To establish correct communication between clients and Adabas databases, it is necessary to install Adabas client link routines in each supported client environment.
The table below lists all supported client environments with links to the corresponding installation instructions.
| Client Environment | Installation Instructions |
|---|---|
| CICS | |
| Batch/TSO | |
| Com-plete | |
| IMS TM |
In addition, the following links provide installation information which is applicable to all the above client environments:
This section describes the preparation of Adabas client link routines. The source modules for Adabas link routines are not provided in the Adabas base source library. The Adabas link routines can only be tailored via zap or using a link globals table.
Important
If an ADALNK batch link routine has been linked or modified by Software GmbH
product modules or user exits, it cannot be used in any application startups of Adabas
utility jobs or Adabas, Entire System Server, Adabas Review Hub, or Entire Net-Work
nuclei.
ADAUSER is a module with an entry point ADABAS that is normally link-edited with batch (single tasking and multi-tasking) application programs.
On the first Adabas call, ADAUSER dynamically loads and calls the ADARUN module which establishes the appropriate Adabas link module to be used for calling Adabas. Subsequent Adabas calls bypass ADARUN and are routed directly to the Adabas link module.
When ADARUN is called it processes its DDCARD control statements. For the ADARUN
control statement PROGRAM=USER (the default), ADARUN loads the
non-reentrant Adabas link module ADALNK. For applications that require use of the
reentrant link module ADALNKR, the ADARUN control statement
PROGRAM=RENTUSER should be used.
Note
When using ADARUN PROGRAM=RENTUSER, for the reentrant link
module ADALNKR to honor the use of the ADARUN control statements DBID= and SVC=, the
ADARUN control statement LNKGNAME= should be used to provide a non-reentrant LNKGBLS
module for ADARUN to propagate the DBID= and SVC= values.
All Adabas link routines include AMODE and RMODE assembly directives. These assembly directives allow the linkage editor to produce warning messages when conflicting AMODE or RMODE linkage-editor control statements are encountered in the link JCL, JCS, or EXECs.
These assembly directives also serve to document the preferred AMODE and RMODE for each link routine. It is important to note that in and of themselves, these directives do not alter the actual addressing mode of the link routine during execution.
This section covers the following topics:
When re-linking the Adabas link routines with certain AMODE
and RMODE combinations, a warning message may be generated by
the linkage editor. This may be safely ignored as long as it pertains to a conflict of
AMODE or RMODE in the ESD record of
one or more of the load modules that comprise the link routine, and as long as the
resulting module has the proper AMODE and
RMODE attributes for execution with the intended calling
application programs.
Care must be taken to ensure that AMODE(24) applications will
operate properly when invoking the link routine with the attributes chosen when it is
re-linked. This is particularly important if the RMODE(ANY)
attribute is associated with a link routine that will be loaded dynamically but
invoked by a program that is AMODE(24). In this case, the link
routine should be re-linked AMODE(31),
RMODE(24) to avoid addressing exception ABENDs because the
AMODE(24) application cannot correctly invoke the link
routine if it resides above the 16-megabyte line.
The Adabas link routines all run AMODE(31) after
initialization, but they will return to the caller in the caller's
AMODE.
Note
Under CICS, the Adabas link routines run AMODE(31), but the
Dataloc RDO parameter governs the AMODE and
RMODE of the running CICS transaction.
The batch/TSO non-reentrant link routine, ADALNK, has been
assembled and linked with AMODE(31),
RMODE(24), and that is the recommended configuration to
support AMODE(24) or RMODE(24)
application programs. It may be re-linked AMODE(31),
RMODE(ANY) if desired, but this should only be done if it is
certain that all calling programs are AMODE(31).
The ADALNKR batch TSO reentrant link routine has been
assembled and link-edited with AMODE(31),
RMODE(ANY). If it is loaded by an application that is
AMODE(24), it should be relinked
AMODE(31), RMODE(24).
The Com-plete module ADALCO has been assembled and linked
AMODE(31), RMODE(ANY). The Com-plete
TP monitor ensures proper AMODE switching between AMODE(24) or
RMODE(24) programs that invoke ADALCO through the Com-plete
Adabas interface routine, TLOPADAB.
All of the CICS link routine modules - ADACICS,
ADACICT, and ADACIC0 - have been
assembled and link-edited AMODE(31),
RMODE(ANY). CICS manages the loading of programs and their
invocation depending on the DATALOC values associated with their program and
transaction definitions.
The Adabas IMS interface link routine ADALNI has been
assembled and link-edited
AMODE(31),RMODE(ANY). This is the
preferred configuration for modern IMS applications, but if there are still
AMODE(24) IMS applications executing at your installation,
ADALNI may be re-linked AMODE(31),
RMODE(24).
ADAUSER has AMODE(31), RMODE(ANY). This
is the most flexible configuration for linking ADAUSER with the widest variety of
application programs. However, if an AMODE 24 application
program loads ADAUSER dynamically, the ADAUSER module should be re-linked to
AMODE(31), RMODE(24) to ensure that
the program can invoke ADAUSER properly below the 16-megabyte line.
A pre-command user exit and a post-command user exit may be linked with the Adabas link globals table for subsequent invocation by the Adabas link module. Refer to the LGBLSET parameters USERX1 and LX1NAME, and USERX2 and LX2NAME respectively for information on how to ensure any linked exits are invoked.
User exit 1 receives control before a command is passed to a target.
Note
Special commands emanating from utilities and from Adabas Online System are marked
as physical calls. These calls must be bypassed in user exits. These calls have X‘04’ in
the first byte (TYPE field) of the command’s Adabas control block (ACBX). Any link
routine user exit 1 must check this byte and return if it is set to X‘04’. Be sure to
reset R15 to zero on return.
User exit 2 receives control after a command has been processed by a target, the Adabas SVC, or the link module itself.
At entry to the exit(s), the registers contain the following:
| Register | Contents |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Address of the User Block (UB). Refer to User Buffers for information regarding the User Block fields which describe the length and location of the user information area when configured using the LGBLSET LUINFO parameter. |
| 2 |
Address of an 18-word format 1 register save area. |
| 13 |
For CICS, on entry to the link user exit, R13 points to the CICS DFHEISTG work area. |
| 14 |
Return address. |
| 15 |
Entry point address: User exit 1 or 2. |
Any registers except register 15 that are modified by the user exits must be saved and restored; the address of a save area for this purpose is in register 2 on entry to the exit.
If at return from user exit 1, register 15 contains a value other than zero (0), the command is not sent to the target but is returned to the caller. The user exit should have set a non-zero response code in the Adabas control block to indicate to the calling program that it has suppressed the command: response code 216 (ADARSP216) is reserved for this purpose.
The source code for the Adabas batch and TSO link routines is not included with Adabas. These modules are delivered with LNKUES along with the ASC2EBC and EBC2ASC translation tables. Please run with these UES components for this version of Adabas. The link routine will detect if a target database is not UES-enabled, and will provide an Adabas response code 228 (ADARSP228) if the call is from a client requiring UES translation.
The Adabas Com-plete link routine determines whether UES support is required from the settings in the LCOGBL module that you modify and assemble when installing Adabas with Com-plete. For complete information, read Installing Adabas with Com-plete.
This section covers the following topics:
By default, the load modules for all Adabas link routines have been linked with LNKUES and the default translation tables.
LNKUES converts data in the Adabas buffers and byte-swaps, if necessary, depending on the data architecture of the caller.
The two standard translation tables are:
ASC2EBC: ASCII to EBCDIC translation; and
EBC2ASC: EBCDIC to ASCII translation.
The Adabas translation table pair is provided in the section Translation Tables.
You may use the load modules with the default translation tables linked in, or you may prepare your own customized translation tables, re-assemble the tables, and link them with the LNKUES module that is delivered.
Notes:
LNKUES is called only on Adabas link routine request (X’1C’) and reply (X’20’) calls if the first byte of the communication ID contains X’01’ and the second byte does not have the EBCDIC (X’04’) bit set. In Adabas requests, LNKUES receives control before UEXIT1. In Adabas replies, LNKUES receives control after UEXIT2.
The following lists the sample jobs provided to manage universal encoding support in Adabas link routines:
| Sample Job | Location | Description |
|---|---|---|
| LNKGCICS | ACIvrs.JOBS | Links the CICS globals table with LNKUES and the default translation tables ASC2EBC and EBC2ASC. |
| LNKLCO8 | ADAvrs.JOBS | Links the Com-plete link globals table with LNKUES and the default translation tables ASC2EBC and EBC2ASC. |
| LNKLNI8 | AIIvrs.SRCE | Links the IMS link routine with the LNIGBL link globals table, LNKUES, and the default translation tables ASC2EBC and EBC2ASC. |
| LNKLNK8 | ADAvrs.JOBS | Links the batch link routine with the LNKGBLS link globals table, LNKUES, and the default translation tables ASC2EBC and EBC2ASC. |
| LNKLNKR8 | ADAvrs.JOBS | Links the reentrant batch link routine with the LNKRGBL link globals table, LNKUES, and the default translation tables ASC2EBC and EBC2ASC. |
Before you can use any of these jobs, they should be edited to prepare the JOB card, update the load library names, and make other changes as necessary for your environment. Refer to the comments in the jobs themselves for more information.
Note
If you use link routine user exits, Adabas Review, or Adabas System Coordinator,
the jobs used to link these components with the batch, reentrant batch or the IMS link
routine should be modified to explicitly include the LNKIND module when the link
routines are relinked to incorporate user or Software GmbH product link routine exits.
This section describes how to disable UES support in the Adabas IMS TM, Com-plete, and batch/TSO link routines, if for some reason you feel it is necessary.
 To disable UES support in link routines:
To disable UES support in link routines:
Edit the link globals table for the associated link routine. Set the UES parameter setting to NO.
Assemble the link globals table after making any other necessary modifications to the equates and other directives in the source module as required by your installation.
Link the Adabas link routine with the newly assembled link globals table and do not include any of the UES components (that is, LNKUES, ASC2EBC, or EBC2ASC).
This section describes installation of the Adabas link routine for the IMS TM TP monitor.
IMS requires an Adabas link routine if it is to communicate with Adabas databases. The Adabas executable default link routine is delivered in member ADALNI of the AIIvrs.LOAD library (where vrs is the number of the latest Adabas version delivered on the tape). If you want to modify this link routine, use member ADALNI8 to do so. ADALNI8 must be linked with a link globals module you prepare and with any link routine exits you require to create the final ADALNI load module that is loaded by the IMS message processing program (MPP) regions when an application calls them. Members ADALNI and ADALNI8 are provided with some default settings.
For a COBOL IMS message processing program (MPP) to call ‘ADABAS’ USING …” in an IMS environment you must link ADALNI to the application that runs in the message processing program (MPP). Since ADALNI is non-reentrant, a link of ADALNI will make the application non-reentrant too. To resolve this:
Add ALIAS ADABAS to the link of ADALNI.
Add the load module name ADABAS to the preload list of the MPP.
Add the load library that contains ADABAS to the steplib chain of the MPP.
Use the DYNAM option of COBOL to force a dynamic load of ADABAS for the CALL ‘ADABAS’ statement.
Note
If CALL ‘ADABAS’ results in a dynamic load of the Adabas link routine, the load module
name of the Adabas link routine must be called ADABAS. As ADALNI saves the address of its
working storage in itself, ADALNI must never be unloaded in the MPP. Otherwise you will
get memory leaks.
This section covers the following topics:
These are Adabas link routines for IMS TM:
ADALNI is the executable default module for message processing programs (MPPs). If you require no changes to the defaults provided in the link routine, use this module.
Use ADALNI8 as the base module for message processing programs (MPPs). If you need to tailor ADALNI for your installation, use ADALNI8 to generate an updated ADALNI.
ADALNK is the batch Adabas link routine for batch message processing (BMP) programs, batch-oriented BMP programs, and batch processing programs (DLIBATCH).
ADALNI and ADALNK use the CSECT name and ENTRY directive ADABAS by default.
The Adabas ADALNI and ADALNK are UES-enabled as distributed. See the section Enabling Universal Encoding Support (UES) for Your Adabas Nucleus for more information.
This section describes using ADALNI and ADALNI8 only. For information on using ADALNK, read General Considerations for Installing Adabas with Batch/TSO.
The Adabas user ID is obtained at execution time by the ADALNI load module from the LTERM field (first eight bytes) of the IOPCB. The user ID is stored in the Adabas user block field UBUID and will be used for the last eight bytes of the Adabas communication ID.
The SAF ID is supported for use by Adabas SAF Security (ADASAF) if an external security package such as IBM’s RACF or CA’s ACF2 is present. The SAF ID is obtained at execution time by the ADALNI load module from the user ID field (bytes 33-40) in the IOPCB. To get a valid SAF user ID, SAF sign-on must be active in your IMS installation and the user must have performed an IMS /SIGN command to log onto an IMS terminal.
 To modify the default settings and prepare the Adabas link routine for IMS:
To modify the default settings and prepare the Adabas link routine for IMS:
Copy the sample member LNIGBL provided in the AIIvrs.SRCE library to any appropriate user source library where they can be modified. These modules contain LGBLSET parameters that are used to create default settings for link components. A complete description of LGBLSET parameters can be found in Modifying Source Member Defaults (LGBLSET Macro).
Modify the LNIGBL member in the user source library.
Note
The OPSYS parameter must be set to ZOS.
Modify and run sample job ASMGBLS as described at the top of the job. ASMGBLS can be found in the ADAvrs.JOBS library. When fully modified, the SET statement in the job should reference the LNIGBL member you prepared in the previous step and the NAME link edit control statement should reference the name specified by the GBLNAME parameter in the LNIGBL member.
