This document covers the following topics:
Notes:
Using Entire Connection, you can upload encrypted files and download data to an encrypted format. To do so, specify enc as the file extension.
Enhanced encryption provides additional security for data transfer. In the Configuration Manager, the user can specify whether enhanced encryption is to be used.
The most common form of data transfer is downloading data that consist of multiple records. These records have a fixed number of fields and can be converted into one of the PC file formats supported by Entire Connection.
Natural program examples: Natex01.nsp and Natex02.nsp.
Data that are not in the form of a record and have neither a
fixed length nor a fixed format are referred to as variable data. Variable data
cannot be uploaded or converted. The Natural statement for downloading variable
data is DOWNLOAD PC FILE n VARIABLE
field1 .. fieldn
or WRITE PC FILE n VARIABLE
field1 .. fieldn.
Variable data can only be downloaded into ASCII format. Binary data are
converted to readable ASCII format, and leading zeros are always substituted
with blanks.
Natural program example: Natex03.nsp.
To download a report, you must associate a printer file number with the file name. The data are downloaded to the PC in a printable format (for example, with headings, page numbers, etc.). Reports cannot be uploaded or converted.
Natural program example: Natex04.nsp.
Binary data are typically object code or executable code which does not contain displayable or printable characters. To avoid the standard character translations that occur during data transfer, Entire Connection uses special methods for transferring binary data.
To download binary data, you must define a binary variable (B1 to B126). The best performance is achieved when you choose a block size of 126 bytes (i.e. a binary variable B126).
With Natural Version 4.1 for Mainframes and Natural Version 6.1 for UNIX, you can use binary variables greater than 126. The maximum value which can be specified depends on your Natural version. See the Natural documentation for further information.
You must mark the end of your binary data with X'FF' (i.e. the hexadecimal value of FF). If the last block of downloaded data contains less data than the chosen block size, you must insert X'FF' at the position that marks the end of binary data and fill the rest of the block with binary zeros. If the amount of data in last block equals the chosen block size, you must include an additional block containing X'FF' and fill the rest of the block with binary zeros to mark the end of binary data.
It is possible to combine binary data and all other types of data (alphanumeric, numeric, integer etc.). Files containing binary data and ASCII data, or multiple binary fields, can be uploaded or downloaded. During data transfer, such a file is treated like an ASCII file. The records within the file must have a fixed length and must end with CR and LF. Spaces at the end of the record are not truncated. Tabulator characters (0X09) are not recognized.
Natural program examples: Natex05.nsp and Natex06.nsp.
When you download data with the extension dbf to dBase, dBase column labels are automatically generated for Natural field names.
When you download data with the extension wkl to Lotus, the first record is reserved for column labels. If field names are available from the host, the names of the variables are automatically entered as column labels in the first row of the file. If field names are not available, the first row is left blank.
When you download data to an HTML file (extension htm or html), Entire Connection creates an HTML format which can be opened with a browser (e.g. Internet Explorer) and with Excel.
The character set to be used is defined in the session properties. It is also possible to download data to a file with the extension htm or html in NCD (ASCII) format. See the description of the Data Transfer property page for further information.
When you download data to an XML file (extension xml), the resulting file has the following structure:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<NATURAL_DOWNLOAD LIBRARY="NATLIB" program="MYPROG" user="THE_USER">
<RECORD>
<. . .>
</RECORD>
. . .
<RECORD>
< . . .>
</RECORD>
</NATURAL_DOWNLOAD>
Each <RECORD> element contains
the fields of a downloaded record. The names of the variables are downloaded as
element names, and the values of the variables are downloaded as element
contents.
