This document describes the entities in Natural Security that are used for security definitions in Predict.
This document covers the following topics:
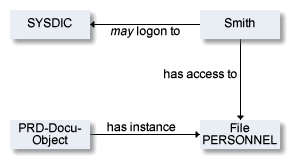
This example illustrates the following situation:
The user Smith is authorized to logon to library SYSDIC and has access to file object PERSONNEL, an instance of NSC external object type PRD-docu-object.
A user is the central point of the Predict Security system. This object represents a person that works with the system.
Users can be a member of one or more groups. See Group.
When a user logs on to a library, the link ID is determined as follows:
If the user is linked directly to the library, the link ID is the same as the user ID.
If the user is linked to the library indirectly as member of a group, the link ID is the group ID.
See your Natural Security documentation for more information.
Note:
See also Concepts of
Incorporation External Objects in Predict
documentation for basic information on how to use incorporation
functions
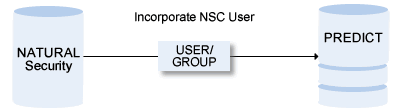
New users can be added manually with the function Add user in Natural Security.
Only a Natural Security System Administrator can incorporate a Natural Security user.
The Incorporate Natural Security user screen is displayed by selecting function code I and object code NS in a Predict main menu or by entering the direct command INCORPORATE Security.
13:32:58 ***** P R E D I C T ***** 2007-05-31
- Incorporate Natural Security User -
User ID..............
Incorporation options
Add user............. N (Y/N)
From date............ 0000-00-00
User type...........*
with comments........ Y (Y/N)
with edit description N (Y/N)
|
| Parameters | |
|---|---|
| User ID | ID of the Natural Security user to be processed. Asterisk notation is allowed. |
| Add user | Y Natural Security users that are not defined in Predict will be added to it. |
| From date | Limit the incorporation to user IDs which were added to the Natural Security system after the specified date. |
| User type |
The type of user defined in Natural Security:
A Administrator |
| with comments | Y User ID comments in the Natural Security system will be copied to Predict. Each comment line will be split and stored as two halves. |
| with edit description | Y User ID comments in the Natural Security system will be copied to the extended description. |
Command: INCORPORATE SECURITY
Enter parameters on next line in positional or keyword form.
| Field | Keyword | Position |
|---|---|---|
| User | USER-ID | 1 |
| Add user | ADD-USER | 2 |
| from date | DATE | 3 |
| User type | TYPE | 4 |
| with comments | COMMENT | 5 |
| with edit description | DESC | 6 |
To incorporate Natural Security administrators whose names start with 'A', code the command:
INCORPORATE SECURITY USER-ID=A*,ADD-USER=Y,TYPE=A
or in positional form:
INCORPORATE SECURITY A*,Y,,A
The example above uses the Natural parameters IA==, ID=, and IM=D
A group in Natural Security is a collection of users. See User.
The number of users in a group is unlimited.
Groups have no relationships with other groups. This means a group cannot be part of another group.
A user can belong to several groups.
New groups can also be added in Natural Security with the function Add user.
To use Predict Security, the libraries SYSDIC, SYSDICBE, SYSDICCO and SYSDICMA must be defined as libraries in Natural Security.
Use the Natural Security function Add Library with the following parameters:
library ID = SYSDIC (for example)
startup transaction = MENU
restart transaction = blank
error transaction = blank
If the use of Natural commands from Predict is to be disallowed, the Predict libraries must be defined in Natural Security accordingly. Use the Natural Security function Modify Predict library > Additional options > Restrictions > Security options to define the following values for parameter Definition of command mode:
Allow NEXT, MORE line = N
Allow System commands = Y
The Natural commands CHECK, LIST, HELP, RETURN, SAVE and RUN are used by Predict internally and must therefore be allowed.
We recommend you set the parameters MADIO and MAXCL to 0 (zero).
Natural Security writes XRef data for programs that are used as startup, restart or error transactions in a library or a special link: this requires that the parameter XREF is set to Y or F in the Natural Security definition of the libraries and that a user system file is defined for the library.