Once modified, submit the ASMGBLS job to assemble and link-edit the link globals module.
A new link globals module (with the name specified by the GBLNAME parameter in LNIGBL) will be generated in the user load library identified in the ASMGBLS job.
Copy sample job LNKLNI8 to a user source library and modify it to link the new link globals module you created in the previous step and any required exits with the ADALNI8 base module. Instructions for modifying the sample job are described at the top of the job. Be sure to direct the output from this job to an appropriate user load library. LNKLNI8 can be found in the AIIvrs.SRCE library.
Note
If you use link routine user exits, Adabas Review, or Adabas System
Coordinator, the jobs used to link these components with the batch, reentrant
batch or the IMS link routine should be modified to explicitly include the LNKIND
module when the link routines are relinked to incorporate user or Software GmbH
product link routine exits.
The module resulting from this job is ADALNI.
Place the ADALNI module in a load library available for IMS MPP regions.
The Adabas link routine is prepared.
The following sections describe specific points of Adabas/CICS installation and operation from the CICS perspective:
If you run with the CICS multiple region option (MRO), you must set the MRO parameter to "YES" and use the default for the NETOPT parameter. These parameters are supplied via the LGBLSET macro (read Modifying Source Member Defaults (LGBLSET Macro)).
You can use the LGBLSET NTGPID parameter to provide a 4-byte literal for the Adabas communication ID to be used by the Adabas SVC when applications that call Adabas span multiple application regions.
The preferred method for defining and installing CICS programs and transactions is RDO (resource definition online). The CICS documentation no longer recommends the assembly of PPT and PCT entries to define resources.
Modify and use the sample DEFINE statements located in member DEFADAC as input to the IBM DFHCSDUP utility to define the Adabas CICS components. Consult the appropriate IBM CICS documentation for information on the DFHCSDUP utility. The DEFADAC member can be found in the ACIvrs.SRCE library.
The Adabas CICS link routines require a command security level of "UPDATE" for the EXITPROGRAM CICS command resource identifier. This allows the Adabas CICS application stub to issue the EXEC CICS EXTRACT EXIT command without raising the NOTAUTH response from CICS and the security software. The Adabas CICS application stub needs to issue the EXEC CICS EXTRACT EXIT to determine that the given Adabas task-related user exit (TRUE) is installed and enabled, and to locate the CICS global work area (GWA) associated with the given TRUE so that various data structures are made available to the Adabas CICS application stub programs.
A CICS application that uses Adabas services requires an Adabas CICS execution unit to function.
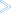
Effective with Adabas 8.2 and later versions, the Adabas CICS execution unit is comprised of:
the Adabas CICS stub, ADACICS
the stub module's direct call interface, ADADCI
an Adabas CICS names module, ACINAMES
one or more Adabas task-related user exits (TRUEs), ADACICT
a globals table associated with the stub module and the TRUE.
The names module (ACINAMES) is linked with the stub (ADACICS) to provide the name of the associated TRUE and the globals table for a given CICS application. In addition, an Adabas CICS installation options table (ACIOPT) is required and used by the Adabas CICS installation program, ADACIC0, to load the Adabas globals tables required by the Adabas CICS execution units that will be installed and activated in the CICS region.
This section covers the following topics:
The Adabas CICS application stub is invoked via EXEC CICS LINK or via the direct-call interface from a CICS application program that intends to use Adabas database services. The stub consists of the ADACICS module, the ADADCI module, the CICS modules DFHEAI and DFHEAI0, and the ACINAMES module. The resultant load module may be given any name that is specified in the link globals ENTPT keyword for the Adabas execution unit. The new module name is most easily created with the linkage editor.
The Adabas CICS names module (ACINAMES) is a small stub containing the name of the TRUE to be invoked from this stub and the name of the link globals table associated with the Adabas CICS execution unit. The link globals table also contains the names of the stub and the TRUE, but linking it with the stub has the following performance disadvantages:
The stub is functionally reentrant and the link globals table in CICS is modifiable during execution
Linking the globals table with the stub would also cause duplicate copies of the link globals table to be kept in CICS storage at the same time, wasting space and possibly leading to problems if the copy loaded by ADACIC0 differs from the copy linked with the Adabas stub
Using the ACINAMES module allows you to relink the Adabas CICS stub with any supported load module name and gives that stub the ability to invoke the Adabas CICS TRUE with the name provided in the ACINAMES module. The TRUE may also be relinked with any given valid load module name. This permits the CICS region to execute different Adabas stubs and TRUEs built out of the same load modules but tailored as required for different CICS applications. No changes are needed in the CICS application programs themselves.
The Adabas CICS names module is built using the MACINS macro. The ACINAMES module may be given any load module name, but the generated CSECT name (ordinarily generated by the MACINS macro assembly job, ASMCINS) within the load module must be ACINAMES.
An additional component, an Adabas CICS installation options table (ACIOPT) is required and used by the Adabas CICS installation program, ADACIC0, to load the Adabas globals tables required by the Adabas CICS execution units that will be installed and activated in the CICS region.
The Adabas CICS installation options table is built using the MACIOPT macro.
Use the MACINS macro to build the Adabas CICS names module, ACINAMES. The ACINAMES module may be given any load module name, but the generated CSECT name (ordinarily generated by the MACINS macro job) within the load module must be ACINAMES. In addition, the ACINAMES module should be included when the Adabas CICS stub is relinked.
The MACINS macro and a sample ACINAMES source member are provided in the ACIvrs.SRCE library.
The syntax of the MACINS macro is shown below:

All MACINS parameters are required and are described in the following table:
In the following example, an ACINAMES module is prepared for an Adabas CICS stub named ADABAS that will use an ADABAS CICS TRUE named ADATRUE and a link globals table named CICSGBL. The source member to create the ACINAMES module might look like this:
* Sample "ACINAMES" for Adabas multiple-TRUE support.
MACINS TRUENAME=ADATRUE, X
GTNAME=CICSGBL
Use the MACIOPT macro to build the Adabas CICS installation options table which may either be linked with ADACIC0 or, if named ACIOPT (the default), is defined to CICS and loaded by ADACIC0 when the Adabas CICS installation process is started.
The MACIOPT macro and sample ACIOPT source member are provided in the ACIvrs.SRCE library.
The syntax of the MACINS macro is shown below:

An ENTRY statement is required on every invocation of the MACIOPT macro. It designates the ENTRY type, which in turn, determines which additional parameters are valid for the given entry. The three types of ENTRY statement and their associated parameters are described in the rest of this document.
The ENTRY=GLOBAL statement is always the first entry for the ACIOPT source member. Only one ENTRY=GLOBAL statement should be specified per source member and it should precede all other MACIOPT statements.
The ENTRY=GLOBAL statement specifies global parameters to be used by the CICS installation program. The parameters associated with ENTRY=GLOBAL are described in the table below:
ENTRY=GROUP statements define the names of the Adabas globals tables that should be loaded and used to install the Adabas CICS execution units. More than one ENTRY=GROUP statement can be specified in the ACIOPT source member; all ENTRY=GROUP statements must be specified after the ENTRY=GLOBAL statement and before the ENTRY=FINAL statement.
Only one parameter can be specified for ENTRY=GROUP:
The ENTRY=FINAL statement must be the last MACIOPT statement in the source member. It causes the actual ACIOPT CSECT statements to be generated. Only one ENTRY=FINAL statement may be specified in the source member.
There are no parameters for the ENTRY=FINAL statement
If assembled and link-edited, the following source member will produce the load module ACIOPT and will install two Adabas CICS execution units. One will load a globals table named LNKCI02 and the other will load a globals table named CICSGBL. Installation messages will be written to the CICS transient data queue named ACIQ, if that queue is available.
MACIOPT ENTRY=GLOBAL,IMSGDEST=TDQ,IMQNAME=ACIQ,MNTRUE=2
MACIOPT ENTRY=GROUP,GTNAME=LNKCI02
MACIOPT ENTRY=GROUP,GTNAME=CICSGBL
MACIOPT ENTRY=FINAL
In a simple Adabas CICS transaction that uses the EXEC CICS LINK command to communicate with Adabas, there should be one invocation of the Adabas Task Related User Exit (TRUE) for each EXEC CICS LINK issued from the application.
If the Adabas CICS interface employs exits such as the Adabas Fastpath exit or other System Coordinator facilities, there may be more than one invocation of the Adabas TRUE for each EXEC CICS LINK issued by the application program. Other Software GmbH products that can have multiple TRUE invocations for each LINK to Adabas are the Adabas Bridge for DL/I and Natural. If the Adabas high-performance stub (BALR interface) is employed by applications, including Natural, there will be multiple invocations of the Adabas TRUE for each EXEC CICS LINK to the Adabas interface module.
Adabas supports the installation of multiple CICS task-related user exits (TRUEs) and Adabas application stubs from a single execution of the ADACIC0 installation program. Multiple TRUEs allow your site to tailor different Adabas CICS execution options in the same CICS region with a centralized installation procedure and software.
The following diagram depicts the processing flow of the installation of multiple Adabas CICS TRUE and application stub support.
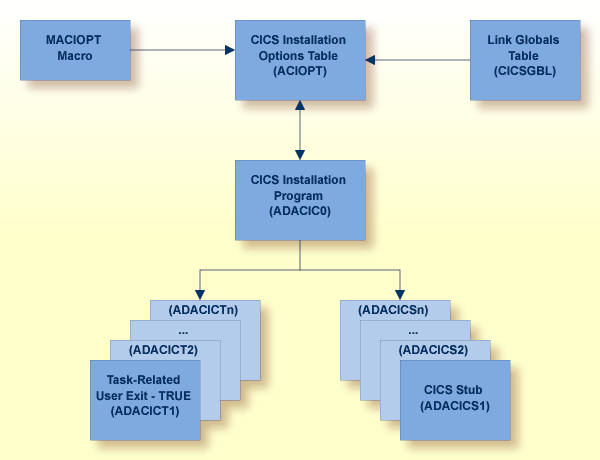
The following diagram depicts the processing flow of the execution of this multiple Adabas CICS TRUE and application stub support.
The following table lists the objects supplied to support the installation of Adabas with CICS.
| Module | Location | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ADACIC0 | ACIvrs.LOAD | Adabas CICS installation program |
| ADACICS | ACIvrs.LOAD | Adabas CICS Application Stub. |
| ADACICT | ACIvrs.LOAD | Adabas CICS task-related user exit (TRUE). |
| ASMCINS | ACIvrs.JOBS | Sample job to assemble the ACINAMES module and link it with the Adabas CICS application stub. |
| ASMCOPT | ACIvrs.JOBS | Sample job to assemble and link the ACIOPT source module as the standalone module named ""ACIOPT"". See Step 2 of the Installation Procedure. |
| ASMGBLS | ADAvrs.JOBS | Sample job to assemble and link the Adabas globals table. See Step 7 of the Installation Procedure. |
| CPYCICSM | ACIvrs.JOBS | Sample job to copy the distributed load modules to a DFHRPL concatenated library. See Step 1 of the Installation Procedure. |
| DEFADAC | ACIvrs.SRCE | Sample CICS DEFINE control statements. See Step 9 of the Installation Procedure. |
| LNKATRU | ACIvrs.JOBS | Sample job to link the Adabas CICS task-related user exit. See Step 3 of the Installation Procedure. |
| LNKGCICS | ACIvrs.JOBS | Sample job to relink the Adabas globals table. See Step 8 of the Installation Procedure. |
To install the Adabas CICS link routine components, complete the following steps:
Copy the Adabas CICS load modules from the Adabas distribution library to a load library that will be in the CICS DFHRPL concatenation (see sample member CPYCICSM in the ACIvrs.JOBS library).
An Adabas CICS installation options table (ACIOPT) is required to identify all the Adabas globals tables that will be needed for the proper execution of each Adabas CICS execution unit in the CICS region or CICSplex. The installation program (ADACIC0) run in Step 12 will obtain information of a global nature from the table such as the destination for writing of installation messages. It will also scan the table and load each Adabas globals table named in the ACIOPT module. In turn, each loaded globals table serves as the basis for installing each Adabas CICS execution unit.
The Adabas CICS installation options table is built by coding a series of MACIOPT macros into a source member, then assembling and linking that source member into a library that will be available during CICS execution. The load module may be linked:
With the ADACIC0 installation program, or
As a standalone module named "ACIOPT", which is then defined as a program of the same name to CICS.
For best performance, we recommend linking a standalone ACIOPT module, defining it to CICS as program ACIOPT. This will allow ADACIC0 to load ACIOPT during the installation process.
 To prepare the Adabas CICS installation options table, complete the following
steps:
To prepare the Adabas CICS installation options table, complete the following
steps:
Code a source member, preferably called ACIOPT that contains MACIOPT macro statements to be loaded by the ADACIC0 program at execution time. The MACIOPT macro statements define each globals table that will be needed by each Adabas CICS execution unit.
The ACIOPT source member will consist of one MACIOPT ENTRY=GLOBAL entry, multiple MACIOPT ENTRY=GROUP entries and one MACIOPT ENTRY=FINAL entry.
The MACIOPT ENTRY=GLOBAL specification must be first specification in the source member; only one MACIOPT ENTRY=GLOBAL specification can be made per ACIOPT generation.
The MACIOPT ENTRY=FINAL specification must be the last entry for the ACIOPT generation; only one MACIOPT ENTRY=FINAL specification can be made per ACIOPT generation.
Multiple MACIOPT ENTRY=GROUP entries may be specified, but they must follow the MACIOPT ENTRY=GLOBAL specification and precede the MACIOPT ENTRY=FINAL specification in the source member.