Example for a simple Natural download to XML format:
0010 DEFINE DATA LOCAL 0020 1 NAME (A40) 0030 1 CITY (A40) 0040 END-DEFINE 0050 NAME := 'SMITH' 0060 CITY := 'NEW YORK' 0070 WRITE WORK 7 NAME CITY 0080 NAME := 'BUSH' 0090 CITY := 'LONDON' 0100 WRITE WORK 7 NAME CITY 0110 END
This results in the following XML file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<NATURAL_DOWNLOAD library="NTWTEST" program="PROG1" user="NTWTEST1">
<RECORD>
<NAME>SMITH</NAME>
<CITY>NEW YORK</CITY>
</RECORD>
<RECORD>
<NAME>BUSH</NAME>
<CITY>LONDON</CITY>
</RECORD>
</NATURAL_DOWNLOAD>
The character set to be used is defined in the session properties. It is also possible to download data to a file with the extension xml in NCD (ASCII) format. See the description of the Data Transfer property page for further information.
The following information is provided below:
For further information on XML, see http://www.w3.org/XML/.
The following special characters, which are allowed in Natural variable names, are not allowed in XML element names:
#
@
/
$
§
&
+
During download, each of these characters in a Natural variable name is converted to an underscore (_) character.
Fields without variable names are downloaded to an
<UNNAMED_FIELD_n> element, where
n represents the index of the downloaded field in
the record.
Example for a Natural download without field names:
0010 WRITE WORK 7 2 3 4 0020 END
This results in the following XML file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<NATURAL_DOWNLOAD library="NTWTEST" program="DN_ARR4" user="NTWTEST1">
<RECORD>
<UNNAMED_FIELD_0>2</UNNAMED_FIELD_0>
<UNNAMED_FIELD_1>3</UNNAMED_FIELD_1>
<UNNAMED_FIELD_2>4</UNNAMED_FIELD_2>
</RECORD>
</NATURAL_DOWNLOAD>
Natural groups are downloaded as parent elements for the fields.
Example for downloading Natural groups:
0010 DEFINE DATA LOCAL 0020 1 NAME 0030 2 FIRST_NAME (A40) 0040 2 LAST_NAME (A40) 0050 1 CITY (A40) 0060 END-DEFINE 0070 FIRST_NAME := 'ALAN' 0080 LAST_NAME := 'SMITH' 0090 CITY := 'NEW YORK' 0100 WRITE WORK 7 NAME CITY 0110 FIRST_NAME := 'TOM' 0120 LAST_NAME := 'BUSH' 0130 CITY := 'LONDON' 0140 WRITE WORK 7 NAME CITY 0150 END
This results in the following XML file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<NATURAL_DOWNLOAD library="NTWTEST" program="PROG2" user="NTWTEST1">
<RECORD>
<NAME>
<FIRST_NAME>ALAN</FIRST_NAME>
<LAST_NAME>SMITH</LAST_NAME>
</NAME>
<CITY>NEW YORK</CITY>
</RECORD>
<RECORD>
<NAME>
<FIRST_NAME>TOM</FIRST_NAME>
<LAST_NAME>BUSH</LAST_NAME>
></NAME>
<CITY>LONDON</CITY>
</RECORD>
</NATURAL_DOWNLOAD>
During download, index
attributes are created for the elements of a unidimensional array.
Example for downloading unidimensional arrays:
DEFINE DATA LOCAL 1 NAME 2 FIRST_NAMES (1:3) 3 FIRST_NAME (A40) 2 LAST_NAME (A40) 1 CITY (A40) END-DEFINE * FIRST_NAME(1):='ALAN' FIRST_NAME(2):='PAUL' FIRST_NAME(3):='OLIVER' LAST_NAME := 'SMITH' CITY := 'NEW YORK' WRITE WORK 7 NAME CITY * RESET FIRST_NAMES(1:3) FIRST_NAME(1) := 'ERIKA' FIRST_NAME(2) := 'CLARA' LAST_NAME := 'BUSH' CITY := 'LONDON' WRITE WORK 7 NAME CITY END
This results in the following XML file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<NATURAL_DOWNLOAD library="NTWTEST" program="ADDRESS" user="NTWTEST1">
<RECORD>
<NAME>
<FIRST_NAME index="1">ALAN</FIRST_NAME>
<FIRST_NAME index="2">PAUL</FIRST_NAME>
<FIRST_NAME index="3">OLIVER</FIRST_NAME>
<LAST_NAME>SMITH</LAST_NAME>
</NAME>
<CITY>NEW YORK</CITY>
</RECORD>
<RECORD>
<NAME>
<FIRST_NAME index="1">ERIKA</FIRST_NAME>
<FIRST_NAME index="2">CLARA</FIRST_NAME>
<FIRST_NAME index="3"></FIRST_NAME>
<LAST_NAME>BUSH</LAST_NAME>
</NAME>
<CITY>LONDON</CITY>
</RECORD>
</NATURAL_DOWNLOAD>
Two- and three-dimensional arrays are downloaded as child elements.