In XRef data, programs used as startup, restart or error transactions are indicated as used by a dummy program *NSC.
If XRef data for startup, restart or error transaction has not yet been created, you can use the conversion function Add Natural Security XRef data. For more information see Add Natural Security XRef Data in the section Conversion in the Predict Administration documentation.
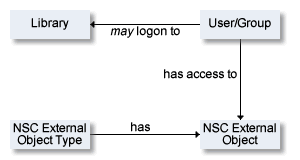
An NSC external object type is a group of things to be protected, such as objects or functions.
These NSC external object types and their standard definitions are added in Natural Security with the special function Maintain NSC Definitions > Add NSC Default Definitions.
Definitions for this NSC external object type are automatically added in Natural Security. For example: FI and FI-A for files or files of type Adabas. See list of Resources for predefined object types in Adding Predefined Object Types.
User-defined object types are also added with this function. Security definitions for instances of this external object type, for example files that begin with ABC, must be added manually in Natural Security. See Security Definitions at Object Level.
For this NSC external object type, the instances are automatically added in Natural Security.
If you wish to protect 3GL libraries, you must define security objects of this type manually in Natural Security.
For this NSC external object type, the instances are automatically added in Natural Security. See Maintain NSC Definitions in the section Special Functions in the Predict Administration documentation.
The default value for all NSC external object types is allowed. If you keep the default value as allowed and do not add any security definitions, each user can execute any function and access any documentation or external object.
If you set the default value for a NSC external object type to disallowed, you have to give each user or group explicit access to all instances of this NSC external object type they needs for their work.
The following access can be given for instances of all NSC external object types except PRD-Function:
READ
ADD
MODIFY
DELETE
The following rules apply:
If a user does not have READ access, he cannot be granted ADD/MODIFY/DELETE access.
READ access is a prerequisite for access modes ADD, MODIFY and DELETE.
The following access can be given for instances of NSC external object type PRD-Function:
EXECUTE
Possible values for the access modes listed above are:
Resources of NSC external object type PRD-Docu-Object can be divided up as follows:
Security Definitions at Object Level for all of the above object types.
Security definitions on this level are usually intended to protect functions. Example: If the user does not have any READ access to object type FI, he cannot execute any Predict functions that process files. He cannot call the File Maintenance or Retrieval Menu.
See also Hierarchy of Security Definitions.
This group includes main object types (for example FI, PR) as well as subtypes of predefined object types (for example FI-A for files of type Adabas).
If you deny a user or group access to a main object type such as FI or PR, it is not possible to call the maintenance or retrieval menu of this type.
In Predict Security, object type field is regarded as an attribute of object type file.
With the Special Function Maintain NSC Definitions you can add all object types and all subtypes as instances of NSC external object type PRD-Docu-Objects automatically:
For main object types, the name of the Resource consists of the two-character object code in Predict, for example DA, FI.
For subtypes, the name of the Resource consists of the two-character object code, a hyphen and the one or two-character code for the subtype, for example DA-A (Database of type Adabas, FI-B (File of type Adabas SQL view). See list below.
| Object Code | Object Type | Subtype Code | Subtype |
|---|---|---|---|
| DA | All database types | DA-A | Adabas database |
| DA-B
|
Adabas D handler | ||
| DC | Dataspace | ||
| ET | Extract | ||
| FI | All file Types | FI-A | Adabas file |
| FI-B
|
Adabas SQL view | ||
| IE | Interface | ||
| KY | Keyword | ||
| LS | Library Structure | ||
| MD | Method | ||
| NO | Node | ||
| NW | Network | ||
| OW | Owner | ||
| PG | All packagelist types | PG-T | Total collection |
| PG-Q
|
DBRM | ||
| PR | All program types | PR-A | Parameter data area |
| PR-C
|
Copy code | ||
| RL | File relation | ||
| PY | Property | ||
| RT | Report listing | ||
| SC | Storagespace | ||
| SV | Server | ||
| SY | All system types | SY-A | Application |
| SY-C
|
Conceptual system | ||
| TR | Trigger | ||
| US | User | ||
| VE | All verification status | VE-A | Automatic verification |
| VE-C
|
Conceptual verification | ||
| VM | Virtual machine | ||
Access to predefined object types in Predict is handled by NSC external object type PRD-Docu-Objects. The following rules apply:
The default value for main object types such as FI or PR is defined with the special function Maintain NSC Definitions > Add NSC Default Definitions. Permitted values are Y and N. See Maintain NSC Definitions in the section Special Functions in the Predict Administration documentation.
