandObject>. Typical command operations
are show, set,
create, delete,
backup. Some of the common command objects are
database,
databaselocation, job,
and extension.
The element <batchEnvironment>
specifies the target node, user and password for the batch operation, the
product and the version necessary to identify an appropriate agent on the
server side. The default target node is localhost; the default version is the
most recently installed version as specified in the registry of the target
node.
A batch command can take one or more parameters that consist of a <parameterName> and a <parameterValue> joined by an equal sign ("=") without blank spaces; for example, target=mypc. A parameter value may include blank spaces, in which case it must be enclosed in inverted commas (double quotes, " "); for example, product="System Management Hub".
Some of the parameters that come directly from a specific product are case sensitive. Otherwise, all batch interface parameters are case insensitive.
A parameter always has following form:
<parameterName><=><parameterValue>
Authorization, for those commands that require it, takes the following form:
user=myuserID password=mypassword
See Batch Authentication for more details.
If a mandatory parameter is omitted you receive an error message of the following type:
| Specification of parameter uvwxyz is mandatory! |
Note:
The <commandIdentifier> must appear
immediately after argbatch. In most installations,
the order of all other parameters is arbitrary. This may, however, vary
depending on the Software AG products installed in your particular environment.
Refer to the online help of the individual command for additional
information.
This section contains details on the batch interface commands. It is intended for reference of system administrators.
The information is structured under the following topics:
![]() To display help for any command
To display help for any command
Type help after the
<commandIdentifier> and
<batchEnvironment>, as illustrated in the
following example for set environment:
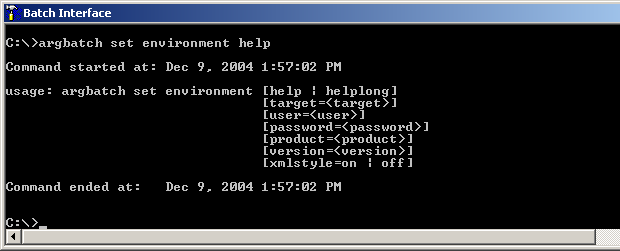
In this example, the command argbatch set environment
help displays help on the usage of the command set
environment. See also section Batch Help.
![]() To display the current environment
To display the current environment
Type in the command:
argbatch show environment
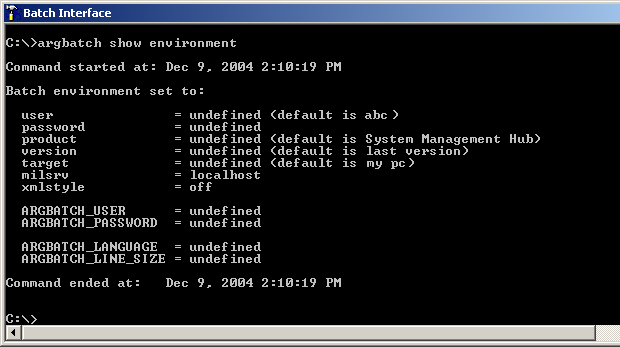
The password is initially set to undefined. Since a password is required for most functions, we recommend setting this parameter first.
The set command can be used for a variety
of functions.
![]() To set the password
To set the password
Type in the command
argbatch set environment password=mypassword
The password is displayed as you type it for the first time. In subsequent batch sessions, however, the password is hidden (as a string of asterisks). Refer also to Batch Mode Password Utility.
Specific target environments can be created in batch representing specific target profiles to include individual user, password, product and version parameters. Unless otherwise specified, the batch environment assumes the default settings.
![]() To set a new target
To set a new target
Type in the command
argbatch set environment target=newtarget
Note:
Once a new target has been specified, the new target becomes
active and all subsequent commands apply by default to that new
target.
When a new target is set, the default values are assumed for any parameter not specified. If you wish to set a different parameter for a new target, add the parameter to the command as in the following example.
argbatch set environment target=newtarget product=newproduct
When new targets have been added, with the show
environment command it is possible to specify a specific
target.
