 To maintain the Kernel filter list:
To maintain the Kernel filter list:
Make sure you have accessed the System Management Hub.
Select the name of the managed host on which Entire Net-Work Server is installed.
Expand the tree-view frame for the managed host by clicking on the plus sign (+) to the left of its name.
Select "Entire Net-Work Server" in the tree-view under the managed host.
The Entire Net-Work Server administration area of the System Management Hub becomes available to you.
Expand Servers in tree-view, by clicking on the plus sign (+) to the left of its label.
The list of installed servers appears.
Expand the name of the server in the server list in tree-view, by clicking on the plus sign (+) to the left of its label.
A list of Kernels defined to the server appears.
In tree-view, right-click on the name of the Kernel for which you want to specify the Kernel filter list and select the command from the resulting drop-down menu.
The Kernel Filters panel appears in detail-view.
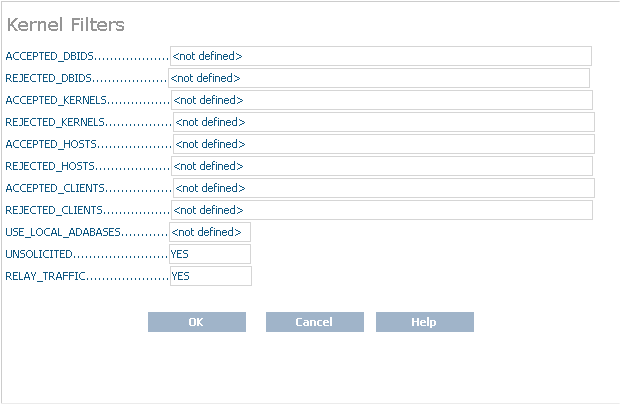
Modify the parameters on the Kernel Filters panel, as described in the following table. When all parameters are set as you want, click to save them.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| ACCEPTED_DBIDS | Specify the database IDs
for which service requests should be processed by this Kernel. If more than one
database ID is needed, separate them with commas. If a range of database
numbers is needed, separate them with a dash. For example,
"4,12-15,62" indicates that the Kernel should
process service requests to databases 4, 62, and any databases with numbers
between 12 and 15 (inclusive). For more information, read
Understanding
Filtering.
If no databases are listed in the ACCEPTED_DBIDS field, the Kernel will process all requests to all databases defined in the Adabas Directory Server, except those listed in the REJECTED_DBIDS field. |
| REJECTED_DBIDS | Specify the database IDs
for which service requests should not be processed by this Kernel. If
more than one database ID is needed, separate them with commas. If a range of
database numbers is needed, separate them with a dash. For example,
"4,12-15,62" indicates that the Kernel should
not process service requests to databases 4, 62, and any databases
with numbers between 12 and 15 (inclusive). For more information, read
Understanding
Filtering.
If no databases are listed in the REJECTED_DBIDS field, the Kernel will process all requests to all databases defined in the Adabas Directory Server, unless a specific list is provided in the ACCEPTED_DBIDS field. |
| ACCEPTED_KERNELS | Specify the Kernel names for which
service requests should be processed by this Kernel. If more than one Kernel
name is needed, separate them with commas. For more information, read
Understanding
Filtering.
If the UNSOLICITED advanced Kernel parameter is set to "YES", any Kernel can submit service requests to this Kernel, except Kernels listed in the REJECTED_KERNELS filter parameter on the Kernel filter list. If the UNSOLICITED advanced Kernel parameter is set to "NO", all unsolicited Kernel service requests are ignored, except for the Kernels listed in the ACCEPTED_KERNELS filter parameter on the Kernel filter list. For complete information about the Kernel filter list, read Maintaining the Kernel Filter List. |
| REJECTED_KERNELS | Specify the Kernel names for which
service requests should not be processed by this Kernel. If more than
one Kernel name is needed, separate them with commas. For more information,
read Understanding
Filtering.
If the UNSOLICITED advanced Kernel parameter is set to "YES", any Kernel can submit service requests to this Kernel, except Kernels listed in the REJECTED_KERNELS filter parameter on the Kernel filter list. If the UNSOLICITED advanced Kernel parameter is set to "NO", all unsolicited Kernel service requests are ignored, except for the Kernels listed in the ACCEPTED_KERNELS filter parameter on the Kernel filter list. For complete information about the Kernel filter list, read Maintaining the Kernel Filter List. |
| ACCEPTED_HOSTS | Specify the host machine names from and to which service requests should be processed by this Kernel. If more than host machine name is needed, separate them with commas. For more information, read Understanding Filtering. |
| REJECTED_HOSTS | Specify the host machine names from and to which service requests should not be processed by this Kernel. If more than host machine name is needed, separate them with commas. For more information, read Understanding Filtering. |
| ACCEPTED CLIENTS | Specify the Entire Net-Work Client names from which service requests should be processed by this Kernel. If more than Entire Net-Work Client name is needed, separate them with commas. For more information, read Understanding Filtering. |
| REJECTED CLIENTS | Specify the Entire Net-Work Client names from which service requests should not be processed by this Kernel. If more than Entire Net-Work Client name is needed, separate them with commas. For more information, read Understanding Filtering. |
| USE_LOCAL_ADABASES | Indicate whether local Adabas databases should be used for this Kernel. Valid values are "YES" and "NO"; the default is "YES". If you only wanted this Kernel to relay calls to other Kernels on other machines and ignore the databases on the local machine, you would set this parameter to "NO". This might be useful in a test situation. |
| UNSOLICITED | Indicate whether or not
this Kernel will process service requests from other Kernels it has not
included in its Kernel filter list. Valid values are
"YES" and "NO", with
"YES" being the default.
If "YES" is specified, any Kernel can submit service requests to this Kernel, except Kernels listed in the REJECTED_KERNELS filter parameter on the Kernel filter list. If "NO" is specified, all unsolicited Kernel service requests are ignored, except for the Kernels listed in the ACCEPTED_KERNELS filter parameter on the Kernel filter list. For complete information about the Kernel filter list, read Maintaining the Kernel Filter List. |
| RELAY_TRAFFIC | Indicate whether this
Kernel should relay requests to other Kernels in the network.
If the value of the RELAY_TRAFFIC field is "YES", requests to other Kernels in the network are relayed. If RELAY_TRAFFIC is set to "NO", requests are not relayed. The default is "YES". For more information, read Understanding Filtering. |
The Kernel filters are updated in the appropriate Kernel definition file. You must restart the Kernel in order for these Kernel filter changes to take effect.