The classes used by the importers are contained in the file
CentraSiteUtils.jar. The
CLASSPATH variable must refer to the JAR files
that are used by CentraSite. It is convenient to include all
JAR files contained in the redist
folder of the CentraSite installation.
After using an instance of the JAXRAccessor class
to establish a valid connection (with user and password) to CentraSite, one
or more imports are possible. Finally, close the session by calling the
close() method of
JAXRAccessor.
The following topics are discussed below:
The basic input when importing a web service is a WSDL file describing one or more services. There are also some setter methods for additional parameters. The organization (per object or per name) must be set; other parameters are optional.
The following example demonstrates how to register a web service to CentraSite:
import com.centrasite.jaxr.JAXRAccessor;
import com.centrasite.jaxr.webservice.WebServiceRegistrator;
String dbURL = "http://localhost:53307/CentraSite/CentraSite";
String organizationName = "MyOrganization";
String wsdlFile = "c:/temp/MyService.wsdl";
String user = ...;
String password = ...;
JAXRAccessor jaxr = new JAXRAccessor(dbURL, user, password);
try
{
WebServiceRegistrator wsr = new WebServiceRegistrator(wsdlFile, jaxr);
wsr.setOrganization(organizationName);
wsr.register();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
// handle error
}
finally
{
jaxr.close();
}
The WebServiceRegistrator class provides the
setter methods listed below. The setter methods must be called before calling
the register() method.
Sets a description text that will appear with the imported
Service object.
public void setDescription(String description)
The description text.
Optional.
Sets the name of the organization under which the service should be registered.
public void setOrganization(String organizationName)
The name of the organization.
Sets the organization object under which the service should be registered.
public void setOrganization(Organization organizationObject)
The organization object under which the service should be registered.
Sets the name of the registry package of which the service should be a member.
public void setPackageName(String packageName)
The name of the registry package of which the service should be a member.
Optional.
Sets the registry package object of which the service should be a member.
public void setPackageObject(RegistryPackage packageObject)
The registry package object of which the service should be a member.
Optional.
Sets a registry object that will point to the imported service with a "Uses" association; in other words, the imported service will be used by the specified object.
public void setUsedObject(RegistryObject usedObject)
The registry object that will point to the imported service.
Optional.
Sets a registry object that will be pointed to by the imported service with a "Uses" association; in other words, the imported service will use the specified object.
public void setUsesObject(RegistryObject usesObject)
The registry object that will be pointed to by the imported service.
Optional.
Changes the path of the folder where the WSDL file is stored in the CentraSite repository.
public void setWebDAVFolder(String folderPath)
The path of the folder where the WSDL file should be stored.
Default: /projects/WSDL.
Optional.
To update a registered web service (for example, when the WSDL file has
been modified or if you want to change the registry package that contains the
web service), call the register() method with the
modified WSDL file – see the example
above for details.
Note:
The key associated with a registered service comprises its
organization, its name and the WSDL file's targetNamespace. If you modify one
or more of these, the service is not updated; rather, a new registry entry is
created.
It is possible to attach a WSDL file to an existing web service. The code for attaching a WSDL file is similar to the code for importing a WSDL file. An example code snippet follows:
WebServiceRegistrator wr = new WebServiceRegistrator("attach.wsdl", jaxr);
wr.setAttachServiceID("uddi...");
wr.register();
where "uddi..." denotes the UDDI key of the service to
which the WSDL file should be attached.
Note the following:
The service can be a manually-created service.
If the service has already been registered with a WSDL, then calling
setAttachServiceID updates the registered
information.
If there are any services within the WSDL, they are registered as usual.
If the service has a ServiceBinding that is not in the WSDL, it is retained.
If the service has a ServiceBinding that is in the WSDL, it is updated. Operations are never deleted.
The WebServiceRegistrator class provides the
setter method listed below (in addition to the
setter methods described under Importing
a Web Service). The setter method must be called before calling the
register() method.
Sets a Service ID (getKey().getId()) for a
WSDL-service attachment.
public final void setAttachServiceID(java.lang.String attachServiceID)
The ID of the service, in the form "uddi:...".
Use the functions described below to remove a registered web service and all its resources, including all associated registry objects and the WSDL file in the CentraSite repository.