![]() To display information for a specific target
To display information for a specific target
Type in the command
argbatch show environment target=newtarget
![]() To display information for all targets
To display information for all targets
Type in the command
argbatch show environment alltargets
The new display is similar to the following example:
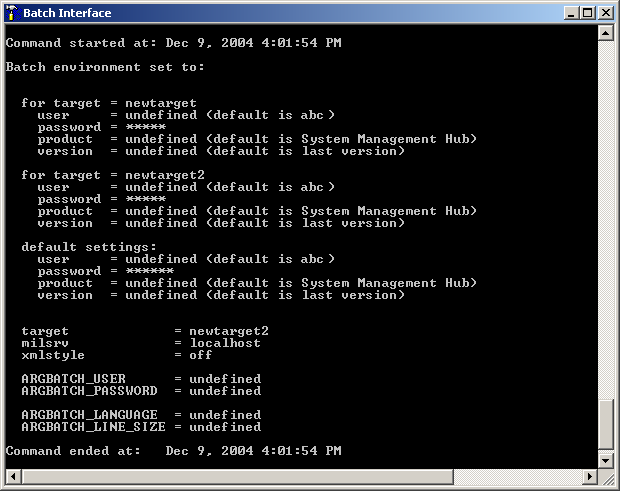
![]() To clear the current active environment
To clear the current active environment
Type in the command
argbatch clear environment
![]() To clear a specific environment
To clear a specific environment
Type in the command with the target
argbatch clear environment target=newtarget2
![]() To clear all environments
To clear all environments
Type in the command
argbatch clear environment alltargets
It is also possible to use the set
environment command to define specific products or versions
within the environment. The syntax is similar to the previous examples.
![]() To set a specific product
To set a specific product
Type in the command
argbatch set environment product=newproduct
![]() To set a specific version
To set a specific version
Type in the command
argbatch set environment version=newversionnumber
![]() To request a list of available commands
To request a list of available commands
Type in the command
argbatch show commands product="System Management Hub" user=abc password=mypassword
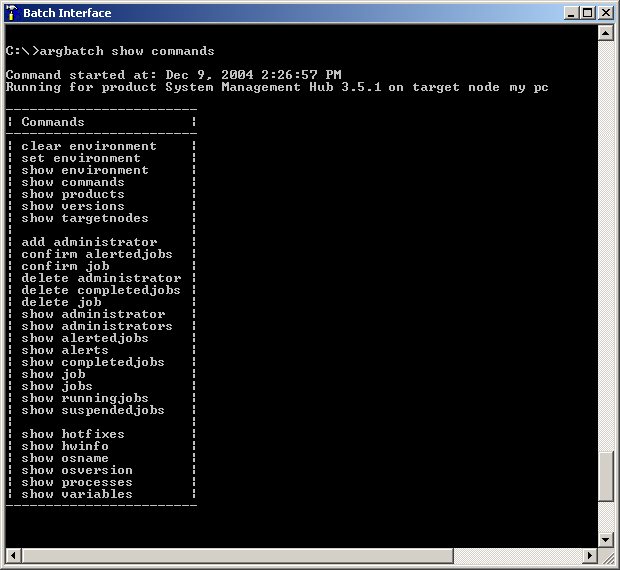
If no other parameters are specified, the commands for the default environment settings are displayed. The actual list of commands in your environment can be much longer than this snapshot.
Commands are organized in three blocks. The commands displayed in the first block are batch specific. The commands displayed in the second block are SMH-specific. Both of these first two blocks of commands apply to every installation of SMH. The final block of commands is product-specific and varies considerably depending on the local environment.