The MACIOPT macro is located in the ACIvrs.SRCE library. For complete information on the MACIOPT macro, read The MACIOPT Macro, elsewhere in this section. A sample source member ACIOPT is provided in the ACIvrs.SRCE library.
Assemble and link the ACIOPT source module either as the standalone module named "ACIOPT" or with any load module name linked with ADACIC0. If linked as a standalone module it must be named "ACIOPT" (see sample job ASMCOPT located in the ACIvrs.JOBS library) and it must be defined as a program to CICS.
The ACIOPT module may be defined to CICS using the CEDA/RDO facility or the DFHCSDUP utility. Sample DFHCSDUP statements are provided in the DEFADAC member in the ACIvrs.SRCE library.
An Adabas task-related user exit (TRUE) is created by relinking the Adabas ADACICT module with a NAME statement, providing the desired TRUE name. One or more Adabas TRUEs can be created.
Note
The Adabas TRUE name is specified later in the TRUENM parameter in the link globals table (set Step
6) and in the TRUENAME parameter when the ACINAMES module (see Step 4) is prepared.
 To prepare the Adabas CICS TRUE, complete the following steps:
To prepare the Adabas CICS TRUE, complete the following steps:
Relink the ADACICT module with a NAME or PHASE statement giving a new name for each Adabas TRUE.
Define each named Adabas TRUE as a program to CICS.
A sample job, LNKATRU, is provided in the ACIvrs.JOBS library. This sample links the Adabas TRUE with a load module named ADATRUE so that it can be installed and referenced in CICS.
The ACINAMES module is a small stub containing the name of the TRUE to be invoked from this stub and the name of the link globals table associated with the Adabas execution unit. After the ACINAMES source member is coded, it should be provided as input to the assembler and either punched by the assembler to a text library or directly link-edited as a load module. The subsequent text deck or load module would then be made available to the linkage editor when the Adabas CICS stub is relinked to change its name or to update the ACINAMES module it uses.
 To prepare the ACINAMES module, complete the following step:
To prepare the ACINAMES module, complete the following step:
Code the source for the ACINAMES module using the MACINS macro. For complete information, read The MACINS Macro.
The MACINS macro is provided in the ACIvrs.SRCE library.
Sample job, ASMCINS, which is provided in the ACIvrs.JOBS library, assembles the ACINAMES module and links it with the Adabas CICS application stub (see Step 5), and names the stub "ADABAS".
Effective with Adabas 8.6 and later versions, the CICS macro library is required to assemble ACINAMES.
For example, the source member to create the ACINAMES module might look like this:
* Sample "ACINAMES" for Adabas multiple-TRUE support.
MACINS TRUENAME=ADATRUE, X
GTNAME=CICSGBL
This ACINAMES module uses an ADABAS CICS TRUE named ADATRUE and a link globals table named CICSGBL.
The Adabas application stub is invoked via EXEC CICS LINK or via the direct-call interface from a CICS application program that intends to use Adabas database services. The application stub consists of the ADACICS module, the ADADCI module, the CICS modules DFHEAI and DFHEAI0 and the ACINAMES module. The resultant load module may be given any name that is specified in the link globals ENTPT keyword for the Adabas execution unit. The new module name is most easily created with the linkage editor.
 To prepare the CICS application stub (ADACICS), complete the following step:
To prepare the CICS application stub (ADACICS), complete the following step:
Relink the Adabas CICS application stub module, ADACICS, replacing ACINAMES in the module with the name of the ACINAMES module created in the previous step (Step 4).
Sample job, ASMCINS, which is provided in the ACIvrs.JOBS library, assembles the ACINAMES module and links it with the Adabas CICS application stub (see Step 4), and names the stub "ADABAS".
For example, the link-edit control statements to create the Adabas module as the Adabas CICS stub might be:
//LKED.SYSIN DD * MODE AMODE(31),RMODE(ANY) REPLACE ACINAMES INCLUDE ADALIB(ADACICS) INCLUDE USERLIB(ACINAMES) ENTRY ADACICS NAME ADABAS(R) /*
In this example, the prepared ACINAMES module is used for an Adabas CICS stub named ADABAS.
Link globals tables must be prepared to match the Adabas CICS execution units defined in the ACIOPT module. These are built by editing or creating source members that use the LGBLSET macro provided in the ADAvrs.SRCE library and its keywords.
Modify the sample CICSGBL member found in the ACIvrs.SRCE library. This member contains sample default installation (LGBLSET) parameter settings. For more information about what to modify in this member, read Modifying Source Member Defaults (LGBLSET Macro).
 To prepare the link globals table, complete the following steps:
To prepare the link globals table, complete the following steps:
Code the link globals table using the LGBLSET macro as described in Modifying Source Member Defaults (LGBLSET Macro).
Be sure to code the ENTPT and TRUENM parameters on each LGBLSET macro so they match the intended Adabas CICS stub name and Adabas CICS TRUE name to be used in a given Adabas CICS execution unit. The Adabas CICS installation program attempts to load each globals table in turn and uses the loaded table to provide the data required to install and activate the components of the execution unit.
In CICS environments only, if you want your security system user IDs to be stored in Adabas user queue elements (making them available for display and review as well as preventing response code 200, ADARSP200, subcode 21 when ADARUN SECUID=REQUIRE is in effect for Adabas), you must code the SAF parameter as YES. This is only required in CICS environments; in other environments, the security system user IDs are automatically stored.
Save the modified CICSGBL member with a unique name in an appropriate user source library.
Modify and run sample job ASMGBLS as described at the top of the job. ASMGBLS can be found in the ADAvrs.JOBS library. When fully modified, the SET statement in the job should reference the CICSGBL member you prepared in Step 6 and the NAME link edit control statement should reference the name specified by the GBLNAME parameter in the CICSGBL member.
Review and run the LNKGCICS member in the ACIvrs.JOBS library to link the newly assembled globals table from the previous step with any user or Software GmbH product exits. (For information about specific Software GmbH product exits, read the installation documentation for the product.) The LNKGCICS member provides specific instructions. Be sure to link the globals table into a load library that will be made available to CICS in the DFHRPL library concatenation. Note that any user or Software GmbH link routine exits should be link-edited with this load module.
Modify the DEFADAC member in ACIvrs.SRCE to provide the correct name of the link routine globals default table created in Step 6. The default module name is CICSGBL. Tailor this member for any other CICS installation values as required.
Run the IBM DFHCSDUP utility to update the CICS CSD file for the desired CICS using the modified DEFADAC member as input.
Modify the CICS PLTPI table to add an entry for the Adabas CICS installation program ADACIC0. The Adabas CICS installation program will be called by CICS to start the Adabas CICS execution units while CICS is starting up. Use member ADAPLTXX from the ACIvrs.SRCE library as a sample.
Once the PLTPI table is modified, assemble and link the modified PLTPI table into a library that will be available to the desired CICS region.
Start the CICS and note any ADAK* messages relating to the execution of the Adabas CICS installation program that appear on the console.
This section describes installation of the CICS high-performance stub routine with Adabas. The modules and installation described here are provided so your existing Adabas applications can continue to function as usual.
The Adabas high-performance stub routine extends the direct call interface (DCI) facility that is available with the Adabas CICS link component to applications written in languages other than Software AG’s Natural (for example, Assembler, COBOL, PL/I).
The DCI enables a CICS/TS application to call Adabas through the Adabas link routine. The overhead incurred when the EXEC CICS LINK and EXEC CICS RETURN command set is used to transfer program control is thus avoided. Once the proper environment has been established with the initial call (IC) command from the high-performance stub or Natural, the DCI permits a BALR interface to be used.
The high-performance stub routine is written in Assembler language. When linked with the application program, it serves as an interface between the application and the Adabas CICS link component. The application program can then issue CALL statements to access the stub routine when executing an Adabas command.
A CICS/TS application derives the following advantages from the high-performance stub:
improved performance and throughput when issuing Adabas commands due to the reduced use of CICS services related to the CICS LINK and RETURN program control mechanism.
a call mechanism for Adabas requests which is simpler than the methods normally employed to pass control with information from one program to another in the CICS environment.
This section covers the following topics:
The following restrictions and requirements apply to the high-performance stub routine:
The Adabas high-performance stub routine is available for all supported versions of CICS/TS.
A CICS transaction work area (TWA) of at least 24 bytes or a CICS COMMAREA of at least 32 bytes must be provided to the application for the proper execution of the high-performance stub routine. The Adabas LNCSTUB module and the Adabas installation verification programs (IVPs) now use the CICS COMMAREA instead of the CICS TWA to pass data between the IVP programs, LNCSTUB, and the CICS link routines. The use of the CICS COMMAREA has the following advantages over the use of the CICS TWA:
The size of the COMMAREA can be set on a call-by-call basis by the application program, while the TWA size is set when the CICS transaction is defined.
Applications using the CICS COMMAREA may run in stages II or III of CICS PLTPI processing. The CICS TWA is not available during PLTPI processing.
The dynamic sizing of the CICS COMMAREA is better suited to the unbounded format of the Adabas ACBX direct call, ACBX control block, and Adabas Buffer Descriptions (ABDs). For more information on the Adabas direct call interface and the data structures it uses, read the Adabas Command Reference Guide.
Supported Programming Languages
The application program may be written in ALC (Assembler language), VS/COBOL, COBOL II, COBOL/LE, PL/I, or C. Installation verification programs (IVPs) are provided in ALC and COBOL in the ACIvrs.SRCE library.
Additional requirements for specific programming languages are discussed later in the sections relating to each language.
| Location | Member | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ACIvrs.SRCE |
ADAGSET |
macro required for assembling LNCSTUB and ALCSIVP |
| ACIvrs.JOBS |
JCLALCI |
sample JCL for ALC install verification |
Use the following procedure to install the Adabas CICS high-performance stub routine:
Edit, preprocess, assemble and link the LNCSTUB module.
Define the application programs, optional IVPs and CICS link components to CICS using RDO or the DFHCSDUP utility.
(Optional) Modify, preprocess, compile or assemble, link, and execute the desired installation verification program (IVP).
Modify, preprocess, compile or assemble, link, and execute the application programs.
This procedure is described in the following steps:
The Adabas CICS high-performance stub routine is an Assembler language source module, provided in member LNCSTUB in the ACIvrs.SRCE library.
Step 1 has the following substeps:
Note
For information about editing the ADAGSET macro, refer to the section Modifying Source Member Defaults (ADAGSET
Macro).
Edit the ADAGSET macro in a library that will be available in the SYSLIB concatenation when LNCSTUB is assembled.
Both the LNCSTUB and the ALCSIVP IVP modules now take values from the following ADAGSET keywords:
LOGID, which identifies the database ID
PARMTYP, which determines whether the TWA or COMMAREA is used by the LNCSTUB and the ALCSIVP programs to pass data
ENTPT, which specifies the name of the Adabas CICS application stub to be invoked by the LNCSTUB and ALCSIVP programs. If your Adabas CICS link component program has been linked with a name other than ADACICS, change the value of the ENTPT keyword in the ADAGSET macro. The value in this field is used in the priming EXEC CICS LINK command issued by LNCSTUB.
The LNCSTUB module provides an assembler GBLC variable (&STBNAME) that sets an entry-point alias that can be used by calling programs. Modify the SETC statement near the top of the LNCSTUB source member to set an alias if desired. The application program can then either issue its call using "LNCSTUB" or the entry-point alias coded in this SETC statement.
Member JCLLNCS (in the ACIvrs.JOBS library) is used to preprocess, assemble, and link the LNCSTUB module. To modify this JCL to meet your site requirements, change the JOB card in the member and the symbolic values as indicated in the following table:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| &SUFFIX | Suffix value used for the CICS translator. The default value is “1$”. |
| &ASMBLR | Assembler program used to assemble the LNCSTUB source (ASMA90). |
| &M | Member name to be processed; code LNCSTUB or ALCSIVP. |
| &STUBLIB | A load library to contain the LNCSTUB load module. This library should be available to application programs when they are linked. |
| &INDEX | High-level qualifier for the CICS macro library used in the SYSLIB DD statement for the assembler. |
| &INDEX2 | High-level qualifier for the CICS load library to use for the translator STEPLIB DD statement, and for the SYSLIB in the link step. |
| &ADACOML | Adabas command-level source library containing the ADACB, ADAGDEF, ADAGSET, and LNCDS copy code and macros. |
| &ADASRCE | Adabas source library used for additional copy code or macro expansion. |
| &STBSRCE | Source library containing the distributed Adabas CICS high-performance stub LNCSTUB. |
| &MAC1 | Primary system macro library, usually SYS1.MACLIB. |
| &OUTC | Output class for messages, SYSPRINT, SYSOUT. |
| ® | Step region size. |
| &NCAL | Value for the linkage editor NCAL parameter. The recommended value is NCAL. |
| &LSIZE | Primary and secondary table sizes used by the linkage editor. |
| &WORK | DASD device type to use for temporary and utility data sets. |
Because of the use of 31-bit instructions, the high-level assembler (ASMA90) should be used to assemble the LNCSTUB module after CICS preprocessing.
Note
The LNCSTUB module can be linked reentrant or reusable. If it is linked reentrant,
it is automatically reusable; if it is linked reusable, it is not automatically
reentrant.
In addition to the CICS macro library, the Adabas CICS source library and standard Adabas source library must be provided to the SYSLIB DD statement in the assembly step:
Do not concatenate any CICS load libraries in the SYSLIB DD statement when linking the LNCSTUB load module.