The default value for subtypes, such as files of type Adabas, is asterisk. This means that the subtype 'inherits' the security definition of the main object type.
Possible access modes for the instances of this NSC external object type are READ, ADD, MODIFY and DELETE.
If a user has no READ access to a main object type such as FI, he cannot execute any functions that process this object type. Nor can he call the Maintenance and Retrieval menus for this object type.
If an access mode is allowed for a main object type and disallowed for a subtype, the definition at subtype level has priority.
Example: A user has MODIFY access to Predict objects of type file (PRD-Docu-Object FI in Natural Security), but has no MODIFY access to files of type Adabas (Resource FI-A). He cannot modify files of type Adabas.
The name of the NSC object type corresponds to the two-character object code for the UDE in Predict.
The same rules apply as for predefined object types. See Access to Predefined Object Types.
Use the special function Maintain NSC Definitions > Add NSC Default Definitions to add all special object types as instances of NSC external object type PRD-Docu-Objects. See relevant parts of section Special Functions in the Predict Administration documentation.
-A
Association Type
-O
Object Type (for UDEs, only applies to Metadata
Administration)
-R
Retrieval Model
-I
Implementation Plan
The following rules apply:
With object type -I you can create a security definition for a unique Plan ID or - with asterisk notation - for a range of Plan IDs, as you can with predefined object types.
With other object types (-A , -O , -R), security definitions at object level have no effect.
Security definitions can be added in Natural Security for documentation objects that can be processed with Predict functions.
All instances must be added manually in Natural Security.
To add security definitions to documentation objects:
Logon to library SYSSEC
Select Maintenance, then choose *PRD-Docu-Object
In the command line enter ADD
In the upcoming window enter <type> <name>
separated by a blank. Where <type> is the object type (e.g.
FI-A) and <name> is the object name (e.g. ABC-TEST). See
also screen below.
+------------------------------------------------------------+ | ADD *PRD-DOCU-OBJECT | | | | Please enter object´s ID | | FI-A ABC-TEST_______________________ | | | | | +------------------------------------------------------------+ |
With the special function Mass Grant you can create security definitions in Natural Security on the basis of data in Predict. Objects for which you wish to create security definitions must be placed in an Extract. See Mass Grant in NSC in the section Special Functions in the Predict Administration documentation.
Possible access modes for instances of this NSC external object type are READ, ADD, MODIFY and DELETE.
With Predict Security you can determine that certain users or groups only have access to certain objects. There are three strategies you can follow when protecting objects:
Protect Individual objects Example: The file SALARY can only be read/modified by certain users.
Protect a range of objects Use naming conventions to group objects and take advantage of asterisk notation in Natural Security. Example: User USER1 has been denied READ access to file objects in general, but READ access for files that begin with his user ID. The more specific authorization has priority.
Protect all objects of a particular type.
All external object types that can be processed with Predict functions can be maintained by Predict Security. Instances of this NSC external object type are for example CO (COBOL Copy Code) or D2 (DB2 database).
Security definitions for PRD-Ext-Objects are used to protect functions.