You must use an instance of the JAXRAccessor
class to establish a CentraSite connection before calling the
removeService or
removeServiceByID function. Finally, close the session
by calling the close() method of
JAXRAccessor.
Also before calling the removeService or
removeServiceByID function, you may call setter
functions, which are also described below.
The following example demonstrates how to remove a web service from CentraSiteCentraSite:
import com.centrasite.jaxr.JAXRAccessor;
import com.centrasite.jaxr.webservice.WebServiceAdministrator;
String dbURL = "http://localhost:53307/CentraSite/CentraSite";
String wsdlFile = "c:/temp/MyService.wsdl";
String user = ...;
String password = ...;
JAXRAccessor jaxr = new JAXRAccessor(dbURL, user, password);
try
{
WebServiceAdministrator wsa = new WebServiceAdministrator(jaxr);
int removeCount = wsa.removeServices(wsdlFile);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
// handle error
}
finally
{
jaxr.close();
}
The WebServiceAdministrator class provides the
methods shown below:
Removes the service specified by the unique name and namespace.
public boolean removeService(String serviceName, String namespace)
The name of the service to be removed.
The namespace of the service to be removed.
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| true | The specified service was successfully found and removed; |
| false | otherwise. |
Removes from CentraSite all services that are indicated by the specified WSDL file.
public int removeServices(String wsdlFilename)
The name of the WSDL file that indicates the services to be removed.
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| int | The number of services that were removed. |
Removes the service with the specified ID.
public boolean removeServiceByID(String serviceID)
The ID of the service to be removed. The ID is the
getKey().getID() value of the associated service
object.
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| true | The specified service was successfully found and removed; |
| false | otherwise. |
Specifies whether or not to delete associations to the service object where the service object is the target of the association. If the parameter is "false" and the service object is the target of one or more associations, the removal of the service object is inhibited.
public void setDeleteTargetAssocs(boolean deleteTargetAssocs)
true: Delete associations to the service object where the service object is the target of the association.
Default: true.
Specifies whether or not to remove from the repository referenced imported WSDL and schema files, together with their controlling ExternalLinks.
public void setRemoveReferencedImports(boolean removeReferencedImports)
true: Remove the referenced imported WSDL and schema files.
Specifies whether or not the WSDL file together with its controlling ExternalLink should also be removed from the repository.
public void setRemoveWsdl(boolean removeWsdl)
true: Remove the WSDL file together with its controlling ExternalLink from the repository.
Default: true.
The Web Service API provides functions with which you can find a registered web service. The following example demonstrates this:
import com.centrasite.jaxr.JAXRAccessor;
import com.centrasite.jaxr.webservice.WebServiceAdministrator;
String dbURL = "http://localhost:53307/CentraSite/CentraSite";
String wsdlFile = "c:/temp/MyService.wsdl";
String user = ...;
String password = ...;
JAXRAccessor jaxr = new JAXRAccessor(dbURL, user, password);
try
{
WebServiceAdministrator wsa = new WebServiceAdministrator(jaxr);
Collection services = wsa.findWebServices(wsdlFile); // Service object coll.
. . .
}
catch (Exception e)
{
// handle error
}
finally
{
jaxr.close();
}
The WebServiceAdministrator class provides the
methods shown below:
Finds the registered web service on the basis of its name and namespace.
public Service findWebServiceByNamespace(String serviceName, String namespace)
The name of the registered web service.
The namespace of the registered web service.
Finds a collection of web service objects that are registered with the specified organization in the specified WSDL file.
public Collection findWebServices(String organizationName, String wsdlFile)
The name of the organization.
The filepath to the WSDL file.