In the SYSLIN data stream after the LNCSTUB object deck, use just the control statement
NAME LNCSTUB(R)
Do not include the CICS stub modules DFHEAI0 & DFHEAI1 with the LNCSTUB load module. As a result, however, the following occurs:
The linkage editor issues IEW462 or similar messages indicating that DFHEAI1 is an unresolved external reference;
The LNCSTUB module may be marked NOT EXECUTABLE by the linkage editor;
A condition code of 8 may be set in the link step.
When the application program is linked with LNCSTUB, all the external references are resolved. Use of the link-edit parameters LET and NCAL are recommended so the missing CICS stub pieces result in a condition code of '04' from the link-edit of LNCSTUB.
The LNCSTUB module has an entry name of ADABAS, which can be used by the application program as the object of a CALL statement to pass control to LNCSTUB with a list of parameters. The language-specific calling conventions for LNCSTUB are discussed later in this section.
The LNCSTUB module has either an entry name of LNCSTUB or the alias entry name as coded in the SETC statement to set the value of &STBNAME. Either value may be used by the application program as the object of a CALL statement to pass control to LNCSTUB with a list of parameters. The language-specific calling conventions for LNCSTUB are discussed later in this section.
The LNCSTUB load module must be available to the link step of the application program that is to use the DCI facility.
Note
In the same step, the CICS load library should be available; otherwise, the
external references to the CICS stub modules will not be resolved.
Place the LNCSTUB load module in a library available to your application language assembler or compiler so that it will be included when the application programs are linked.
Two installation verification programs (IVPs) are provided in source form: one for Assembler language, and one for COBOL/VS. These programs are samples for implementing the Adabas high-performance stub routine in your applications. They also provide a way of verifying the proper installation of the LNCSTUB module.
This section describes each of these IVPs:
Note
The two installation verification programs ALCSIVP and COBSIVP only use fields AA
and AE from the provided demonstration EMPLOYEES file. For more
information about the provided demonstration files, read Load the Demonstration
Files in the installation instructions.
The source member ALCSIVP is provided to demonstrate and verify the use of the Adabas DCI using the LNCSTUB module. This program issues a series of Adabas commands using the conventional CICS LINK/RETURN mechanism, produces a partial screen of output data, then reexecutes the same call sequence using the Adabas DCI and the LNCSTUB subprogram.
 To install and execute the Assembler IVP, ALCSIVP:
To install and execute the Assembler IVP, ALCSIVP:
Modify the source member ALCSIVP in ACIvrs.SRCE:
Edit the file number field DBFNR to be sure it matches the value needed to access the EMPLOYEES file on the provided demonstration database you intend to use. For more information about the provided demonstration files, read Load the Demonstration Files in the installation instructions.
The ALCSIVP program will take the database-id from the LOGID keyword specified in the ADAGSET macro.
Check the fields FBUFF, SBUFF and VBUFF for values consistent with your EMPLOYEES file’s FDT and data content.
Check the name used in the EXEC CICS LINK statement to be sure it matches the name of your Adabas CICS application stub. The field LNCNAME is now used and it derives its value from the ENTPT keyword of the ADAGSET macro.
The entry-point alias of the LNCSTUB module can be tested in ALCSIVP by changing the SETC statement for the field &STUBNM to match the entry-point name coded in the LNCSTUB source module using its SETC fieldname &STBNAME.
Note
The ALCSIVP program will use the value of the ADAGSET keyword PARMTYP to
determine whether to use the CICS TWA or CICS COMMAREA to pass data between
itself and the Adabas CICS link routine during the first part of its
processing when it uses the CICS LINK command to invoke the Adabas CICS link
routine. If PARMTYP=TWA is coded in the ADAGSET macro used when ALCSIVP is
assembled the CICS TWA is used, otherwise the CICS COMMAREA is used on the
EXEC CICS LINK commands.
Modify the sample job stream, JCLALCI in ACIvrs.JOBS:
Member JCLALCI is used to preprocess, assemble, and link the installation verification program ALCSIVP. Place the load module in your CICS DFHRPL library concatenation..
To modify this JCL to meet your site requirements, change the JOB card in the member and the symbolic values as indicated in the table used in step 1 (see Step 1, Modify Member JCLLNCS).
The JCLALCI member uses one additional symbolic parameter: &CICSLIB. This is the name of your CICS RPL library.
Using the modified sample JCLALCI member, preprocess, assemble, and link ALCSIVP.
Add the following RDO entries to your CICS system, or use the RDO facility to add the STB1 transaction to run the ALCSIVP program:
DEFINE PROGRAM(ALCSIVP) GROUP(ADABAS) DESCRIPTION(ADABAS s ASSEMBLER IVP FOR HIGH-PERFORMANCE STUB) LANGUAGE(ASSEMBLER) RELOAD(NO) RESIDENT(NO) USAGE(NORMAL) USELPACOPY(NO) STATUS(ENABLED) CEDF(YES) DATALOCATION(ANY) EXECKEY(USER) EXECUTIONSET(FULLAPI) DEFINE TRANSACTION(STB1) GROUP(ADABAS) DESCRIPTION(TRANSACTION TO EXECUTE THE ASSEMBLER IVP FOR HIGH-PERFORMANCE STUB) PROGRAM(ALCSIVP) TWASIZE(32) PROFILE(DFHCICST) STATUS(ENABLED) TASKDATALOC(ANY) TASKDATAKEY(USER) STORAGECLEAR(NO) RUNAWAY(SYSTEM) SHUTDOWN(DISABLED) ISOLATE(YES) DYNAMIC(NO) PRIORITY(1) TRANCLASS(DFHTCL00) DTIMOUT(NO) INDOUBT(BACKOUT) RESTART(NO) SPURGE(NO) TPURGE(NO) DUMP(YES) TRACE(YES) RESSEC(NO) CMDSEC(NO)
Run the STB1 transaction to execute ALCSIVP. Executing ALCSIVP verifies the LNCSTUB module.
Member COBSIVP illustrates the use of the Adabas DCI with a COBOL program. COBIVP produces a screen showing output lines produced by a series of Adabas calls executed by the CICS LINK/RETURN facility, followed by the reexecution of these Adabas commands using the DCI.
 To install and execute the COBOL IVP, COBSIVP:
To install and execute the COBOL IVP, COBSIVP:
Modify the source member, COBSIVP in ACIvrs.SRCE:
Edit the fields WORK-DBID and WORK-FNR to place the desired database ID and file number in the VALUE clauses to access the EMPLOYEES file on the provided demonstration database you intend to use. For more information about the provided demonstration files, read Load the Demonstration Files in the installation instructions.
Ensure that the value in the field LINK-NAME matches the name used in your Adabas CICS command-level link component program.
Ensure that the values (literals in the PROCEDURE DIVISION) in the following fields are consistent with the requirements of the EMPLOYEES file FDT and data content you are using:
ADABAS-FORMAT-BUFFER, ADABAS-SEARCH-BUFFER, and ADABAS-VALUE-BUFFER
Modify the sample job stream, JCLCOBI in ACIvrs.JOBS:
Member JCLCOBI is used to preprocess, compile, and link the COBSIVP installation verification program. To modify the JCLCOBI example to meet site requirements, change the JOB card in the member and provide values for the symbolic procedure variables as described in the following table:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| &ADALIB | Adabas load library used to provide the ADASTWA load module for the linkage editor. |
| &MEM | Member name to be processed; in this case, COBSIVP. |
| &CICSLIB | CICS RPL library where the COBSIVP load module is placed for execution under CICS. |
| &COBLIB | COBOL compiler STEPLIB. |
| &INDEX | High-level qualifier for the CICS macro library used in the SYSLIB DD statement for the compiler. |
| &INDEX2 | High-level qualifier for the CICS load library to use for the translator STEPLIB DD statement, and for the SYSLIB in the link step. |
| &LINKLIB | COBOL LINKLIB. |
| &STBSRCE | Source library containing the distributed Adabas CICS high-performance stub LNCSTUB. |
| &STUBLIB | A load library to contain the LNCSTUB load module. This library should be available to your application programs when they are linked. |
| &SYSMSG | Output class for translator messages. |
| &SYSOUT | Output class for SYSOUT and SYSPRINT messages. |
| &WORK | DASD device type to use for temporary and utility data sets. |
Preprocess, compile, and link COBSIVP:
Use the modified JCLCOBI job to preprocess, compile, and link the COBSIVP program.
The LNCSTUB subroutine does not use ADASTWA because it places the passed Adabas parameters in the COMMAREA. Thus, the ADASTWA routine is not required when linking COBOL applications that utilize the Adabas DCI through the LNCSTUB module.
Link the COBSIVP program with the LNCSTUB load module and make the LNCSTUB load module available to the linkage editor to be included with the COBSIVP load module.
Note
The IBM CICS stub modules are also resolved in the link step.
Add the following RDO entries to your CICS system, or use the RDO facility to add the STB2 transaction to run the COBSIVP program:
DEFINE PROGRAM(COBSIVP) GROUP(ADABAS) DESCRIPTION(ADABAS s COBOL IVP FOR HIGH-PERFORMANCE STUB) LANGUAGE(COBOL) RELOAD(NO) RESIDENT(NO) USAGE(NORMAL) USELPACOPY(NO) STATUS(ENABLED) CEDF(YES) DATALOCATION(ANY) EXECKEY(USER) EXECUTIONSET(FULLAPI) DEFINE TRANSACTION(STB2) GROUP(ADABAS) DESCRIPTION(TRANSACTION TO EXECUTE THE COBOL IVP FOR HIGH-PERFORMANCE STUB) PROGRAM(COBSIVP) TWASIZE(32) PROFILE(DFHCICST) STATUS(ENABLED) TASKDATALOC(ANY) TASKDATAKEY(USER) STORAGECLEAR(NO) RUNAWAY(SYSTEM) SHUTDOWN(DISABLED) ISOLATE(YES) DYNAMIC(NO) PRIORITY(1) TRANCLASS(DFHTCL00) DTIMOUT(NO) INDOUBT(BACKOUT) RESTART(NO) SPURGE(NO) TPURGE(NO) DUMP(YES) TRACE(YES) RESSEC(NO) CMDSEC(NO)
Run the STB2 transaction to execute COBSIVP. Executing COBSIVP verifies the LNCSTUB module.
Once the IVP programs have been successfully executed, the Adabas DCI is ready to be used with real application programs. In step 3, the application program interface (API) is coded to utilize the LNCSTUB subprogram.
Step 3 has the following substeps:
Modify the application programs that will utilize the Adabas CICS high-performance stub routine in accordance with the guidelines described in the following section.
Preprocess, compile or assemble, and link the application programs to include the LNCSTUB module.
Execute the application programs using the Adabas CICS high-performance stub.
The LNCSTUB load module must be linked with your application program. The application program invokes the DCI interface using a standard batch-like call mechanism. The LNCSTUB module makes any additional CICS requests required to pass data to the Adabas CICS command-level link component.
Programming Languages Supported by LNCSTUB
The LNCSTUB program functions with application programs written in Assembler language, VS/COBOL, COBOL II, COBOL/LE PL/I, and C.
Use of the CICS Transaction Work Area
A transaction that uses the Adabas DCI or the Adabas CICS command-level link component may provide a transaction work area (TWA) at least 28 bytes long. Failure to provide an adequate TWA will result in an abend U636 (abnormal termination of the task).
Use of the CICS COMMAREA
Use of a CICS COMMAREA to pass data on EXEC CICS LINK commands is strongly recommended. The CICS COMMAREA must be at least 32 bytes in length and the first 8 bytes of the COMMAREA must contain the string "ADABAS52" or "ADABAS8X". The string "ADABAS8X" is for applications that exclusively use the new Adabas Version 8 ACBX direct call interface and its parameter list.
Reentrant Requirement
The application program may or may not be reentrant. The LNCSTUB module has been written to be reentrant, but using linkage editor parameters to mark the LNCSTUB load module as reentrant is not recommended unless the application program will also be marked as reentrant.
CICS Requests Issued by LNCSTUB
The LNCSTUB module issues the following command-level CICS requests whenever it is invoked:
EXEC CICS ADDRESS EIB EXEC CICS LINK
If the TWA is used to pass data to the Adabas command-level link:
EXEC CICS ADDRESS TWA EXEC CICS ASSIGN TWALENG
DCI Entry Point Address
An EXEC CICS LINK command is issued by LNCSTUB at least once to acquire the DCI entry point from the Adabas CICS link component program. This address is then used for BALR access on all subsequent Adabas calls for a transaction. Thus, the calling application program must provide a fullword (4-byte) field to hold the DCI entry point address obtained by LNCSTUB. This 4-byte field is the first parameter passed to the LNCSTUB module by the call mechanism. The remaining parameters comprise the Adabas parameter list needed to execute an Adabas request. (Either a version 7 or version 8 parameter list may be used)
DCI Parameter List
The Adabas DCI parameter list expected by the LNCSTUB program is composed of a pointer to the DCI entry point in the Adabas CICS command-level link component followed by the six pointers to the Adabas control block and buffers: format, record, search, value, and ISN.
For information on coding the standard Adabas control block and buffers, refer to the Adabas Command Reference.
The Adabas parameter list offsets are summarized in the table below (note that an ACB call is used):
| Offset | Pointer to the ... |
|---|---|
| 0 | DCI entry point in the Adabas command-level link component |
| 4 | Adabas control block |
| 8 | Adabas format buffer |
| 12 | Adabas record buffer |
| 16 | Adabas search buffer |
| 20 | Adabas value buffer |
| 24 | Adabas ISN buffer |
All of the parameters except the first (the DCI entry point) are built and maintained by the application program in accordance with the requirements of an Adabas call.
