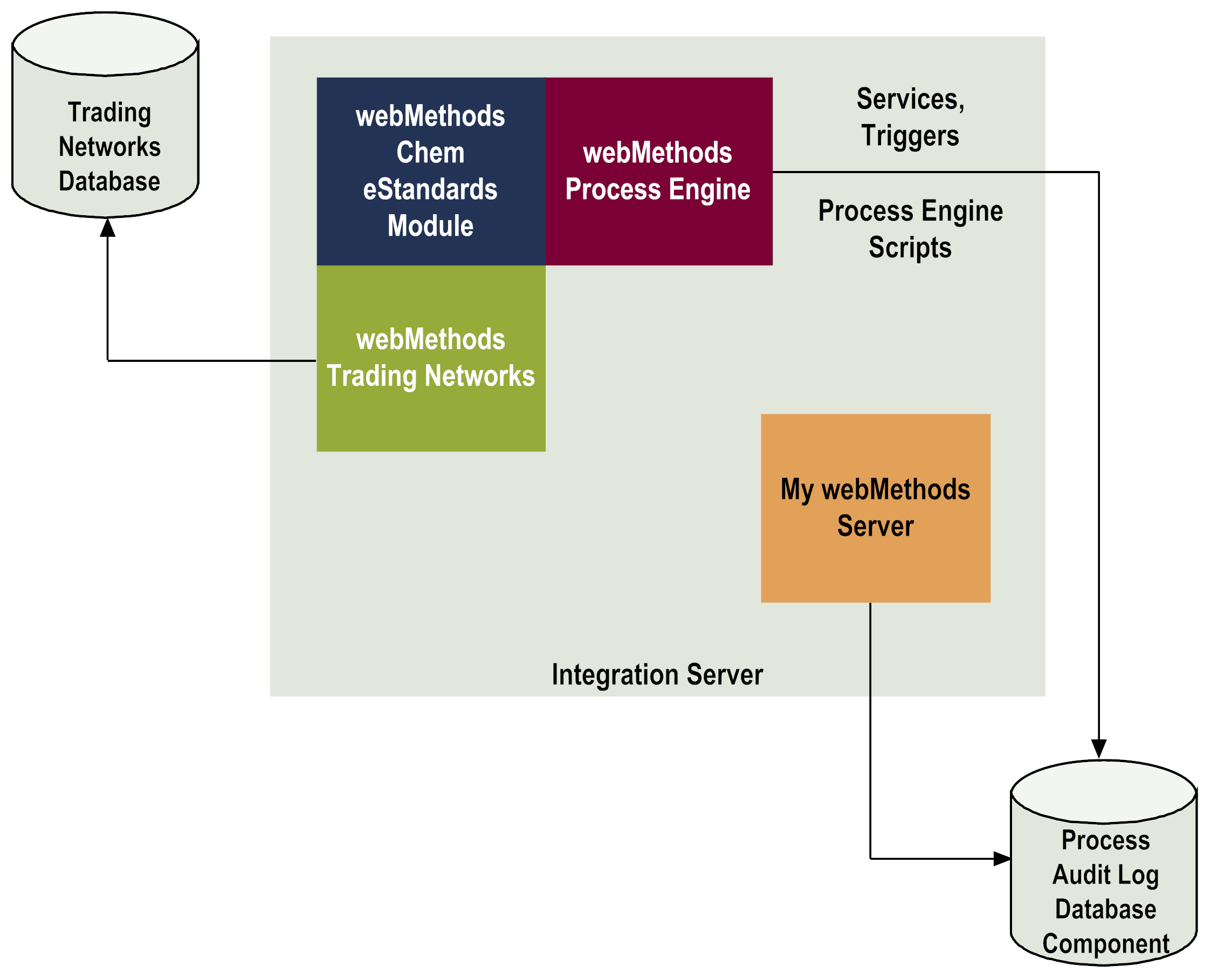

Component | Description |
webMethods Chem eStandards Module | During run time, the webMethods Chem eStandards Modulereceives a business document from a back‐end system or trading partner. It invokes a Trading Networks service to: Chem eStandards passes the business document to the webMethods Process Engine. For more information about the Process Engine, see the webMethods Process Engine row in this table. |
Trading Networks | Trading Networks enables your enterprise to link with trading partners with whom you want to exchange business documents, thereby forming a business‐to‐business trading network. During run time, the Chem eStandards uses Trading Networks services and TN XML document types to: The Chem eStandards uses the trading partner profiles in Trading Networks to determine, for example, the methods by which to send business documents to its trading partners. The webMethods Chem eStandards Module uses TPAs in Trading Networks to determine information such as whether an outbound business document should be signed or whether the Service Header of the business document (along with any attachments) should be encrypted. For more information about Trading Networks, trading partner profiles, TN XML document types, and TPAs, see the webMethods Trading Networks Administrator’s Guide. You can also find information about trading partner profiles in Chapter, "
Defining Trading Partner Profiles in
Trading Networks" and information about TPAs in Chapter, "
Customizing Trading Partner Agreements". |
Trading Networks Database | The Trading Networks database stores TN XML document type, TPA, and trading partner profile information. |
webMethods Process Engine | The Process Engine is a facility of the Integration Server that manages the execution of Chem eStandards conversations. The Process Engine ensures the integrity, traceability, observability, and controllability of Chem eStandards conversations by performing the following functions: During processing of a business document, the Process Engine uses the ConversationID associated with the business document to determine whether the business document belongs to a new or existing conversation. TheProcess Engine looks for a matching ConversationID among the running process instances, and if it finds one, the business document rejoins the running conversation. If it does not find a running process instance with a matching ConversationID, it starts a new conversation (process) by finding an enabled process model that starts with the received business document. For more information about the Process Engine, see the webMethods Process Engine User's Guide. For more information about ConversationIDs, see
Running a Conversation and the ConversationID
|
My webMethods Server | Use webMethods Monitor functionality that you access via My webMethods Server to manage and monitor conversations. webMethods Monitor displays information about a conversation by retrieving information from the Process Audit Log database component. You can manage a conversation with commands such as, suspend, resume, restart, and stop. |
Process Logging Database | webMethods Monitor and the Process Engine log audit data about running conversations to the Process Audit Log database component. |
Integration Server | TheIntegration Server contains the run‐time elements that were generated from the automated controlled steps within the process model. The run‐time elements are services, triggers, and Process Engine scripts (or fragments). |