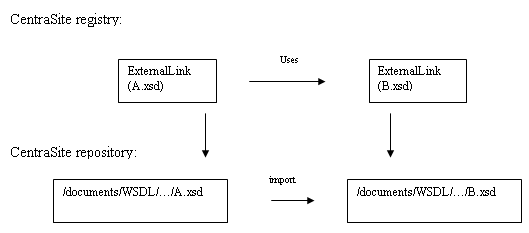
The schema importer works closely together with the web service importer. Since a WSDL file of a web service may import or include schema files, CentraSite enables you to design and store a schema before referencing WSDL files. Similarly, if a schema file is imported by more than one WSDL file, it could be beneficial to register the schema first, before registering the WSDL files. When a schema is imported, the file is copied into the CentraSite repository and an ExternalLink that controls the resource is created. If a schema imports (includes) further schemas, then the referenced schemas are also imported. The referenced relations are established by means of a "Uses" association in the registry. The following picture illustrates the relationship:
The following example demonstrates how to import a schema file into CentraSite:
import com.centrasite.jaxr.JAXRAccessor;
import com.centrasite.jaxr.schema.SchemaImporter;
String dbURL = "http://localhost:53307/CentraSite/CentraSite";
String xsdFile = "c:/temp/MySchema.xsd";
String user = ...;
String password = ...;
JAXRAccessor jaxr = new JAXRAccessor(dbURL, user, password);
try
{
SchemaImporter si = new SchemaImporter(xsdFile, jaxr);
si.add();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
// handle error
}
finally
{
jaxr.close();
}
You can remove a schema from CentraSite. This function deletes the XML Schema object, the ExternalLink and the resource in the repository.
Note:
If a schema is referenced by another object, for example if it is
referenced by the ExternalLink of a WSDL object, then it cannot be
deleted.
The following example demonstrates how to remove a schema from CentraSite:
import com.centrasite.jaxr.JAXRAccessor;
import com.centrasite.jaxr.schema.SchemaAdministrator;
import javax.xml.registry.infomodel.ExternalLink;
String dbURL = "http://localhost:53307/CentraSite/CentraSite";
String user = ...;
String password = ...;
ExternalLink schemaExtLink = ...;
JAXRAccessor jaxr = new JAXRAccessor(dbURL, user, password);
try
{
SchemaAdministrator sa = new SchemaAdministrator(jaxr);
sa.remove(schemaExtLink);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
// handle error
}
finally
{
jaxr.close();
}
The SchemaAdministrator class provides the
following methods for removing a schema:
Removes the schema at the specified location in the CentraSite repository, which may be relative or absolute.
public boolean remove(String schemaLocation)
The repository location, which may be relative or absolute.
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| true | The specified schema was found and removed. |
Removes the schema specified by its XML schema object.
public boolean remove(RegistryObject schemaObject)
The XML schema object or the external link of the schema.
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| true | The specified schema was found and removed. |
Removes the specified schema and also all schemas that are related to it by import and/or include. The initial schema is specified by its location in the CentraSite repository, which may be relative or absolute.
public boolean removeCascading(String schemaLocation)
The repository location, which may be relative or absolute.
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| true | The specified schema and all related schemas were found and removed. |
Removes the specified schema and also all schemas that are related to it by import and/or include. The initial schema is specified by its XML schema object or by its external link.
public boolean removeCascading(RegistryObject schemaObject)
The XML schema object or the external link of the schema.
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| true | The specified schema and all related schemas were found and removed. |
The XML service importer utilizes an XML Schema Documentation (XSD) as the basic input. The importer internally works with the schema importer for importing the schema file.
The following example demonstrates how to import an XML Service to CentraSite:
import javax.xml.registry.Connection;
import javax.xml.registry.JAXRException;
import javax.xml.registry.infomodel.Organization;
import com.centrasite.jaxr.xmlservice.HttpMethods;
import com.centrasite.jaxr.xmlservice.XMLService;
import com.centrasite.jaxr.xmlservice.XMLServiceInfo;
import com.centrasite.jaxr.xmlservice.XMLServiceManager;
String dbUrl = "http://localhost:53307/CentraSite/CentraSite";
String user = "...";
String password = "...";
String xsdFile = "C:/temp/myschema.xsd";
// create the required objects
Connection connection = createCentrasiteConnection(dbUrl, user, password);
Organization submittingOrganization = getSubmittingOrganization();
Organization providingOrganization = getProvidingOrganization();
// http methods to be supported
Collection<HttpMethods> httpMethods = new HashSet<HttpMethods>();
httpMethods.add(HttpMethods.GET);
httpMethods.add(HttpMethods.POST);
// configuration
XMLServiceInfo xmlServiceInfo = new XMLServiceInfo();
xmlServiceInfo.setName("service name");
xmlServiceInfo.setDescription("service description");
xmlServiceInfo.setVersion("1.1");
xmlServiceInfo.setSubmittingOrganization(submittingOrganization);
xmlServiceInfo.setProvidingOrganization(providingOrganization);
xmlServiceInfo.setSchemaUrl(xsdFile);
xmlServiceInfo.setEndpoint("http://endpointurl");
xmlServiceInfo.setHttpMethods(httpMethods);
// create XMLService
XMLServiceManager xmlServiceManager = new XMLServiceManager(connection);
XMLService xmlService = xmlServiceManager.createXMLService(xmlServiceInfo);
There are also some setter methods for additional parameters. The name, organization, native service URL, HTTP method must be set; other parameters are optional.