![]() To request a list of commands for a specific product on a specific
node
To request a list of commands for a specific product on a specific
node
Add the desired environment variables to the previous command as in this example:
argbatch show commands product=myproduct user=abc password=mypassword
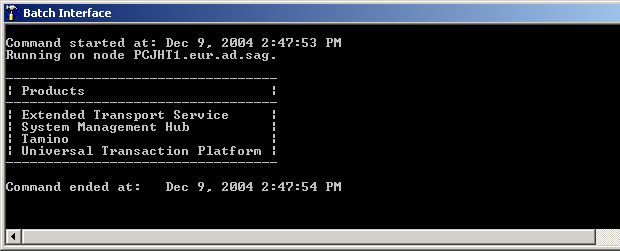
![]() To display a list of the products installed
To display a list of the products installed
Type in the command
argbatch show products
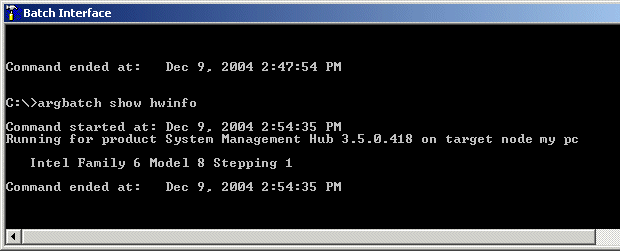
![]() To display hardware information for a particular target
To display hardware information for a particular target
Type in
argbatch show hwinfo
![]() To display information on hotfixes in batch
To display information on hotfixes in batch
In batch mode, type in the command "show hotfixes" and the product name as in the example below:
show hotfixes product="System Management Hub"
The batch interface displays a frame with information on the hot fixes installed, similar to the example below.
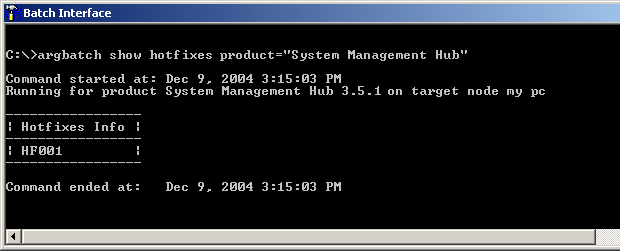
The contents of this frame varies from installation to installation.
SMH 9.0 comes with SSX disabled by default. It can be enabled via the batch interface.
C:\Program Files\Software AG\System Management Hub\bin>argbatch set ssxenabled Running for product System Management Hub 9.0 on target node R1.sag Specification of parameter enable is mandatory! usage: set ssxenabled [help | helplong] [user=<user>] [password=<password>] [target=<target node>] [product=<product>] [version=<version>] enable="true" | "false"
![]() To check current SSX configuration
To check current SSX configuration
argbatch show ssxenabled
SSX authentication is currently disabled
![]() To enable SSX authentication
To enable SSX authentication
Set the SSX configuration to "true"
argbatch set ssxenabled enable=true
SSX Authentication enabling successful
![]() To disable SSX authentication
To disable SSX authentication
Set the SSX configuration to "false"
argbatch set ssxenabled enable=false
SSX Authentication disabling successful
For details on the SSX module and the authentication scenarios, see Authentication in SMH.
If you do not ignore the SSL error message (that reports of a problem with your SSL communication) you may have problems to execute commands.
For example, if there is a problem with the SSL configuration of the host you are trying to connect to, you must either transmit data in plain text or solve the problem first.
![]() To ignore an SSL error message
To ignore an SSL error message
Append the parameter skipsslerror=1 to each command
you run in batch interface to ignore an SSL error message.
Following is an example of running a command to show information for a specific target:
argbatch show environment target=newtarget skipsslerror=1
Refer to Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) in SMH for a list of possible SSL configuration problems.
For the target node, a user and a password must be specified. There are three ways to define the target user and password:
Directly as parameters in the batch command, for example, :
start database user=abc password=defghijk ...
This setting has the highest priority. If a target user and password are specified in this way, all other settings are ignored.
With the environment variables
ARGBATCH_USER and
ARGBATCH_PASSWORD. If
these two environment variables have been defined on the client side, their
values are taken. Specifying user and password directly as parameters in the
batch command overrides these values (as stated above).
Specifying the target user with the setEnvironment
statement is the recommended method, as password and user ID are
encrypted and stored. This means, you do not have to enter them in the command
prompt for every sub-sequent command (see also Batch Environment). If no
user and password information has been specified with the other two methods,
the user and password information set here are applied.
Note:
If the target node is a Windows machine that is part of a Windows
domain, the logon user name must be provided as:
<Domain>\<user>, for example, ,
sag\myself
It is possible to pipe one or more batch commands into the batch client
if they are specified in a file separated by semicolons. for example, :
argbatch < commands.in > commands.out.
| Command | Parameters | Description |
|---|---|---|
| argpswd | -help | Displays a short help message |
This utility is run from the command prompt. The first thing displayed is the current user ID that is stored in the registry. The tool then prompts you whether you would like to change the user ID, in case you have a different user ID on the target you are connecting to. To continue, enter the new user ID and password (that is masked as you type it).
