The EntireX z/OS Batch RPC Server allows standard RPC clients to communicate with RPC servers on the operating system z/OS running in batch mode. It supports the programming languages COBOL, PL/I and C.
This document covers the following topics:
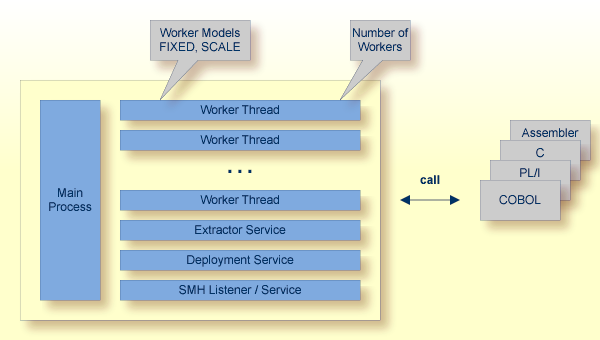
RPC requests are worked off inside the RPC server in worker threads, which are controlled by a main thread. Every RPC request occupies during its processing a worker thread. If you are using RPC conversations, each RPC conversation requires its own thread during the lifetime of the conversation. The Batch RPC Server provides two worker models:
FIXED
The fixed model creates a fixed number of worker threads.
The number of worker threads does not increase or decrease during the lifetime of an RPC server instance.
SCALE
The scale model creates worker threads depending on the incoming load of RPC requests.
A maximum number (thru value of the workermodel parameter)
of worker threads created can be set to restrict the system load.
The minimum number (from value of the workermodel parameter),
allows you to define a certain number of threads - not used by the currently executing RPC request -
to wait for new RPC client requests to process.
In this way the RPC server is ready to handle many RPC client requests arriving at the same time.
See parameter workermodel under Configuring the RPC Server.
Batch RPC Server provides several services for ease-of-use:
The Extractor Service is a prerequisite for remote extractions with the IDL Extractor for COBOL and IDL Extractor for PL/I. See Extractor Service for more information.
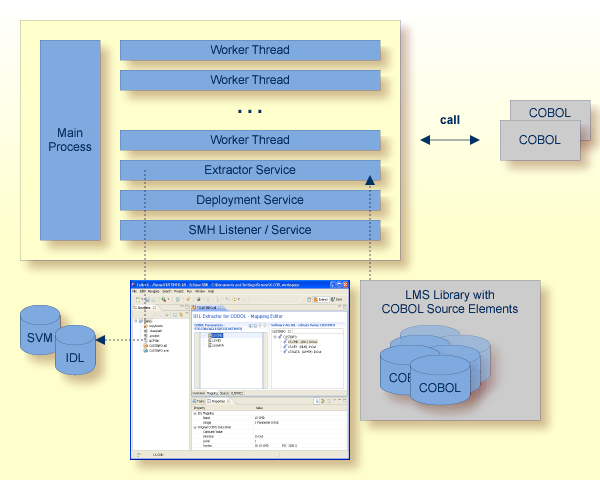
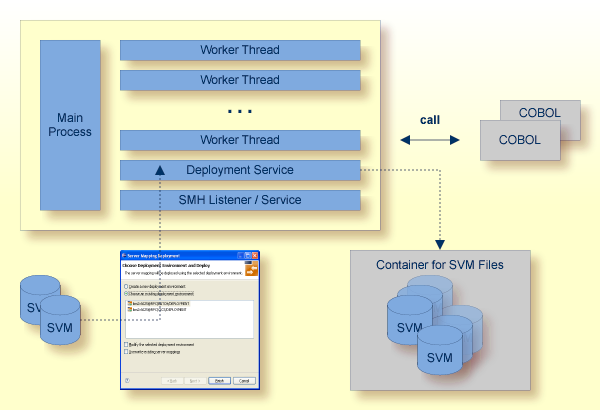
The Deployment Service allows you to deploy server mapping files (SVM files) interactively using the Deployment Wizard (see Server Mapping Deployment). On the RPC server side, the SVM files are stored in a VSAM file as the container. See Deployment Service for configuration information.
With the SMH Listener Service you use the System Management Hub to monitor the RPC server. See Administering the EntireX RPC Servers using System Management Hub under UNIX | Windows.