The DCI entry point parameter should be set to binary zeros at the beginning of a task, and should not be modified by the application program thereafter. Software AG strongly recommends that the fields comprising the parameter list be placed in CICS storage (WORKING-STORAGE for COBOL and the DFHEISTG user storage area for Assembler) to maintain pseudo-reentrability.
The following is a sample parameter list for an assembler language program:
DFHEISTG DSECT . PARMLIST DS 0F DS A(DCIPTR) DS A(ADACB) DS A(ADAFB) DS A(ADARB) DS A(ADASB) DS A(ADAVB) DS A(ADAIB) . DCIPTR DS F ADACB DS CL80 ADAFB DS CL50 ADARB DS CL250 ADASB DS CL50 ADAVB DS CL50 ADAIB DS CL200 . DFHEIENT CODEREG=(R12),EIBREG=(R10),DATAREG=(R13) . LA R1,PARMLIST L R15,=V(LNCSTUB) BALR R14,R15 . END
Note
The DFHEIENT macro in the Assembler example uses a DATAREG parameter of
register 13. This is a strict requirement of the LNCSTUB program. When the LNCSTUB
program is invoked, register 13 should point to the standard CICS save area
(DFHEISA) and register 1 should point to the parameter list. The best way to
ensure this standard is to code the Assembler application with a DFHEIENT macro
like the one in the example.
The following is a sample parameter list for a COBOL language program:
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION. . 01 STUB-DCI-PTR PIC S9(8) COMP VALUE ZERO. 01 ADACB PIC X(80). 01 ADAFB PIC X(50). 01 ADARB PIC X(250). 01 ADASB PIC X(50). 01 ADAVB PIC X(50). 01 ADAIB PIC X(200). . PROCEDURE DIVISION. . CALL ’LNCSTUB’ USING STUB-DCI-PTR, ADACB, ADAFB, ADARB, ADASB, ADAVB, ADAIB. . EXEC CICS RETURN END-EXEC. . GOBACK.
Restrictions on Application Program Coding
In all other respects, the application program should be coded like a standard CICS routine. As long as the DCI parameter list is correct when LNCSTUB is called, there are no restrictions on the CICS commands that an application can issue.
Standard Batch Call Mechanism Used
As shown in the Assembler and COBOL language program parameter list examples above, the call to the LNCSTUB entry point is accomplished like a batch application. Likewise, calls for the other supported languages should be coded with their standard batch call mechanisms.
To properly link the LNCSTUB module with application programs, link the application program to include the LNCSTUB module and the IBM CICS stub modules. The method for doing this varies with the programming language used for the application:
Assembler language programs should include the DFHEAI and DFHEAI0 CICS modules;
COBOL applications should include DFHECI and DFHEAI0.
To avoid a double reference to the DFHEAI0 module, code the linkage editor REPLACE DFHEAI0 control statement at the beginning of the SYSLIN data deck.
 For linking Assembler language programs:
For linking Assembler language programs:
For an Assembler program, the SYSLIN input is similar to:
INCLUDE DFHEAI
The Assembler object input is similar to:
REPLACE DFHEAI0 INCLUDE SYSLIB(LNCSTUB) INCLUDE SYSLIB(DFHEAI0) NAME ALCSIVP(R)
When examining the cross-reference from the linkage editor, the symbol "entry-name" must have the same starting location as the LNCSTUB module in the link map.
 For linking COBOL language programs:
For linking COBOL language programs:
For a COBOL program, the SYSLIN input is similar to:
REPLACE DFHEAI0 INCLUDE SYSLIB(DFHECI)
The COBOL object input is similar to:
INCLUDE SYSLIB(LNCSTUB) INCLUDE SYSLIB(DFHEAI0) NAME COBSIVP(R)
When examining the cross-reference from the linkage editor, the symbol “entry-name” must have the same starting location as the LNCSTUB module in the link map.
 For linking PL/I and C language programs:
For linking PL/I and C language programs:
Refer to the IBM manual CICS System Definition Guide for information about linking PL/I and C applications under CICS.
To obtain the best performance from applications using the Adabas direct call interface (DCI), examine how the DCI interface functions at the logical level.
A CICS application using the standard LINK/RETURN mechanism to access the Adabas link routines invokes the CICS program control service for every Adabas request made to the link routine. The LNCSTUB module permits a BALR interface to be used. A BALR interface can substantially reduce the CICS overhead required to pass control from the application program to the Adabas CICS command-level link component.
The LNCSTUB module accomplishes this by using the standard EXEC CICS LINK/RETURN mechanism to make an Initial Call (IC) to the Adabas CICS link routine. The link routine recognizes this call, and returns the entry point address of the DCI subroutine to LNCSTUB. LNCSTUB must then save this address in a location that can be assured of existence throughout the duration of the invoking task. This is why the calling program must provide the 4-byte field to hold the DCI entry point address. After the DCI address has been obtained, and for as long as LNCSTUB receives this address as the first parameter passed to it on subsequent Adabas calls, LNCSTUB utilizes the BALR interface to pass control to the Adabas CICS link component program.
As a consequence of this logic, the more Adabas requests made between ICs, the more efficient the application in terms of passing data to and from Adabas under CICS. In fact, pseudo-conversational applications that issue one Adabas call each time a task is invoked should not be coded to use the DCI because there will be an IC request for each Adabas command issued by the calling program.
An additional performance improvement can be realized by taking advantage of the fact that the Adabas CICS link component program must be defined as resident in CICS. This fact should allow the DCI entry point to be stored across CICS tasks, making it possible for different programs to call the LNCSTUB module with a valid DCI entry point. The IC at each program startup is thus avoided. When this procedure is used, however, any change to the CICS environment that invalidates the entry point address (such as a NEWCOPY) will lead to unpredictable and possibly disastrous results.
It is imperative that at least one IC be made to the Adabas CICS link component program using CICS services. This call is used to trigger the acquisition of shared storage for the Adabas user block (UB) and an array of register save areas. If no IC request is made, Adabas calls will not execute due to a lack of working storage, and to the fact that critical control blocks used by the link routines and the Adabas SVC are not built.
| Warning: The ADAGSET macro found in the Adabas ACIvrn.SRCE library, should only be used for generating default values for the Adabas CICS high-performance stub routine. |
To facilitate the assembly of the Adabas CICS high-performance stub routine, Software AG recommends that you program the ADAGSET macro with site-specific default values and put it in a source library that is available in the SYSLIB concatenation during assembly.
The applicable ADAGSET parameter options, with their default values (underlined), are described below (all other ADAGSET parameters are obsolete and will be removed in a future version):
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| ENTPT |
The name of the Adabas CICS Application Stub used in the priming EXEC CICS LINK command issued by LNCSTUB. |
ENTPT={'ADACICS' | 'name'}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| LOGID |
The database ID used by the (optional) Assembler IVP, ALCSIVP.. Valid ID numbers are 1-65535. |
LOGID= nnn |
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| PARMTYP |
The area which is to contain the Adabas parameter list. If PARMTYP=TWA is specified the CICS TWA is used, otherwise the CICS COMMAREA is used. This value should match that specified for the LGBLSET parameter of the same name in use by the Adabas CICS Application Stub. |
PARMTYP={ ALL | COM | TWA }
|
Certain Adabas parameters are required by Com-plete, Software AG’s TP monitor, when installing Adabas. For more information, see the Com-plete System Programmer’s manual.
Software AG’s TP monitor, Com-plete requires an Adabas link routine if it is to communicate with Adabas databases, use Software AG’s Entire Net-Work product, or use products like Entire System Server running under Com-plete.
The Adabas link routine is delivered in member ADALCO of the Adabas load library. This member must be linked with a link globals module you prepare and with any link routine exits you require to create the final ADALCO load module that is loaded by Com-plete when Com-plete is initialized. The final ADALCO load module and any exits linked with it must be reentrant.
The following table lists the modules supplied in your Adabas installation to support the installation of Adabas with Com-plete.
| Module | Description |
|---|---|
| ADALCO8 | Base module |
| ADALCO | Executable default module |
 To prepare the Adabas link routine:
To prepare the Adabas link routine:
Copy sample member LCOGBL provided in the ADAvrs.SRCE library to any appropriate user source library where it can be modified (where vrs is the number of the latest Adabas version delivered on the tape). LCOGBL is a module containing LGBLSET parameters that are used to create default settings for Adabas link components. A complete description of LGBLSET parameters can be found in Modifying Source Member Defaults (LGBLSET Macro).
Modify the LCOGBL member in the user source library.
At a minimum supply values for the following LGBLSET parameters in LCOGBL:
| Parameter | Specify... |
|---|---|
| LOGID | The default database or target ID. This should be a
numeric value between "1" and
"65535". The default value is
"1".
Note |
| SVCNO | The default Adabas SVC number. This number should be
between "200" and
"255".
Note |
| TPMON | COM. This keyword specifies the three-character TP monitor abbreviation. For Com-plete, this value should be "COM". |
| RENT | YES. This keyword indicates whether or not the module is serially reentrant. For Com-plete, this value should be "YES". |
| GEN | CSECT. This keyword indicates whether a CSECT or DSECT is generated. CSECT must be specified so an object module is generated that can be linked as the link routine globals load module. |
| UES | Whether Adabas Universal Encoding Support (UES) should be enabled. The default is YES. For more information, read Enabling Universal Encoding Support (UES) for Your Adabas Nucleus. |
| exit parameters | Whether any other exits are to be active, and in the case of user exits you provide, specify the user exit module names. Specify this information in other parameters of LGBLCOM, as described in Modifying Source Member Defaults (LGBLSET Macro). |
Modify and run sample job ASMGBLS as described at the top of the job. ASMGBLS can be found in the ADAvrs.JOBS library. When fully modified, the SET statement in the job should reference the LCOGBL member you prepared in the previous step and the NAME link edit control statement should reference the name specified by the GBLNAME parameter in the LCOGBL member.
Once modified, submit the ASMGBLS job to assemble and link-edit the link globals module.
A new link globals module (with the name specified by the GBLNAME parameter in LCOGBL) will be generated in the user load library identified in the ASMGBLS job.
Copy sample job LNKLCO8 to a user source library and modify it to link the new link globals module you created in the previous step and any required exits with the ADALCO8 base module. Instructions for modifying the sample job are described at the top of the job. Be sure to direct the output from this job to an appropriate user load library. LNKLCO8 can be found in the ADAvrs.JOBS library.
The module resulting from this job is called ADALCO.
Place the ADALCO module in a load library available in the job step that will start Com-plete.
The Adabas link routine is prepared.
When installing Adabas on TSO systems, Adabas-TSO communication is provided by the batch link routines ADALNK8 (non-reentrant) and ADALNKR8 (reentrant).
In this version of Adabas, the ADALNK routines are UES-enabled as distributed. See the section Enabling Universal Encoding Support (UES) for Your Adabas Nucleus for more information.
However, it is important to note that user programs linked with ADAUSER also load ADARUN. ADARUN, in turn, loads other modules.
To start a user program linked with ADAUSER, the following modules must all be available from the defined load libraries for that specific TSO user at execution time:
ADAIOR ADAMLF ADAIOS ADAPRF ADALNK ADARUN
This section covers the following topics:
Important
If an ADALNK batch link routine has been linked or modified by Software GmbH
product modules or user exits, it cannot be used in any application startups of Adabas
utility jobs or Adabas, Entire System Server, Adabas Review Hub, or Entire Net-Work
nuclei.
The ADALNK module in the Adabas load library operates when the following conditions are met:
The calling application must be linked with ADAUSER. If the calling application is not linked with ADAUSER, the ADALNK will not work.
The ADARUN module from the most recent Adabas load library must be used.
The database ID and Adabas SVC number must be provided as input through DD statements. Otherwise, the values in the link globals table will override these values.
If all three of these conditions are met, the default database ID and Adabas SVC number will be overridden by the values provided in the DD statement input and passed to the link routine by ADARUN.
Operating in this fashion requires the fewest changes on the part of your data base administrator (DBA) and application programmer. This is also the recommended mode of operation when executing Adabas utilities.
Several Software GmbH products require the use of a reentrant batch link routine and the ADALNKR load module is provided in the Adabas load library to support them. The ADALNKR source module is not provided.
You can change default values for these reentrant batch link routines. For more information, read one of the following sections:
we recommend that batch application programs be linked with the ADAUSER module, not ADALNK or ADALNKR. The ADAUSER load module is not reentrant, but the reentrant link routine module may be linked with it as long as the application program conforms to the calling requirements described in Batch/TSO Reentrant Link Routine (ADALNKR) Calling Requirements and the PROG=RENTUSER ADARUN parameter is provided in DDCARD input instead of the keyword parameter PROG=USER.
When using the latest ADALNKR module to obtain reentrant operation under batch or TSO, you must prepare the ADALNKR module in advance. It must be linked with a customized link globals table that provides defaults for the database ID, Adabas SVC number, and other requirements. Any reentrant exits should also be linked with it as required.
When installing Adabas on TSO systems, the standard Adabas 8 batch link routine (ADALNK) provides Adabas/TSO communication (SMA job number I056).
This section covers the following topics:
Important
If an ADALNK batch link routine has been linked or modified by Software GmbH
product modules or user exits, it cannot be used in any application startups of Adabas
utility jobs or Adabas, Entire System Server, Adabas Review Hub, or Entire Net-Work
nuclei.
The following table lists the modules supplied in your Adabas installation to support the installation of Adabas with batch/TSO.
| Module | Description |
|---|---|
| ADALNK8 | Base module |
| ADALNKR8 | Base reentrant module |
| ADALNK | Executable default module |
| ADALNKR | Executable default reentrant module |
You can change default values for various link routine parameters used by the ADALNK and ADALNKR modules.