The XMLServiceManager class provides the setter
methods listed below.
Sets a name text that will appear with the imported
Service object.
xmlServiceInfo.setName(String serviceName)
Name for the service.
Sets a description text that will appear with the imported
Service object.
xmlServiceInfo.setDescription(String serviceDescription)
The description text.
Optional.
Sets a version number that will appear with the imported
Service object.
xmlServiceInfo.setVersion(String version)
An initial version identifier of the service.
Optional.
Sets the name of the organization under which the service should be registered for the purposes of governance within CentraSite.
xmlServiceInfo.setSubmittingOrganization(Organization submittingOrganization)
The name of the submitting organization.
Sets the name of the organization under which the service should be registered from a business perspective.
xmlServiceInfo.setProvidingOrganization(Organization providingOrganization)
The name of the providing organization.
Sets the URL of a native XML service to route the requests.
xmlServiceInfo.setSchemaUrl(String xsdFileUrl)
URL to the schema file of the native XML service.
Sets the schema endpoint of the native XML service to which the requests should be routed.
xmlServiceInfo.setEndpoint(String endpoint)
The native XML service's endpoint.
Sets a protocol over which the native service should accept requests.
xmlServiceInfo.setHttpMethods(Collection<HttpMethods> httpmethods)
The protocol to route the requests
You can remove an XML service from CentraSite. This function deletes the XML service and the associated schemas in the repository
Note:
If an XML service is referenced by another object, then it cannot be
deleted.
The following example demonstrates how to remove an XML service from CentraSite:
String xmlServiceKey = "uddi:..."; XMLServiceManager xmlServiceManager = new XMLServiceManager(connection); xmlServiceManager.deleteXMLService(xmlServiceKey);
The XMLServiceManager class provides the
following methods for removing an XML service:
Sets a UDDI key for the native XML service.
XMLServiceManager.deleteXMLService(String xmlServiceKey)
UDDI key of the native XML service.
The REST service importer utilizes an XML Schema Documentation (XSD) as the basic input. The importer internally works with the schema importer for importing the schema file.
The following example demonstrates how to import an XML Service to CentraSite:
import javax.xml.registry.Connection;
import javax.xml.registry.JAXRException;
import javax.xml.registry.infomodel.Organization;
import com.centrasite.jaxr.xmlservice.HttpMethods;
import com.centrasite.jaxr.xmlservice.XMLService;
import com.centrasite.jaxr.xmlservice.XMLServiceInfo;
import com.centrasite.jaxr.xmlservice.XMLServiceManager;
String dbUrl = "http://localhost:53307/CentraSite/CentraSite";
String user = "...";
String password = "...";
String xsdFile = "C:/temp/myschema.xsd";
// create the required objects
Connection connection = createCentrasiteConnection(dbUrl, user, password);
Organization submittingOrganization = getSubmittingOrganization();
Organization providingOrganization = getProvidingOrganization();
// http methods to be supported
Collection<HttpMethods> httpMethods = new HashSet<HttpMethods>();
httpMethods.add(HttpMethods.GET);
httpMethods.add(HttpMethods.POST);
// configuration
XMLServiceInfo xmlServiceInfo = new XMLServiceInfo();
xmlServiceInfo.setName("service name");
xmlServiceInfo.setDescription("service description");
xmlServiceInfo.setVersion("1.1");
xmlServiceInfo.setSubmittingOrganization(submittingOrganization);
xmlServiceInfo.setProvidingOrganization(providingOrganization);
xmlServiceInfo.setSchemaUrl(xsdFile);
xmlServiceInfo.setEndpoint("http://endpointurl");
xmlServiceInfo.setHttpMethods(httpMethods);
// create XMLService
XMLServiceManager xmlServiceManager = new XMLServiceManager(connection);
XMLService xmlService = xmlServiceManager.createXMLService(xmlServiceInfo);
There are also some setter methods for additional parameters. The name, organization, native service URL, HTTP method must be set; other parameters are optional.