In case the tool has been run by accident, you are asked to confirm that you wish to change the password. If you do so, the user name and password are stored in the SMH registry and you receive either the message that the password has been changed successfully or an error message if problems have occurred.
Note:
Changes are reflected in the argbatch environment when you make an
"argbatch show environment" call.
| Registry init failure | This error occurs if SMH registry initialization fails. This error normally occurs if SMH is not running. |
| Registry Access Failed on set user | This error occurs when the tool is unable to store the user information in SMH registry. The most common cause of this error is when the SAG environment has not been set up correctly, causing in turn incorrect settings for the SMH environment variables. |
| Registry Access Failed on set password | This error occurs when the tool is unable to store the password information. |
As mentioned previously, the batch help command has the following form:
[<commandIdentifier>] [<batchEnvironment>] help
Following are its characteristics:
When both <commandIdentifier> and <batchEnvironment> are specified, the help information is restricted to those batch environment parameters.
If only <commandIdentifier> is specified, information about the batch command on the localhost is given.
If only <batchEnvironment> is specified, all available batch commands for the specified target node, product and version are given.
If neither <commandIdentifier> nor <batchEnvironment> is specified, some general information about batch is displayed.
An alternative help command is also available:
helplong. This command, where available, displays
more detailed information than the standard help
command. Where it is not available, the helplong
command produces the same output as the help
command.
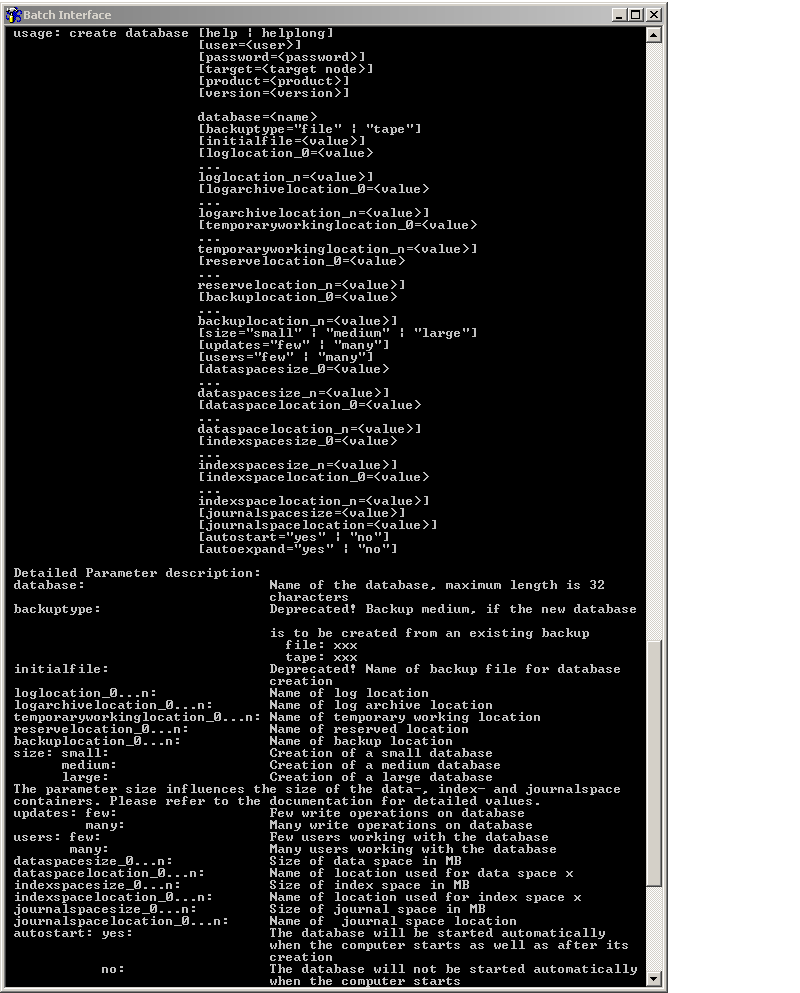
The following screen capture shows a sample of the output of the
helplong command with the create
database command. The information is part the create
database command with the product Tamino.