 To change default values, complete the following steps:
To change default values, complete the following steps:
Copy the sample member LNKGBLS (for non-reentrant links) or LNKRGBL (for reentrant links) members provided in the ADAvrs.SRCE library to any appropriate user source library where they can be modified. These modules contain LGBLSET parameters that are used to create default settings for link components. A complete description of LGBLSET parameters can be found in Modifying Source Member Defaults (LGBLSET Macro).
Modify the LNKGBLS or LNKRGBL member in the user source library. Provide values for the LOGID, SVC, and other keywords to suit your installation requirements.
Modify and run sample job ASMGBLS as described at the top of the job. ASMGBLS can be found in the ADAvrs.JOBS library. When fully modified, the SET statement in the job should reference the LNKGBLS or LNKRGBL member you prepared in the previous step and the NAME link edit control statement should reference the name specified by the GBLNAME parameter in the LNKGBLS or LNKRGBL member.
Once modified, submit the ASMGBLS job to assemble and link-edit the link globals module.
A new link globals module (with the name specified by the GBLNAME parameter in the LNKGBLS or LNKRGBL member) will be generated in the user load library identified in the ASMGBLS job.
Copy sample job LNKLNK8 or LNKLNKR8 (reentrant) to a user source library and modify it to link the new link globals module you created in the previous step and any required exits with the appropriate ADALNK8 or ADALNKR8 (reentrant) base module. Instructions for modifying the sample job are described at the top of the job. Be sure to direct the output from the job to an appropriate user load library. LNKLNK8 and LNKLNKR8 can be found in the ADAvrs.SRCE library.
Note
If you use link routine user exits, Adabas Review, or Adabas System
Coordinator, the jobs used to link these components with the batch, reentrant
batch or the IMS link routine should be modified to explicitly include the LNKIND
module when the link routines are relinked to incorporate user or Software GmbH
product link routine exits.
The module resulting from this job is called ADALNK or ADALNKR (as appropriate).
Tailor the ADARUN DDCARD input for the job steps that will use the batch/TSO link routines. The DDCARD input should include the following updates:
Specify the ADARUN PROG=USER parameter for a non-reentrant link routine, or specify ADARUN PROG=RENTUSER to use a reentrant link routine in the job step. For more information about the PROG parameter, read PROGRAM : Program to Run.
Make sure the appropriate load libraries are made available to the job step. These may be STEPLIB, TASKLIB, JOBLIB, or, for reentrant modules, the LPA or LINKLIB.
You can change default values for various link routine parameters used by the ADALNK and ADALNKR modules.
Changes to some default values for the batch/TSO link routines, ADALNK and ADALNKR, may occur with a zap to either the ADALNK or ADALNKR module. This includes the default values for the database ID and the Adabas SVC number. All other default values should be set using the link globals table, as described in Changing Default Values for the ADALNK or ADALNKR Modules. we recommend changing all values in the link globals table and relinking ADALNK or ADALNKR (as appropriate).
Use the following IMASPZAP control statements to change default values in ADALNK or ADALNKR (as appropriate):
NAME ADALNK LNKGBLS VER 0030 0001 Default DBID REP 0030 #### Site-specific DBID VER 0032 0AF9 Default Adabas SVC number REP 0032 0A## Site-specific Adabas SVC number * NAME ADALNKR LNKRGBL VER 0030 0001 Default DBID REP 0030 #### Site-specific DBID VER 0032 0AF9 Default Adabas SVC number REP 0032 0A## Site-specific Adabas SVC number
This section covers the following topics:
Prerequisite to the enabling of TCP/IP socket support for Batch/TSO is the following:
Refer to Enabling Direct TCP/IP Access (ADATCP) To Your Adabas Nucleus for information on how to enable your Adabas nuclei to accept direct TCP/IP access.
The Adabas Directory Server provides all necessary information required to accomplish communication between Batch/TSO jobs and Adabas nuclei.
Refer to the Adabas Directory Server documentation for information on how to install Adabas Directory Server on z/OS.
When installed, the location of the Adabas Directory Server is derived from the values defined to the LTCPSET parameters ADIHOST and ADIPORT.
The following table lists the components supplied to support the enabling of TCP/IP socket support for Batch/TSO:
| Dataset | Member | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MVSJOBS | ASMANCR | Sample job to assemble and link the LTCPSET TCP/IP parameter module (TCPANCR). |
|
TCPLNK TCPLNKR |
Sample jobs to link ADALNK/ADALNKR with the TCP/IP communications interface module LNKTCP. | |
| MVSLOAD | LNKTCP | TCP/IP communications interface module. |
| MVSSRCE | LTCPSET | Macro for creating the TCPANCR module from the defined TCP/IP parameters. |
| TCPGBLS | Sample TCP/IP parameters. |
To enable the use of TCP/IP socket support for Batch/TSO, complete the following steps:
Step 1. Create a new Batch link globals table with LGBLSET TCPIP=YES
Step 4. Make all applicable modules available to the Batch/TSO job
To enable the use of TCP/IP socket support, the LGBLSET parameter TCPIP: TCP/IP Support must be set to Yes.
First, modify the sample TCPGBLS member in the Adabas source library, and supply values for the following parameters:
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
ADIHOST |
This parameter specifies the hostname of the Adabas Directory Server (ADI).
The hostname is used to attempt to acquire the TCP/IP address of the system
where the Adabas Directory Server resides. If used,
Valid values are 1-255 characters with no embedded blanks. |
ADIHOST={hostname}
|
ADIPART |
This optional parameter specifies the partition name to be used with the Adabas Directory Server (ADI). The partition name is used to restrict database access by TCP/IP; when the Adabas link module queries ADI for a database target and specifies a partition name, only database entries with the same partition name are eligible for access by TCP/IP. Likewise, if the query does not specify a partition name, only database entries that do not have a partition name are eligible Valid values are 1-32 characters with no embedded blanks. |
ADIPART={partition name}
|
ADIPORT |
This parameter specifies the port number used to communicate with the
Adabas Directory Server (ADI). If used, Valid values are 1-65535. |
ADIPORT={port number}
|
RCVTIME |
This is the number of seconds that a task will wait for a reply. If RCVTIME=0 the wait is indefinite. If RCVTIME > 0 and the wait exceeds the specified value, a RSP218 sub-code 130 is returned to the caller. |
RCVTIME={0-134217727}
|
MSGLVL |
This parameter controls what LNKTCP* messages are written to the console. The default value of 0 means no messages are written. Refer to LNKTCP* Adabas Link Routine TCP/IP Socket Support Messages to determine what messages may be written for a particular MSGLVL value. |
0-255 |
TRACE |
Indicates whether or not tracing should be written out to TCPPRNT. (DD statement TCPPRNT is required in the Batch/TSO job) Note: |
TRACE={NO|YES}
|
Note:
The location of the Adabas Directory Server is derived using the following
order:
Use the supplied ADIHOST and
ADIPORT values.
Resolve SAGXTSDSMF and SAGXTSDSMFPORT using DNS services.
Use localhost with a default port of 4952.
Next, modify and run sample member ASMANCR in the Adabas jobs library as described at the top of the job. This job will assemble and link-edit the TCP/IP parameter module TCPANCR using the TCPGBLS source member as input.
With reference to the sample members TCPLNK and TCPLNKR in the Adabas jobs library, modify your existing ADALNK/ADALNKR jobs to include the module LNKTCP.
Ensure the following modules are available to the Batch/TSO job:
Link globals table with LGBLSET parameter TCPIP=YES.
TCP/IP parameter module TCPANCR.
ADALNK/ADALNKR with LNKTCP included.
Currently, the following limitations and restrictions exist in the TCP/IP socket support for Batch/TSO:
Adabas commands issued to an Adabas database protected by Adabas SAF Security using TCP/IP socket support are allowed or disallowed based on either the User ID of the user who started the Adabas nucleus or on the identifier of the nucleus started task, and not on the User ID of the user issuing the Adabas command.
TCP/IP socket support should not be used when performing SYSxxx administration on an Adabas nucleus, Adabas Audit Server, or Adabas Event Replicator Server - doing so may result in response code 218 subcode 113.
Your application programs that use Adabas link routines can route database calls through specific Adabas SVCs, based on the database ID used in the call. SVC routing is managed through the use of a DBID/SVC routing table you supply. Up to 1000 database IDs may be specified in the table and associated with any number of valid SVC numbers installed in the z/OS system. The DBID/SVC routing table is created using the MDBSVC macro.
Duplicate database IDs are not allowed in the DBID/SVC routing table as there is no reliable way for the link routine to determine which SVC should be used for a database ID if it is listed more than once. If duplicate database IDs are found while the table is being assembled, they are flagged with an assembler MNOTE and a return code of 16 is returned for the assembly attempt.
Notes:
Caution
This feature should be used with caution. Transactional integrity is not guaranteed. If
an application makes calls to multiple databases that are routed to more than one Adabas SVC,
it becomes possible to issue ET, BT, OP, CL, RC, or other Adabas commands that may affect the
transaction on one database, but not on the other databases running on different Adabas SVCs
that were accessed previously. It therefore is the responsibility of the application program
to ensure that all necessary logic is included to ensure transactional integrity across
multiple databases where multiple Adabas SVCs are employed.
This section covers the following topics:
The general steps for installing the Adabas DBID/SVC routing feature are:
Define the DBID/SVC routing table in a library member using MDBSVC macro statements. For more information about the DBID/SVC routing table and the MDBSVC macro, read Using the MDBSVC Macro.
Assemble and link-edit the DBID/SVC routing table member to create a load module that will be made available to the operating environment where the SVC routing feature will be used.
Modify a link globals table for the operating environment, specifying the LGBLSET keywords DYNDBSVC=YES and DBSVCTN=name, where name is the name of the DBID/SVC routing table load module that should be used by the link routine. Assemble and link-edit the updated link globals table as required for the operating environment. For more information about the link globals table and the LGBLSET macro, read Modifying Source Member Defaults (LGBLSET Macro). For information on assembling and link-editing the link globals table once the table is updated, refer to the instructions for each TP monitoring environment, provided elsewhere in this section.
Make the prepared DBID/SVC routing table available in a load library that is accessible by the application program's job step, so it can be loaded by the link routine when it runs.
Except for CICS systems, you will need to relink ADALNK or ADALNKR making sure that the INCLUDE statements for the LNKDSL and DEPRTR modules are included in the job.
This section covers the following topics:
The installation steps for the Adabas SVC routing feature under batch, TSO, and IMS are the same.
 To install the Adabas DBID/SVC routing feature under batch, TSO, or IMS, complete the
following steps:
To install the Adabas DBID/SVC routing feature under batch, TSO, or IMS, complete the
following steps:
Define or modify the DBID/SVC routing table by coding a series of MDBCSVC macros in a library member. Sample member ADASVCTB is provided in the ADAvrs.SRCE library as a template for preparing this member. For more information about using the MDBSVC macro, read Using the MDBSVC Macro.
Assemble and link-edit the DBID/SVC routing table member to create the table as a load module that you can make available to the application execution job step. The load module should be linked non-reusable and non-reentrant because the link routine subprogram LNKDSL will need to store the addresses of the Adabas SVC IDT headers in the DBID/SVC module to reduce the operating overhead on multiple commands accessing the same Adabas SVC.
Define or modify a link globals table for the execution environment. The following LGBLSET keywords are required to support the Adabas SVC routing feature:
| LGBLSET Keyword Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| DYNDBSVC=YES | This keyword and setting indicate that Adabas SVC routing is active for this job step. |
| DBSVCTN=name | This keyword specifies the name of the DBID/SVC table for this job step. This name must match the name of the load module created to ensure the proper table is loaded when the link routine runs. |
Assemble and link-edit the updated link globals table, as described for the appropriate TP monitor. For batch/TSO, read Installing Adabas with Batch/TSO; for IMS, read Installing Adabas with IMS TM.
Relink ADALNK or ADALNKR, making sure that the INCLUDE statements for the LNKDSL and DEPRTR modules are included in the job. Samples of the jobs used to relink ADALNK and ADALNKR are listed in the following table:
| Link Routine | Sample Job | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Batch | TSO | IMS | |
| ADALNK | LNKLNK8 | LNKLNK8 | --- |
| ADALNKR | LNKLNKR8 | LNKLNKR8 | --- |
| ADALNI8 | --- | --- | LNKLNI8 |
 To install the Adabas DBID/SVC routing feature under CICS, complete the following
steps:
To install the Adabas DBID/SVC routing feature under CICS, complete the following
steps:
Define or modify the DBID/SVC routing table by coding a series of MDBCSVC macros in a library member. Sample member ADASVCTB is provided in the ADAvrs.SRCE library as a template for preparing this member. For more information about using the MDBSVC macro, read Using the MDBSVC Macro.
Assemble and link-edit the DBID/SVC routing table member to create the table as a load module and place it in a library that will be part of the CICS DFHRPL concatenation. The load module should be linked non-reusable and non-reentrant because the link routine subprogram LNKDSL will need to store the addresses of the Adabas SVC IDT headers in the DBID/SVC module to reduce the operating overhead on multiple commands accessing the same Adabas SVC.
Define the load module as a program to CICS using RDO, or the DFHCSDUP utility. See member DEFADAC in the ACIvrs.SRCE libarary for sample DFHCSDUP definition statements. The program attributes should be Reload(No), Resident(Yes), Dataloc(Any), and Execkey(CICS).