Use the special function Maintain NSC Definitions > Add NSC Default Definitions to add all external object types as instances of the NSC external object type PRD-Ext-Objects. The following external objects can be added:
| Code | External Object |
|---|---|
| AC | ADACMP/ADAWAN |
| AD | Adabas database |
| AF | Adabas file |
| AI | ADAINV cards |
| AT | Vista table |
| AS | ADASCR |
| AV | Adabas - VSAM |
| BA | BAL/ASSEMBLER |
| BF | Adabas D table/view |
| CC | Language C |
| CO | COBOL |
| CR | SQL CREATE Statement |
| DD | DDM for Natural |
| D2 | DB2 database |
| EQ | Adabas table/view |
| FO | FORTRAN |
| JF | Ingres table/view |
| LA | Language ADA |
| ND | Natural DBD |
| NF | NSC file |
| NO | No synonyms |
| NS | NSC user |
| OF | Oracle table/view |
| PA | Pascal |
| PL | PL/I |
| RC | Server table |
| RU | Verification rule |
| SN | NSP file |
| SG | DB2 storagegroup |
| SQ | Static SQL |
| SU | NSP user |
| TS | DB2 tablespace |
| T2 | DB2 table/view |
| UD | UDF for DL/1 |
| UL | User language |
| W | Sequential file |
| XF | Informix table/view |
| YF | Sybase table/view |
The default value for NSC external object type PRD-Ext-Objects is Y (allowed).
Possible access modes for instances of this NSC external object type are READ, ADD, MODIFY and DELETE.
Each user or group can be granted or denied access to certain external object types.
A security definition at External-Type level is generally used to protect functions. Example: A user without ADD or MODIFY access to object type CO cannot execute the function Generate COBOL Copy Code.
A security check is carried out when you access XRef data in 3GL libraries from Predict (Preprocessor, List XRef for 3GL). This check accesses the security definition for the 8-character library name in Natural Security.
If you wish to protect 3GL libraries, you must define security objects of this type manually in Natural Security.
The following default libraries must be defined with a hyphen instead of an asterisk, for example -SYSCOB-.
| Language | Library | NSC Object to be added |
|---|---|---|
| Language ADA | *SYSADA* | -SYSADA- |
| BAL/Assembler | *SYSBAL* | -SYSBAL- |
| Language C | *SYSCCC* | -SYSCCC- |
| COBOL | *SYSCOB* | -SYSCOB- |
| FORTRAN | *SYSFOR* | -SYSFOR- |
| PL/I | *SYSPLI* | -SYSPLI- |
| Static SQL | *SYSSTA* | -SYSSTA- |
Possible access modes are READ, ADD, MODIFY and DELETE.
As a rule, security definitions in Predict are defined at object type or object level. The following areas of Predict do not process any objects in Predict and are therefore protected with objects of NSC external object type PRD-Function in Natural Security:
Resources of the NSC external object type PRD-Function are divided into the following groups:
You can grant or deny access to all Special Functions. If all Special Functions are allowed, you can disallow individual Special Functions.
The following objects are added automatically with the special function Maintain NSC Definitions > Add NSC Default Definitions:
| Natural Security Object | Predict Special Function |
|---|---|
| SPECIAL* | all Special Functions |
| SPECIAL-ADABAS_DEVICE_TYPES | Adabas device types |
| SPECIAL-MAINTAIN_NSC_DEF | Maintain NSC Definitions |
| SPECIAL-MASS_GRANT | Mass Grant in NSC |
| SPECIAL-DELETE_SETS | Delete old sets |
| SPECIAL-MAINTAIN_HELP_TEXTS | Maintain Predict help texts |
| SPECIAL-RECOVER | Recover |
| SPECIAL-REPOSITION_IMPL_DATA | Reposition implementation data |
| SPECIAL-SECURITY_FOR_AOS | Security for AOS |
| SPECIAL-CONSISTENCY* | Consistency of Predict (see note below) |
| SPECIAL-CONSISTENCY-B | - check database |
| SPECIAL-CONSISTENCY-D | - check extended descriptions |
| SPECIAL-CONSISTENCY-E | - convert EDIT MASKS |
| SPECIAL-CONSISTENCY-F | - check files and fields |
| SPECIAL-CONSISTENCY-H | - compress help texts |
| SPECIAL-CONSISTENCY-K | - check keywords |
| SPECIAL-CONSISTENCY-P | - check programs |
| SPECIAL-CONSISTENCY-R | - convert rules |
| SPECIAL-CONSISTENCY-V | - check verifications |
| SPECIAL-DELETE_REPORTS | Mass delete of report listings |
| SPECIAL-MAINTAIN_ACT_REF* | Maintain XRef data |
| SPECIAL-MAINTAIN_ACT_REF-A | - delete preprocessor ABEND data |
| SPECIAL-MAINTAIN_ACT_REF-G | - delete 3-GL data |
| SPECIAL-MAINTAIN_ACT_REF-N | - delete Natural data |
| SPECIAL-MAINTAIN_STD_FIELDS | Maintain standard fields |
| SPECIAL-REFRESH | Refresh Coordinator FDIC |
With the object SPECIAL* you can define access rights for all Special Functions in Predict.