The SMH Service is switched on if the parameter smhport is set. See parameter smhport under Configuring the RPC Server.
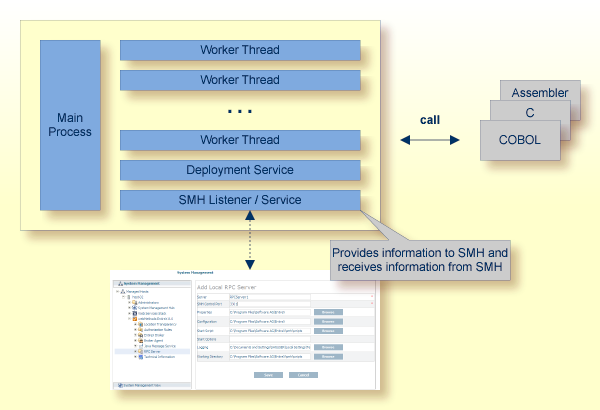
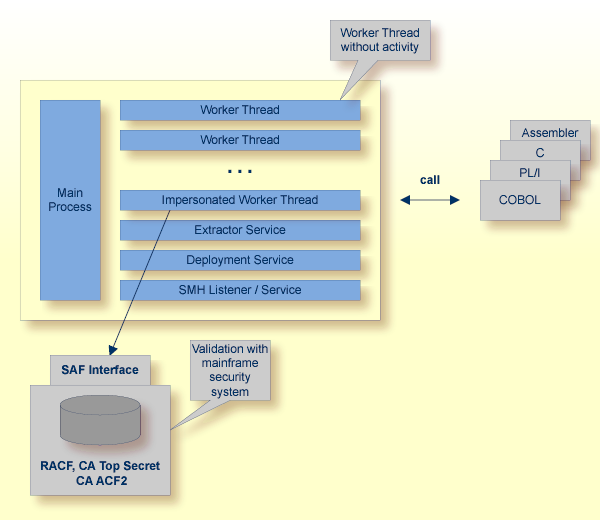
The Batch RPC Server can be configured to execute the RPC request impersonated under the RPC client user ID. This means that
for the request execution, the worker thread gets the identity of the RPC client.
This is necessary when accessing (security) protected data sets, for example with the Extractor Service.
The way authentication is carried out can be controlled by the RPC parameter impersonation.
For impersonation value AUTO, the Batch RPC Server does not validate RPC passwords, so you have to make sure the RPC client is
correctly authenticated, either by using a secure EntireX Broker (validation must be against the correct mainframe security
repository where z/OS user IDs are defined) or with your own security implementation.
For impersonation value YES, the Batch RPC Server uses the RPC user ID and password supplied by the RPC client for authentication and impersonation of
the client.
This means that the RPC server validates the password.
The picture above shows the configuration impersonation=yes.
The lifetime of an impersonated task starts when an open request for an RPC conversation or a non-conversational RPC request is received. It ends when the RPC conversation stops (after a commit operation or timeout) or when the non-conversational RPC request has been performed.
There are many situations where the Batch RPC Server requires a server mapping file to correctly support special COBOL syntax
such as JUSTIFIED,
SYNCHRONIZE and OCCURS DEPENDING ON clauses, LEVEL-88 fields, etc.
the .
SVM files contain COBOL-specific mapping information that is not included in the IDL file and therefore not sent by an EntireX RPC client to the RPC server. See also When is an SVM File Required? under SVM Files.
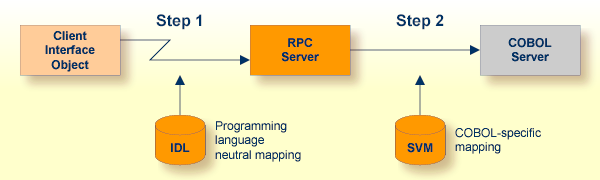
The RPC server marshalls the data in a two-step process: the RPC request coming from the RPC client (Step 1) is completed with COBOL-specific mapping information taken from the SVM file (Step 2). In this way the COBOL server can be called as expected.
The SVM files are retrieved as a result of the IDL Extractor for COBOL extraction process and the COBOL Wrapper if a COBOL server is generated.
You can customize the usage of the SVM file using parameter
svm. See Configuring the RPC Server.
Note:
SVM files are used for COBOL only.