Define or modify a link globals table for the execution environment. The following LGBLSET keywords are required to support the Adabas SVC routing feature:
| LGBLSET Keyword Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| DYNDBSVC=YES | This keyword and setting indicate that Adabas SVC routing is active for this job step. |
| DBSVCTN=name | This keyword specifies the name of the DBID/SVC table for this job step. This name must match the name of the load module created to ensure the proper table is loaded when the link routine runs. |
Assemble and link-edit the updated link globals table, as described in Installing Adabas with CICS.
When the Adabas SVC routing feature is installed, as described earlier in this section, it is loaded as described below:
In batch, TSO, or IMS environments, the DBID/SVC routing table is loaded when the link routine initializes if the LGBLSET DYNDBSVC parameter is set to YES in the link globals table. The address of the routing table is kept in the link routine work area for use by all subsequent calls.
In CICS environments, the Adabas CICS Installation Program ADACIC0, normally run during PLTPI processing, loads and validates the DBID/SVC routing table, if the LGBLSET DYNDBSVC parameter was set to YES in the link globals table for the CICS region. The address of the routing table is kept in the global work area associated with the Adabas CICS task-related user exit (TRUE) module, ADACICT, and is made available on each application call to the TRUE by the Adabas application stub ADACICS.
When an application call is made, the DBID/SVC routing table is searched by the LNKDSL subroutine which is linked with the appropriate link routine for each operating environment. LNKDSL is called after any LUEXIT1 (link routine user exit 1) is invoked, in case the pre-Adabas call user exit modifies the command's database ID for subsequent processing. The call to LNKDSL is made before any monitoring or Adabas Fastpath exits are called, so the monitoring product, such as Adabas Review, Adabas Fastpath, or Adabas Transaction Manager, will perform their processing based on the appropriate Adabas SVC found in the DBID/SVC routing table.
If the database ID associated with a particular call is not found in the DBID/SVC routing table, the default value for the Adabas SVC as specified by the MDBSVC macro's TYPE=INIT parameter is used. If the SVC located is not an Adabas SVC, an Adabas response code of 213 with subcode 16 or 20 is returned to the application. If the calling database is not active for an SVC number, an Adabas response code of 148 (ADARSP148) is returned to the application.
Duplicate database IDs are not allowed in the DBID/SVC routing table as there is no reliable way for the link routine to determine which SVC should be used for a database ID if it is listed more than once. If duplicate database IDs are found while the table is being assembled, they are flagged with an assembler MNOTE and a return code of 16 is returned for the assembly attempt.
Use the MDBSVC macro to define various aspects of the Adabas DBID/SVC routing table. Several MDBSVC macros are coded together using TYPE=INIT, TYPE=GEN, and TYPE=FINAL keywords to comprise a source module or member. This source module or member is then assembled and link-edited to build the DBID/SVC routing table load module. Sample member ADASVCTB in ADAvrs.SRCE can be used as a template for creating site-specific versions of the DBID/SVC routing table source module. Here is a sample DBID/SVC routing table source member that uses the CSECT name TESTDBT; when the table is assembled, its load module name will be TESTDBT:
TESTDBT CSECT
MDBSVC TYPE=INIT,SVC=249,DBID=001
MDBSVC TYPE=GEN,SVC=237,DBID=(2,10,21,33,175,1149), X
DBID2=(100,101,102,13500)
MDBSVC TYPE=GEN,SVC=231,DBID=(226,899)
MDBSVC TYPE=GEN,SVC=206,DBID=(15,16,69,99,500,12144)
MDBSVC TYPE=GEN,SVC=248,DBID=(14,54,111,177,1213,5775)
MDBSVC TYPE=GEN,SVC=249,DBID=(17,19,25,35,42,44,61,76)
MDBSVC TYPE=FINAL
END
When coding keyword values of MDBSVC macro statements, the assembler rules for continuing lines, identifying lists, and providing keyword values must be followed or assembly errors will result. Keywords and values with lists coded as objects of keywords must be separated by commas. There are no positional parameters used with the MDBSVC macro.
The MDBSVC macro can include the following four types of statements, as described in the following table:
The MDBSVC TYPE=INIT statement can be preceded by a named CSECT statement and named AMODE and RMODE statements. If the CSECT, AMODE, or RMODE statements are included, the name used in them must agree with the name for the DBID/SVC routing table, as coded in the TABNAME parameter on the MDBSVC TYPE=INIT statement and as specified in the DBSVCTN keyword of the LGBLSET macro used for creating the link globals table.
This section covers the following topics:
The syntax for the MDBSVC TYPE=INIT statement is:
MDBSVC TYPE=INIT,SVC=svcno,DBID=dbid[,TABNAME={name|ADBSVCT}][,OPSYS={ZOS}]
The parameters you can code on the MDBSVC TYPE=INIT statement are described in MDBSVC Parameters.
The syntax for the MDBSVC TYPE=GEN statement is:
MDBSVC TYPE=GEN,SVC=svcno,DBID={id | (id1,id2[,idn]...) }[,DBID2={id | (id1,id2[,idn]...) } ]
The parameters you can code on the MDBSVC TYPE=GEN statement are described in MDBSVC Parameters.
The syntax for the MDBSVC TYPE=FINAL statement is:
MDBSVC TYPE=FINAL
No parameters are valid on the MDBSVC TYPE=FINAL statement.
The parameters that can be specified on various MDBSVC statements are as follows:
- DBID
The DBID parameter is required on both the MDBSVC TYPE=INIT and MDBSVC TYPE=GEN statements.
When specified on the MDBSVC TYPE=INIT statement, it lists the default database ID associated with the SVC specified in the SVC parameter. In this case, only one database ID can be listed in the DBID parameter on a TYPE=INIT statement.
When specified on a MDBSVC TYPE=GEN statement, it lists the database IDs associated with the SVC specified in the SVC parameter. If more than one database ID is listed, they should be enclosed in parentheses and separated by commas.
Database IDs listed in the DBID parameter must be numeric and must correspond to the IDs of installed Adabas databases. Database IDs must range from 1 to 65535. The same database ID cannot be specified on multiple MDBSVC statements; they must be unique across all of the DBID and DBID2 statements in the DBID/SVC routing table. Duplicate values are flagged with an MNOTE, which causes the assembly of the DBID/SVC routing table to stop with return code 16.
The following is an example of some DBID parameters on various MDBSVC statements. Note that two MDBSVC statements list database IDs associated with SVC 237. This allows more database IDs to be coded for the same SVC number. Compare the way this is coded to the way the same example is coded for the DBID2 parameter. Both codings produce the same end result.
MDBSVC TYPE=INIT,SVC=249,DBID=1 MDBSVC TYPE=GEN,SVC=237,DBID=(2,4,10,16,21,33) MDBSVC TYPE=GEN,SVC=237,DBID=(175,1149,1221) MDBSVC TYPE=GEN,SVC=242,DBID=(3,18) MDBSVC TYPE=FINAL END- DBID2
The DBID2 parameter can be coded only on MDBSVC TYPE=GEN statements. It lists additional database IDs to be associated with an Adabas SVC specified in the SVC parameter. The DBID2 parameter is optional, but when it is specified, it must follow a DBID parameter.
Database IDs listed in the DBID2 parameter must be numeric and must correspond to the IDs of installed Adabas databases. Database IDs must range from 1 to 65535. The same database ID cannot be specified on multiple MDBSVC statements; they must be unique across all of the DBID and DBID2 statements in the DBID/SVC routing table. Duplicate values are flagged with an MNOTE, which causes the assembly of the DBID/SVC routing table to stop with return code 16.
The following is an example of some MDBSVC statements that includes a DBID2 parameter. Compare the way this example is coded to the way the same example is coded for the DBID parameter. Both codings produce the same end result.
MDBSVC TYPE=INIT,SVC=249,DBID=1 MDBSVC TYPE=GEN,SVC=237,DBID=(2,4,10,16,21,33), X DBID2=(175,1149,1221) MDBSVC TYPE=GEN,SVC=242,DBID=(3,18) MDBSVC TYPE=FINAL END- OPSYS
The OPSYS parameter is an optional parameter that can be coded only on the MDBSVC TYPE=INIT statement. This parameter identifies the operating system where the DBID/SVC routing table is assembled. The OPSYS parameter must be set to "ZOS".
- PREFIX
The PREFIX parameter can only be coded only on the MDBSVC TYPE=DSECT statement, which is reserved for internal use by Software AG. Do not use this parameter.
- SVC
The SVC parameter is required on both the MDBSVC TYPE=INIT and MDBSVC TYPE=GEN statements.
When specified on the MDBSVC TYPE=INIT statement, it specifies the default Adabas SVC number to be used when the calling application provides a database ID that is not found in the DBID/SVC routing table.
When specified on a MDBSVC TYPE=GEN statement, it specifies the Adabas SVC number to be associated with the Adabas databases identified by the DBID and DBID2 parameters.
The SVC number listed in the SVC parameter must be numeric and must correspond to the SVC number of an installed Adabas SVC. The SVC number must range from 200 to 255. Duplicate SVC values can be coded on multiple MDBSVC statements; this allows you to code long lists of database IDs and associate them with the same Adabas SVC.
In the following example, notice that there are two MDBSVC statements for SVC 249. It is the default SVC for the link routine and is also used for database 1, 3, and 18. There are also two MDBSVC statements for SVC 237; the two statements are used to list nine databases associated with SVC 237 (2, 4, 10, 16, 21, 33, 175, 1149, and 1221).
MDBSVC TYPE=INIT,SVC=249,DBID=1 MDBSVC TYPE=GEN,SVC=237,DBID=(2,4,10,16,21,33) MDBSVC TYPE=GEN,SVC=237,DBID=(175,1149,1221) MDBSVC TYPE=GEN,SVC=249,DBID=(3,18) MDBSVC TYPE=FINAL END- TABNAME
The TABNAME parameter is an optional parameter that can be coded only on the MDBSVC TYPE=INIT statement. This parameter specifies the name of the DBID/SVC routing table when the source member does not include a separate (and previously coded) CSECT statement. In this case, the name you specify on the TABNAME parameter is used to generate a named CSECT statement and named AMODE and RMODE directives.
The DBID/SVC routing table name that you specify should be between 1 and 8 alphanumeric characters long. In the following example, a DBID/SVC routing table with the name TESTDBT is coded.
MDBSVC TYPE=INIT,SVC=249,DBID=1,TABNAME=TESTDBT MDBSVC TYPE=GEN,SVC=237,DBID=(2,4,10,16,21,33) MDBSVC TYPE=GEN,SVC=237,DBID=(175,1149,1221) MDBSVC TYPE=GEN,SVC=249,DBID=(3,18) MDBSVC TYPE=FINAL END
The LGBLSET macro is used to set default installation values for the Adabas link routines. It is used to prepare an object module which may either be link-edited with the link routines or provided to the link routines in the job step where they are run. Your Adabas libraries include sample members provided to support the various teleprocessing (TP) monitors in each environment. Each of these sample members may be copied to an appropriate library and modified to provide the necessary customization required for the link routine that is intended to run in a given environment.
The LGBLSET parameter options with their default values (underlined) are described in the rest of this section:
LUINFO: Length of User Data Passed to Adabas LUEXIT1 and LUEXIT2
LUSAVE: Size of User Save Area for Adabas LUEXIT1 and LUEXIT2
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| ADL |
Indicates whether or not the Consistency Interface of Software AG’s Adabas Bridge for DL/I is to be supported by this command-level link routine.
|
ADL={NO|YES}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| AUDIT |
Indicates whether or not Adabas Auditing is to be activated for the link module(s) using this link globals table.
|
AUDIT={NO|YES}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| AVB |
Indicates whether or not Software AG’s Adabas Bridge for VSAM is to be supported by this command-level link routine.
|
AVB={NO|YES}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| CITSNM |
Specifies the 16-byte string that represents the CICS TS queue name for Adabas. The default is "ADACICS". |
CITSNM={ADACICS|qname}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| COR |
Indicates whether or not the Adabas System Coordinator (COR) client component is to be activated for the link module(s) using this link globals table (as required by Adabas Fastpath, Adabas Vista, and Adabas Transaction Manager).
|
COR={NO|YES}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| DBSVCTN |
Provides the name of the DBID/SVC routing table that should be used by the link routine during its execution, if any. The routing table name is used by a LOAD macro/SVC during batch, TSO, or IMS operation or by an EXEC CICS LOAD PROGRAM command during CICS operation. If the load module listed is not found, or if it is found to contain invalid header information, user abend U657 is issued in batch, TSO, or IMS environments. If the load module is not defined to CICS or not found in the CICS DFHRPL concatenation, the Adabas CICS link routine environment is not initialized. Note For more information about SVC routing by database ID, read Establishing Adabas SVC Routing by Adabas Database ID. Note |
DBSVCTN={name|ADASVCTB}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| DYNDBSVC |
Indicates whether Adabas SVC routing by database ID should be enabled for the link routine. DYNDBSVC=YES enables Adabas SVC routing by database ID; DYNDBSVC disables it. The default is NO. For more information about SVC routing by database ID, read Establishing Adabas SVC Routing by Adabas Database ID. |
DYNDBSVC={YES|NO}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| ENTPT |
The name given to the Adabas CICS command-level link routine. This name is used in EXEC CICS LINK commands to invoke Adabas services from CICS application programs. See also notes 1 and 2 in the installation procedure. |
ENTPT={ADACICS|name}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| FIXLOGID |
Note This parameter prevents the runtime modification of the default database ID defined by the LOGID parameter.