In a two-dimensional array, the first child element is
<COLUMN>. Its
pos attribute indicates the position of the
column in the array. <ROW> is a child element
of <COLUMN>. Its
pos attribute indicates the position of the row
in the array. The downloaded two-dimensional array has the following
structure:
<DIM2ARRAY>
<COLUMN pos="1">
<ROW pos="1">data1</ROW>
<ROW pos="2">data2</ROW>
. . .
</COLUMN>
<COLUMN>
. . .
</COLUMN>
</DIM2ARRAY>
A three-dimensional array contains the additional element
<PLANE>. Its
pos attribute indicates the position of the
plane in the three-dimensional array. The downloaded three-dimensional array
has the following structure:
<DIM3ARRAY>
<PLANE>
<COLUMN pos="1">
<ROW pos="1">data1</ROW>
<ROW pos="2">data2</ROW>
. . .
</COLUMN>
<COLUMN>
. . .
</COLUMN>
</PLANE>
<PLANE>
. . .
</PLANE>
</DIM3ARRAY>
Example for downloading a three-dimensional array:
DEFINE DATA LOCAL
1 ARRAY
2 MYROW (2:3)
3 MYCOLUMN (1:2)
4 MYPLANE (1:2)
5 FIELD (P3) INIT (2:3,1:2,1:2) <99>
END-DEFINE
WRITE WORK 7 FIELD (*,*,*)
END
This results in the following XML file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<NATURAL_DOWNLOAD library="NTWTEST" program="DN_ARR4" user="NTWTEST1">
<RECORD>
<ARRAY>
<FIELD>
<PLANE pos="1">
<COLUMN pos="1">
<ROW pos="2">99</ROW>
<ROW pos="3">99</ROW>
</COLUMN>
<COLUMN pos="2">
<ROW pos="2">99</ROW>
<ROW pos="3">99</ROW>
</COLUMN>
</PLANE>
<PLANE pos="2">
<COLUMN pos="1">
<ROW pos="2">99</ROW>
<ROW pos="3">99</ROW>
</COLUMN>
<COLUMN pos="2">
<ROW pos="2">99</ROW>
<ROW pos="3">99</ROW>
</COLUMN>
</PLANE>
</FIELD>
</ARRAY>
</RECORD>
</NATURAL_DOWNLOAD>
You can use XSL style sheets with your downloaded XML files. This is helpful, for example, if you want to display the contents of an XML file in a browser. To do so, you must first create an appropriate style sheet (see http://www.w3.org/Style/) and then insert the style sheet definition in the header of your downloaded XML file.
Note:
With the SET command, a style
sheet definition can be added automatically to all downloaded XML files. See
Specifying a
File Name Using the SET Command.
