The EntireX z/VSE Batch RPC Server allows standard RPC clients to communicate with RPC servers on the operating system z/VSE under Batch. It supports the programming language COBOL and works together with the COBOL Wrapper and IDL Extractor for COBOL.
This document covers the following topics:
The name of the delivered example configuration file is RPCPARM.CFG (see sublibrary EXP960).
The configuration file contains the configuration for the Batch RPC Server.
The following settings are important:
connection information such as broker ID, server address (class, name, service)
location and usage of server-side mapping container, see Usage of Server Mapping Files
scalability parameters
trace settings
etc.
For more information see Configuring the RPC Server.
The following rules apply:
In the configuration file:
Comments must be on a separate line.
Comment lines can begin with '*', '/' and ';'.
Empty lines are ignored.
Headings in square brackets [<topic>] are ignored.
Keywords are not case-sensitive.
Underscored letters in a parameter indicate the minimum number of letters that can be used for an abbreviated command.
For example, in brokerid=localhost,
brok is the minimum number of letters that
can be used as an abbreviation, i.e. the commands/parameters broker=localhost
and brok=localhost are equivalents.
| Parameter | Default | Values | Req/ Opt |
||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
brokerid |
localhost |
Broker ID used by the server. See Using the Broker ID in Applications.
Example: |
R | ||||||||||||||||
class |
RPC |
Server class part of the server address used by the
server. The server address must be defined as a service in the broker attribute file (see Service-specific Attributes under Broker Attributes).
Case-sensitive, up to 32 characters. Corresponds to CLASS.
Example: |
R | ||||||||||||||||
codepage |
Depending on the internationalization approach, the codepage (locale string)
where incoming data is provided to the COBOL server. Conversely, the COBOL server must provide outgoing data in the
given codepage, otherwise unpredictable results occur. See What is the Best Internationalization Approach to use? under Internationalization with EntireX for information
on which internationalization approach requires a codepage (locale string).
By default, no codepage is transferred to the broker. For the most popular internationalization approach, ICU Conversion, the correct codepage (locale string) must be provided. This means it must:
Example: |
||||||||||||||||||
compresslevel |
N |
Enforce compression when data is transferred between
broker and server. See Data Compression in EntireX Broker.
Example: |
O | ||||||||||||||||
deployment |
NO |
Activates the deployment service, see Deployment Service. Required to
use the Server Mapping Deployment Wizard. See Server Mapping Deployment Wizard in the EntireX Workbench documentation.
Example: |
O | ||||||||||||||||
encryptionlevel |
0 | Deprecated. For encrypted transport we strongly recommend using the Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security protocol. See SSL/TLS and Certificates with EntireX. | O | ||||||||||||||||
etblnk |
BKIMB |
Define the broker stub to be used. See Administration of Broker Stubs under z/VSE for available stubs.
Example: |
O | ||||||||||||||||
logon |
YES |
Execute broker functions LOGON/LOGOFF in worker
threads. Must match the setting of the broker attribute
AUTOLOGON. Reliable RPC requires logon set to YES. See Reliable RPC.
Example: |
O | ||||||||||||||||
marshalling |
COBOL |
|
O | ||||||||||||||||
password |
no default | Password for broker logon. Case-sensitive, up to 32
characters. For more information see broker ACI control block field
PASSWORD.
Example: |
O | ||||||||||||||||
restartcycles |
15 | Number of restart attempts if the broker is not
available. This can be used to keep the Batch RPC Server running while
the broker is down for a short time. A restart cycle will be
repeated every 60 seconds.
When the number of cycles is reached and a connection to the broker is not possible, the RPC server stops. Example: |
O | ||||||||||||||||
runoption |
no default | This parameter is for special purposes. It provides the Batch RPC Server with additional information.
The runoptions are normally set to meet the platform's requirements. Set this parameter only if a support representative
provides you with an option and asks you to do so. The parameter can be defined multiple times.
Example: |
O | ||||||||||||||||
servername |
SRV1 |
Server name part of the server address used by the server.