|
FIXLOGID={NO|YES}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| GBLNAME |
The name of the link globals module. |
GBLNAME={LNKGBLS|name}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| GEN |
Indicates whether a CSECT or DSECT is generated. |
GEN={CSECT|DSECT}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| LMINFO |
The length of the client monitoring information area for use by Adabas Auditing
( If Refer to the relevant Adabas Auditing and/or Adabas Review documentation for any additional information regarding the setting of this parameter. If both products are to be activated, then specify the larger of any documented lengths |
LMINFO={0|length}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| LOGID |
The value of the default target database ID. Valid ID numbers are 1-65535. The default is "1". |
LOGID={nnn|1}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| LUINFO |
The length of the user data to be passed to target user exit 4. Valid values are numbers from zero (0) through 32,767. If LUINFO is not specified, the default is zero (no user data is passed). |
LUINFO={0|length}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| LUSAVE |
The size of the user save area to be used by Adabas user exits LUEXIT1 and LUEXIT2. Valid values range from zero (0) through 256. The default is "72". If LUSAVE is not specified, the default is zero (no user save area is passed). |
LUSAVE={72|size}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| LX1NAME |
The name of the link user exit 1 module |
LX1NAME={LUEXIT1|name}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| LX2NAME |
The name of the link user exit 2 module |
LX2NAME={LUEXIT2|name}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| MRO |
Indicates whether or not the CICS multiple region option (MRO) support is required. If you run the CICS command-level link with the CICS MRO, set this to MRO=YES; otherwise, use the default value MRO=NO. If MRO=YES, NETOPT must be set to NETOPT=NO (the default) to prevent non-unique LU names from multiple application regions. If NETOPT=YES and MRO=YES are specified, an assembler MNOTE and a return code of 16 are produced from the assembly step. |
MRO={NO|YES}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| NAZPDO |
Note A A The Notes:
For more information on the use of this parameter contact your Adabas technical support representative. |
NAZPDO={0|offset}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| NETOPT |
If NETOPT=YES is specified, an 8-byte user ID will be constructed from the VTAM LU name. If NETOPT=NO is specified, the user ID is created from the constant "CICS" plus the four-byte CICS terminal ID (TCTTETI) for terminal tasks. For non-terminal tasks, the user ID comprises the constant "C" plus the CICS task number, in zoned decimal format, including leading zeroes. If you run with the CICS multiple region option (MRO), you must use the default value for this option. If NETOPT=YES and MRO=YES are specified, an assembler MNOTE and a return code of 16 are produced from the assembly step. |
NETOPT={NO|YES}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| NTGPID |
Specifies a four-byte Natural group ID as required for unique Adabas user ID generation in the CICS sysplex environment with Natural Version 2.2 SP8 and above. The value is associated with all users who call the Adabas command-level link routine assembled with the specified value. There is no default value. If no value is specified, the Adabas internal user ID is built in the conventional manner. Any four-byte alphanumeric value may be specified, but it must be unique for each Adabas command-level link routine running in a CICS sysplex, or z/OS image. If more than one NTGPID is required (for example, both test and production Natural 2.2 SP8), more than one Adabas command-level link routine with associated TRUE must be generated. If you run with the CICS multiple region option (MRO), you may use NTGPID to provide a 4-byte literal for the Adabas communication ID to be used by the Adabas SVC when multiple application regions call Adabas. |
NTGPID=4-byte-value |
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| NUBS |
The number of user blocks (UBs) to be created in the user block pool by the CICS link routine. The number of blocks must be large enough to handle the maximum possible number of concurrent Adabas requests. Note |
NUBS={100|blocks}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| OPSYS |
The operating system in use. |
OPSYS={ZOS}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| PARMTYP |
The CICS area which is to contain the Adabas parameter list. "TWA" picks up the parameter list in the first six fullwords of the transaction work area (TWA). When PARMTYP=COM, the Adabas parameters are supplied in the CICS COMMAREA provided by the calling program with the EXEC CICS LINK command. The COMMAREA list for an ACB call must be at least 32 bytes long and begin with the label "ADABAS52". The COMMAREA list for an ACBX call must be at least 24 bytes long and begin with the label "ADABAS8X". In addition, the last ABD in the COMMAREA list for an ACBX call must be indicated by setting the VL-bit -- in other words, the high bit in the address must be on (X'80'). PARMTYP=ALL (the default) uses both the COMMAREA and TWA to pass the Adabas parameters; in this case, the COMMAREA is checked first. We do not recommend that you attempt to map the CICS TWA to an Adabas ACBX direct call. This is because the TWA is of finite size per transaction and because the TWA is not available at CICS startup. We therefore recommend that CICS programs use the COMMAREA only for passing data. |
PARMTYP={ALL|COM |TWA}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| PRE |
The two-byte string to be used as the DSECT data prefix. The default is "LG". |
PRE={LG|prefix}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| PURGE |
The PURGE parameter is used when assembling with CICS 3.2 or above. If PURGE=YES is specified, the CICS WAIT EXTERNAL will contain PURGEABLE as one of its parameters, allowing the transaction to be purged by CICS if the DTIMOUT value is exceeded and PURGE is specified. If PURGE=NO (the default) is specified, the NONPURGEABLE option is generated. |
PURGE={NO|YES}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| RENT |
Indicates whether the globals module is reentrant. |
RENT={NO|YES}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| RETRYX |
Indicates whether the retry command exit is active. |
RETRYX={NO|YES}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| REVHID | Specifies the preferred Adabas Review hub ID. This value can be
checked during the Adabas TP monitoring installation or during the monitor activate
process.
If REVHID is set to zero (0), the preferred Adabas Review hub ID is dynamic. When the hub ID is dynamic, it cannot be checked during the Adabas TP monitoring installation and the call to turn on client reporting must supply the correct Adabas Review hub ID to use. If REVHID is specified, REVIEW=YES must also be specified. If REVHID is specified and REVIEW=NO is also specified, the assembly of the globals table will abort with condition code 16 and the following message is given: REVHID requires REVIEW=YES |
REVHID=hubid |
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| REVIEW |
Indicates whether or not Software AG’s Adabas Review performance monitor is to be activated for the link module(s) using this link globals table.
|
REVIEW={NO|YES|COR}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| REVREL |
This parameter is redundant and will be dropped in a future Adabas version. Please remove any use of this parameter from your LGBLSET input. Continued use of this parameter will result in the following informational MNOTE message: REVREL= is redundant and is no longer required. The assembly of the globals table is unaffected. |
REVREL={}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| RMI |
The RMI parameter is used to indicate whether or not the CICS Resource Manager Interface is in use. If RMI=YES is specified, the Adabas task-related user exit (TRUE) will be executed as a resource manager (RM) using the CICS Resource Manager Interface (RMI). RMI=YES is valid only when the Adabas Transaction Manager is installed, enabled, and available to users executing in the CICS environment. Consult the Adabas Transaction Manager documentation for additional instructions related to the installation and use of the CICS Resource Manager Interface. |
RMI={NO|YES}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| RST1BDB |
Note For ACB calls using a single-byte DBID, this parameter determines if the DBID supplied in the first byte of the ACBFNR field is restored before returning the completed call to the application If RST1BDB is NO (the default), the DBID will not be restored. If RST1BDB is YES, the DBID will be restored. |
RST1BDB={NO|YES}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| RTXNAME |
The name of the command retry exit module. |
RTXNAME={LUEXRTR|name}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| RVCLNT |
Indicates whether Adabas Review client reporting should be allowed and available for activation. RVCLNT=YES requires REVIEW=YES and indicates Adabas Review client reporting is allowed and available for the manual activation of all clients. Refer to the Adabas Review documentation for the means of activation. RVCLNT=COR requires REVIEW=YES or COR and is only applicable to clients running with the Adabas System Coordinator. RVCLNT=COR indicates Adabas Review client reporting is allowed and activation is deferred to the setting of the Adabas System Coordinator’s client runtime control ‘Client Monitor’. Refer to the Adabas System Coordinator documentation for more information on this client runtime control. |
RVCLNT={NO|YES|COR}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| SAF |
Indicates whether Software AG's Adabas SAF Security support is required. In CICS environments only, if you want your security system user IDs to be stored in Adabas user queue elements (making them available for display and review as well as preventing response code 200, ADARSP200, subcode 21 when ADARUN SECUID=REQUIRE is in effect for Adabas), you must code the SAF parameter as YES. This is only required in CICS environments; in other environments, the security system user IDs are automatically stored. |
SAF={NO|YES}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| SAP |
Indicates whether or not SAP user ID generation is supported. If SAP=YES is specified, the program will detect a SAP initialization call and set the user ID for SAP applications from the constant provided on the initialization call, plus the field ACBADD2. For more information, refer to the supplementary information provided to customers using the SAP application system. |
SAP={NO|YES}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| SAPSTR |
The four-byte SAP ID string to use. |
SAPSTR={'SAP*'|string}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| SVCNO |
The value of the Adabas SVC number. Valid values range from 200-255 and the default is "249". |
SVCNO=nnn |
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| TCPIP |
Indicates whether communication using TCP/IP sockets is supported. If TCPIP=YES then communication to any database registered in the Adabas Directory Server will be performed using TCP/IP sockets. |
TCPIP={NO|YES}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| TPMON |
The TP monitor operating environment. Valid values should be specified as follows:
Warning |
TPMON={BAT|CICS|COM|IMS}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| TRUENM |
Specifies the module name of the Adabas CICS task-related user exit (TRUE). The default is ADACICT. |
TRUENM={ADACICT|name}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| UBPLOC |
Specifies whether the user block (UB) pool is to be obtained above (the default) or below the 16-megabyte line in CICS. The ECB used by the EXEC CICS WAIT WAITCICS or the EXEC CICS WAIT EXTERNAL is included in the UB pool. The UBPLOC=BELOW setting supports versions of CICS that do not allow ECBs above the 16-megabyte line; that is, CICS/ESA 3.2 or below. Refer to the IBM manual CICS Application Programming Reference for more information. |
UBPLOC={ABOVE|BELOW}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| UBSTIME |
Specifies the user block (UB) scan time in fat seconds. A fat second is the interval required to change bit-31 of the doubleword set by an STCK instruction. The default is 1800 seconds. This parameter sets the minimum interval at which the Adabas task-related user exit (TRUE) will decide that a user block entry in the user block pool is eligible for release, if (for some reason) the user block entry was not released by normal Adabas CICS processing. Thus, UBSTIME=1800 indicates that a locked user block entry will be released by the Adabas TRUE if more than 1800 fat seconds have elapsed since the user block entry was locked for an Adabas call. The value of UBSTIME should be set higher than the Adabas CT (transaction time) ADARUN parameter. An ADAM93 message indicating either a post failure or a missing 16 call is likely to occur around the time the user block entry is released or prior to the user block entry's release if the Adabas CT timeout value has been exceeded. Note |
UBSTIME={seconds|1800}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| UBTYPE |
Identifies the kind of user block (UB) storage the Adabas CICS installation program and Adabas task-related user exit (TRUE) should obtain and use. Valid values are TASK and POOL. POOL is the default. UBTYPE=POOL causes the installation program to obtain a pool of user blocks in CICS storage. This is the classic mechanism used by Adabas CICS link routines. UBTYPE=TASK changes the behavior of the Adabas CICS installation program and Adabas TRUE so they obtain a single user block element, including any required extensions for user data and Software AG products, for each CICS task that invokes the Adabas TRUE. The user block is obtained in CICS shared storage in user-key. It is released when the Adabas TRUE is driven by CICS at the end of the CICS task. The advantage of UBTYPE=TASK is that there is no scan time required to locate and lock a given UB pool element on each Adabas call. The disadvantages of using UBTYPE=TASK are that a CICS GETMAIN must be issued for each CICS task the first time the Adabas TRUE is invoked for the task and that a CICS FREEMAIN must be issued to release the user block storage at the end of the CICS task. UBTYPE=POOL should be used if any of the following are true:
Otherwise, UBTYPE=TASK may be considered if:
|
UBTYPE={POOL|TASK}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| UES |
Indicates whether or not Universal Encoding Support (UES) is required. |
UES={NO|YES}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| USERX1 |
Indicates whether or not user exit 1 is active. |
USERX1={NO|YES}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| USERX2 |
Indicates whether or not user exit 2 is active. |
USERX2={NO|YES}
|
| Parameter | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| XWAIT |
Indicates whether a standard EXEC CICS WAITCICS (XWAIT=NO) or a WAIT EVENTS EXTERNAL (XWAIT=YES) will be executed by the Adabas task-related user exit (TRUE). XWAIT=YES is the default. The CICS WAIT EVENTS EXTERNAL (XWAIT=YES) is the recommended interface for all supported versions of CICS/TS. The CICS WAITCICS statement (XWAIT=NO) is provided but may result in poor CICS transaction performance or unpredictable transaction results in busy CICS environments. |
XWAIT={NO|YES}
|
Notes:
CICS WAITCICS (XWAIT=NO) can support a soft post of the specified ECB. This has the disadvantage of becoming a low priority dispatchable unit of work in a CICS environment, since the hand-postable work is not processed by CICS on every work cycle.
EXEC CICS WAIT EXTERNAL (XWAIT=YES), on the other hand, allows CICS to make use of its special post exit code, and will always be checked and processed (if posted) on every CICS work cycle.
For more details on the differences between the various CICS WAIT commands and their relationship to hard and soft posting mechanisms, consult the IBM CICS Application Programming Reference and the texts accompanying IBM APAR PN39579 or “Item RTA000043874” on the IBM InfoLink service.
The Adabas SVC is fully compatible with the XWAIT=YES setting. The SVC performs the necessary hard post for Adabas callers under CICS using the Adabas command-level link routine. The same SVC performs a soft post for batch callers where the hard post is not required.