Example for downloading data and displaying it as a simple table using a style sheet:
0010 DEFINE DATA LOCAL 0020 1 EMPLOY-VIEW VIEW OF EMPLOYEES 0030 2 FULL-NAME 0040 3 FIRST-NAME 0050 3 MIDDLE-NAME 0060 3 NAME 0070 2 PERSONNEL-ID 0080 1 VEHIC-VIEW VIEW OF VEHICLES 0090 2 MAKE 0100 2 REG-NUM 0110 END-DEFINE 0120 FIND EMPLOY-VIEW WITH CITY = 'DARMSTADT' SORTED BY NAME 0130 FIND VEHIC-VIEW WITH PERSONNEL-ID = PERSONNEL-ID 0140 WRITE WORK 7 FULL-NAME MAKE 0150 END-FIND 0160 END-FIND 0170 END
This results in the following XML file (the style sheet definition that is to be entered manually is indicated in boldface):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<?xml-stylesheet type="text/xsl" href="employ2.xsl"?>
<NATURAL_DOWNLOAD library="NTWTEST" program="EMPLOYE2" user="NTWTEST1">
<RECORD>
<EMPLOY-VIEW>
<FIRST-NAME>KRISTINA</FIRST-NAME>
<MIDDLE-NAME>MARIA</MIDDLE-NAME>
<NAME>FALTER</NAME>
</EMPLOY-VIEW>
<VEHIC-VIEW>
<MAKE>FORD</MAKE>
</VEHIC-VIEW>
</RECORD>
<RECORD>
<EMPLOY-VIEW>
<FIRST-NAME>DIETER</FIRST-NAME>
<MIDDLE-NAME>PETER</MIDDLE-NAME>
<NAME>MUELLER</NAME>
</EMPLOY-VIEW>
<VEHIC-VIEW>
<MAKE>FORD</MAKE>
</VEHIC-VIEW>
</RECORD>
<RECORD>
<EMPLOY-VIEW>
<FIRST-NAME>CHRISTIAN</FIRST-NAME>
<MIDDLE-NAME></MIDDLE-NAME>
<NAME>SCHIRM</NAME>
</EMPLOY-VIEW>
<VEHIC-VIEW>
<MAKE>BMW</MAKE>
</VEHIC-VIEW>
</RECORD>
<RECORD>
<EMPLOY-VIEW>
<FIRST-NAME>ROLAND</FIRST-NAME>
<MIDDLE-NAME>KARL</MIDDLE-NAME>
<NAME>VOGEL</NAME>
</EMPLOY-VIEW>
<VEHIC-VIEW>
<MAKE>VOLVO</MAKE>
</VEHIC-VIEW>
</RECORD>
</NATURAL_DOWNLOAD>
The name of the following style sheet (employ2.xsl) has been manually inserted in the above XML file:
<?xml version='1.0'?>
<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/TR/WD-xsl">
<xsl:template match="/">
<HTML>
<BODY>
<table border="5">
<tr>
<th colspan="3" bgcolor="#99CCCC">Name</th>
<th rowspan="2" bgcolor="#99CCCC">Vehicle</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th bgcolor="#0099CC">First</th>
<th bgcolor="#0099CC">Middle</th>
<th bgcolor="#0099CC">Last</th>
</tr>
<xsl:for-each select="NATURAL_DOWNLOAD/RECORD">
<tr>
<xsl:for-each select="EMPLOY-VIEW">
<td><xsl:value-of select="FIRST-NAME"/></td>
<td><xsl:value-of select="MIDDLE-NAME"/></td>
<td><xsl:value-of select="NAME"/></td>
</xsl:for-each>
<xsl:for-each select="VEHIC-VIEW">
<td><xsl:value-of select="MAKE"/></td>
</xsl:for-each>
</tr>
</xsl:for-each>
</table>
</BODY>
</HTML>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
When you display your XML file in a browser, it looks as follows:
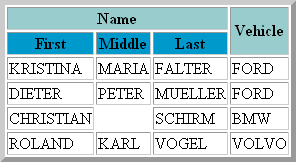
When you download data to Excel (xls or xlsx, depending on the installed Excel version), Entire Connection does not create the file itself. Instead, it starts the automation server for the corresponding Excel version. Depending on the Excel version installed on your PC, data are thus downloaded to the corresponding Excel format. If Excel 2007 or above is the installed version, the file that is created has the new Excel file format and the corresponding new extension xlsx.