The server address must be defined as a service in the broker attribute file.
See Service-specific Attributes under Broker Attributes.
Case-sensitive, up to 32 characters.
Corresponds to SERVER of the broker attribute file.
Example: |
R | ||||||||||||||||
service |
CALLNAT |
Service part of the server address used by the server.
The server address must be defined as a service in the broker attribute file.
See Service-specific Attributes under Broker Attributes.
Case-sensitive, up to 32 characters.
Corresponds to SERVICE attribute of the broker attribute file.
Example: |
R | ||||||||||||||||
smhport |
0 | The port where the server listens for commands from
the System Management Hub (SMH). If this port is 0 (default), no port is used and
management by the SMH is disabled.
Example: |
O | ||||||||||||||||
svm |
ERXSVM |
Usage and location of server-side mapping files; see Server-side Mapping Files in the RPC Server.
If no svm parameter is given, the RPC server tries to open the
server-side mapping container using DLBL name ERXSVM.
If this DLBL name is not available, no server-side mapping files are used.
If you use server-side mapping files, the server-side mapping container must be installed and configured;
see Step 3: Customize the Batch RPC Server Startup JCL - RUNRPC.J in the z/VSE Installation documentation.
There are also client-side mapping files that do not require configuration here; see
Server Mapping Files in the EntireX Workbench in the EntireX Workbench documentation.
Example: For the example above, define the DLBL name // DLBL MYSVM,'ENTIREX.SVMDEV.KSDS',0,VSAM,CAT=VSESPUC See also Usage of Server Mapping Files. |
O | ||||||||||||||||
timeout |
60 | Timeout in seconds,
used by the server to wait for broker requests. See broker ACI control block field
WAIT for more information. Also influences restartcycles.
Example: |
O | ||||||||||||||||
tracelevel |
None |
Trace level for the server. See also Activating Tracing for the RPC Server.
tracelevel = None | Standard | Advanced | Support
Example: |
O | ||||||||||||||||
userid |
ERX-SRV |
Used to identify the server to the broker.
See broker ACI control block field USER-ID.
Case-sensitive, up to 32 characters.
Example: |
R | ||||||||||||||||
workermodel |
SCALE,1,3,slowshrink |
|
O | ||||||||||||||||
The IDL library and IDL program
names that come from RPC client are used to locate the RPC server.
See library-definition and program-definition.
This two-level concept (library and program) has to be mapped to the Batch RPC Server environment.
Different mechanisms are used depending on the language:
The approach used to derive the z/VSE module name for the RPC server depends on whether server mapping is used or not. See Usage of Server Mapping Files for an introduction.
If the RPC client sends a client-side type of server mapping with the RPC request, this server mapping is used first.
If no server mapping is available from step 1 above, and if server-side type of server mapping is used, the IDL library and IDL program names are used to form a key to locate the server mapping in the server-side mapping container. If a server mapping is found, this is then used.
If a server mapping is available from step 1 or 2 above, the z/VSE module name of the RPC server is derived from this mapping. In this case the IDL program name can be different to the z/VSE module name if it is renamed during wrapping process (see Customize Automatically Generated Server Names) or during the extraction process in the COBOL Mapping Editor.
If no server mapping is used at all, the IDL program name is used as the z/VSE module name of the RPC server (the IDL library name is ignored).
![]() To use the Batch RPC Server with COBOL
To use the Batch RPC Server with COBOL
Make sure that all z/VSE modules called as RPC servers
are compiled with IBM's Language Environment (see LE/VSE V1R4 Programming Guide for more information)
use COBOL calling conventions
can be called dynamically ("fetched") from any Language Environment program
are accessible through the Batch RPC Server JCL LIBDEF chain.
Configure the parameter marshalling for COBOL, for example:
marshalling=COBOL
Configure the parameter svm depending on whether
server-side mapping files are used or not. See Usage of Server Mapping Files.
See also Scenario I: Calling an Existing COBOL Server or Scenario II: Writing a New COBOL Server.