If SPECIAL* is disallowed, all Special Functions are disallowed.
If SPECIAL* is allowed, you can disallow individual Special functions, for example SPECIAL-DELETE_SETS.
Access to special functions is defined using access mode EXECUTE. The following values are possible:
Possible values for the access modes listed above are:
Y
Function can be executed.
N
Function cannot be executed.
*
Inherit. The security definition of the higher-level object is
taken if appropriate.
For example:
If the individual Consistency subfunctions are set to inherit, the access rights to these subordinate objects are taken from the definition for object SPECIAL-CONSISTENCY*.
All the necessary Natural Security objects are added automatically with the special function Maintain NSC Definitions > Add NSC Default Definitions. See table below.
| Natural Security Object | Predict Coordinator Function |
|---|---|
| CO-IMPORT | Import, Test, Load |
| CO-EXPORT | Export, Unload |
Access to Coordinator functions is defined using access mode EXECUTE. Possible values are Y, N, * . See Access Mode Values.
With object DEFAULTS* you can define access rights for all Default functions. See list below.
If DEFAULTS* is disallowed, all Default functions are disallowed. If DEFAULTS* is allowed, you can disallow individual Default functions, for example DEFAULTS-NATIVE-SQL.
All required Natural Security objects are added automatically with the special function Maintain NSC Definitions > Add NSC Default Definitions. See table below.
| Natural Security Object | Predict Default |
|---|---|
| DEFAULTS* | all Defaults |
| DEFAULTS-GENERAL* | all General Defaults |
| DEFAULTS-GENERAL-M | - Maintenance options |
| DEFAULTS-GENERAL-R | - Redocumentation using source code |
| DEFAULTS-GENERAL-G | - Redocumentation using xref data |
| DEFAULTS-GENERAL-P | - Protection |
| DEFAULTS-GENERAL-S | - Synonyms |
| DEFAULTS-GENERAL-D | - Suppress display of products |
| DEFAULTS-GENERAL-C | - Miscellaneous |
| DEFAULTS-SKELETONS* | Extended Description Skeletons |
| DEFAULTS-PROFILE | Default Profile |
| DEFAULTS-LX_PROFILE | List XREF Default Profile |
| DEFAULTS-GENERATION* | Generation Defaults |
| DEFAULTS-COORDINATOR | Coordinator Defaults |
| DEFAULTS-NATIVE_SQL | Adabas Native SQL Defaults |
| DEFAULTS-USER_EXITS | Activate User Exits |
Under certain circumstances it can be useful if you define your own security objects:
All Extended Description Skeletons are protected with the object DEFAULTS-SKELETONS* as standard. If you want to grant different access rights at object type or subtype level, you need to define a corresponding object manually in Natural Security.
Examples: DEFAULTS-SKELETONS-FI-A for skeletons of files of type Adabas. DEFAULTS-SKELETONS-FI* for skeletons of all files.
All Predict generation defaults are protected with the object DEFAULTS-GENERATION* as standard. To protect generation defaults for a particular external object type, you need to add a corresponding object manually in Natural Security.
Example: DEFAULTS-GENERATION-AF for Adabas files.
Access to defaults is defined using access mode EXECUTE. Possible values are:
Y , N , *.
See Access Mode Values.
| Natural Security Object | Predict Function | Note |
|---|---|---|
| LIST_XREF_3GL | LIST XREF for 3GL | If this Security object is protected, the user cannot access the LIST XREF for 3GL menu. |
| METADATA-DEFAULTS | Metadata Administration function Defaults |