When you download numeric data to ASCII format, the position preceding a number is reserved to indicate negative or positive numbers. For positive numbers, this position contains a blank character. For negative numbers, it contains a minus (-) character.
You can upload data from any of the supported file formats. Exception: variable data and reports cannot be uploaded. Once the data are uploaded, you can use them in a Natural application.
Natural program examples: Natex07.nsp and Natex08.nsp.
Binary data are typically object code or executable code which does not contain displayable or printable characters. To avoid the standard character translations that occur during data transfer, Entire Connection uses special methods for transferring binary data.
To upload binary data, you must define a binary variable to which the data are uploaded.
With Natural Version 4.1 for Mainframes and Natural Version 6.1 for UNIX, you can use binary variables greater than 126. The maximum value which can be specified depends on your Natural version. See the Natural documentation for further information.
It is possible to combine binary data and all other types of data (alphanumeric, numeric, integer etc.). Files containing binary data and ASCII data, or multiple binary fields, can be uploaded or downloaded. During data transfer, such a file is treated like an ASCII file. The records within the file must have a fixed length and must end with CR and LF. Spaces at the end of the record are not truncated. Tabulator characters (0X09) are not recognized.
Entire Connection marks the end of the binary data with X'FF' (i.e.the hexadecimal value of FF) and fills the rest of the upload buffer with binary zeros.
Natural program examples: Natex09.nsp and Natex06.nsp.
Column labels are not uploaded.
When you upload a Lotus file with the extension wkl, Entire Connection assumes that the first record contains column labels and thus does not upload it.
When you upload a dBase file with the extension dbf, all records are uploaded.
In addition to regular HTML files, you can also upload HTML files that have been edited using Excel (up to Excel 2007). Because of the new file format of HTML files that are created with Excel 2007 or above, these HTML files cannot be uploaded.
Supported encodings for upload are ISO-8859 and Windows Encoding. Make sure that you have defined one of these encodings in Excel. Starting with Excel 2000, you can check/set the encoding as follows: from the menu, choose . In the resulting dialog box, select the General tab and then choose the button. In the resulting dialog box, select the Encoding tab. You can now select the required encoding from a drop-down list box.
It is also possible to upload HTML files so that they are written in NCD (ASCII) format. See the description of the Data Transfer property page for further information.
You can upload your downloaded XML files or create
XML files for upload yourself. The upload procedure checks for data in the
<RECORD> elements. The names of the child
elements are not considered. Thus, the following two sample uploads produce
identical results:
<NATURAL_DOWNLOAD>
<RECORD>
<NAME>
<FIRSTNAME>
<FIRST>KLAUS</FIRST>
<SECOND>OTTO</SECOND>
</FIRSTNAME>
</NAME>
<AGE>88</AGE>
</RECORD>
</NATURAL_DOWNLOAD>
<NATURAL_DOWNLOAD> <RECORD> <DATA>KLAUS</DATA> <DATA>OTTO</DATA> <DATA>88</DATA> </RECORD> </NATURAL_DOWNLOAD>
The character set to be used is defined in the session properties. It is also possible to upload XML files so that they are written in NCD (ASCII) format. See the description of the Data Transfer property page for further information.
When you upload data from an Excel file (xls or xlsx, depending on the installed Excel version), make sure that the option in the session properties which defines whether the first row in Excel is used for the Natural field names corresponds to the contents of your Excel file. Otherwise an error message appears and the upload does not complete. An error message appears in the following cases:
When there are no column labels (Natural field names) in the Excel sheet, but the above mentioned option has been switched on.
When there are column labels (Natural field names) in the Excel sheet, but the above mentioned option has been switched off.
See the description of the Data Transfer property page for further information.
When the format used for uploading is too small for the data in the file to be uploaded, the excess data for each record are truncated (i.e. they are not uploaded).
The following operations are not supported for Unicode data:
Writing Unicode data to an NCC file and reading Unicode data from an NCC file.
Sending Unicode data directly to the printer.
Uploading binary data from UTF-16 files.