The approaches needed to derive the names for the Batch RPC Server are more complex for C, for the following reasons:
the limitation of characters per (physical) member name
the maximum length of 128 characters per IDL library name. See Rules for Coding Library, Library Alias, Program, Program Alias and Structure Names under Software AG IDL File in the IDL Editor documentation.
You need to restrict yourself to short IDL library names.
![]() To use the Batch RPC Server with C
To use the Batch RPC Server with C
Configure the parameter marshalling for C, for example
marshalling=C
See Using the C Wrapper for the Server Side (z/OS, UNIX, Windows, BS2000/OSD, IBM i).
RPC servers can use Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS) as the transport medium. The term "SSL" in this section refers to both SSL and TLS. RPC-based servers are always SSL clients. The SSL server can be either the EntireX Broker, Broker SSL Agent, or Direct RPC in webMethods Integration Server (IS inbound). For an introduction see SSL/TLS and Certificates in the Security documentation.
Establishing an SSL connection on z/VSE requires BSI's Automatic Transport Layer Security (ATLS). This facility is similar to z/OS Application Transparent - Transport Layer Security (AT-TLS). ATLS is supported by the BSI stack only.
Together with SSL parameters (to provide certificates), define ATLS rules for socket interception in the ATLS daemon startup
job BSTTATLS ![]() .
If the rules match, the socket connection is turned into an SSL connection
.
If the rules match, the socket connection is turned into an SSL connection ![]() .
Refer to your IBM documentation for further information. For an overview, refer to the IBM Redbook Enhanced Networking on IBM z/VSE; for a more detailed description, refer to BSI SSL Installation, Programming and User's Guide.
.
Refer to your IBM documentation for further information. For an overview, refer to the IBM Redbook Enhanced Networking on IBM z/VSE; for a more detailed description, refer to BSI SSL Installation, Programming and User's Guide.
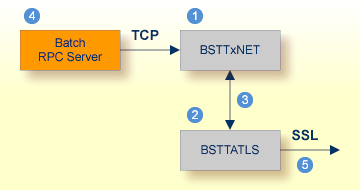
| BSI TCP/IP Stack, either BSTTINET (IPv4) or BSTT6NET (IPv6). | |
| ATLS rules are defined manually. See Sample ATLS Daemon Configuration below. | |
| BSTTATLS is associated with a TCP/IP stack. | |
| Application using TCP connection. | |
| BSTTATLS intercepts outbound TCP connection and converts it to SSL connection. For inbound, SSL connections can also be intercepted and converted to TCP connections. |
![]() To set up SSL with ATLS
To set up SSL with ATLS
To operate with SSL, certificates need to be provided and maintained. Depending on the platform, Software AG provides default certificates, but we strongly recommend that you create your own. See Default Certificates Delivered with EntireX under SSL/TLS and Certificates with EntireX in the Security documentation.
Set up the Batch RPC Server for a TCP/IP connection. On mainframe platforms, use Transport-method-style Broker ID. Example:
ETB024:1699:TCP
Configure ATLS to turn the TCP/IP connection to an SSL connection, see above.
Make sure the SSL server to which the Batch RPC Server connects is prepared for SSL connections as well. The SSL server can be EntireX Broker, Broker SSL Agent, or Direct RPC in webMethods Integration Server (IS inbound). See:
![]() To start the Batch RPC Server
To start the Batch RPC Server
Run the job RPCRPC.J.
![]() To stop the Batch RPC Server
To stop the Batch RPC Server
Use the console command STOP. For example:
task_id STOPOr:
Use the System Management Hub. This method ensures that the deregistration from the Broker is
correct.
![]() To activate tracing for the Batch RPC Server
To activate tracing for the Batch RPC Server
Set the parameter tracelevel.
Dynamically change the trace level with the operator command
port_numberTRACELEVEL=tracelevel
See the table below for supported trace levels.
The TRACELEVEL command without tracelevel option will report the
currently active trace.