The XMLServiceManager class provides the setter
methods listed below.
Sets a name text that will appear with the imported
Service object.
xmlServiceInfo.setName(String serviceName)
Name for the service.
Sets a description text that will appear with the imported
Service object.
xmlServiceInfo.setDescription(String serviceDescription)
The description text.
Optional.
Sets a version number that will appear with the imported
Service object.
xmlServiceInfo.setVersion(String version)
An initial version identifier of the service.
Optional.
Sets the name of the organization under which the service should be registered for the purposes of governance within CentraSite.
xmlServiceInfo.setSubmittingOrganization(Organization submittingOrganization)
The name of the submitting organization.
Sets the name of the organization under which the service should be registered from a business perspective.
xmlServiceInfo.setProvidingOrganization(Organization providingOrganization)
The name of the providing organization.
Sets the URL of a native REST service to route the requests.
xmlServiceInfo.setSchemaUrl(String xsdFileUrl)
URL to the schema file of the native REST service.
Sets the schema endpoint of the native REST service to which the requests should be routed.
xmlServiceInfo.setEndpoint(String endpoint)
The native REST service's endpoint.
Sets a protocol over which the native REST service should accept requests.
xmlServiceInfo.setHttpMethods(Collection<HttpMethods> httpmethods)
The protocol to route the requests
You can remove a REST service from CentraSite. This function deletes the REST service and the associated schemas in the repository
Note:
If the REST service is referenced by another object, then it cannot
be deleted.
The following example demonstrates how to remove a REST service from CentraSite:
String xmlServiceKey = "uddi:..."; XMLServiceManager xmlServiceManager = new XMLServiceManager(connection); xmlServiceManager.deleteXMLService(xmlServiceKey);
The XMLServiceManager class provides the
following methods for removing an REST service:
Sets a UDDI key for the native REST service.
XMLServiceManager.deleteXMLService(String xmlServiceKey)
UDDI key of the native REST service.
The BPEL importer imports objects of a Business Process Execution Language file. In CentraSite there are various specific predefined BPEL-ObjectTypes. A BPEL process flow usually references certain web services. Note that those web services should be registered prior to the BPEL registration; otherwise the references to the services cannot be established. The top-level controlling object is a BPELProcess object.
The following example demonstrates how to import a BPEL file:
import com.centrasite.jaxr.JAXRAccessor;
import com.centrasite.jaxr.bpel.BPELRegistrator;
String dbURL = "http://localhost:53307/CentraSite/CentraSite";
String bpelFile = "c:/temp/MyBPEL.bpel";
String user = ...;
String password = ...;
JAXRAccessor jaxr = new JAXRAccessor(dbURL, user, password);
try
{
BPELRegistrator br = new BPELRegistrator(bpelFile, jaxr);
br.register();
int warnings = br.getWarningCount(); // are there unreferenced services?
}
catch (Exception e)
{
// handle error
}
finally
{
jaxr.close();
}
The BPELRegistrator class provides the following
optional setter methods. If you want to use them, they must be called before
calling the register() method.
Specifies a project name, i.e. an internal RegistryPackage. The named project will receive the created top-level object (a BPELProcess) as a member.
public void setProjectName(String projectName)
The desired name of the project.
Specifies how CentraSite should react if a service that has not yet been registered in CentraSite is encountered.
public void setWarningIfPLTNotFound(boolean warningIfPLTNotFound)
Each time a service that has not yet been registered in
CentraSite is encountered, a counter is incremented. Use the
getWarningCount() method to get the current value of
the counter.
If a service that has not yet been registered in CentraSite is encountered, an exception is thrown.
The default value of the parameter is "true".
You can remove a registered BPEL process object. The BPEL file is
removed from the repository, and all associated registry objects are also
removed. Like the import class, you must first establish
a CentraSite connection with an instance of the
JAXRAccessor class before calling the
remove or removeProcess
method. The BPELAdministrator class provides the
following methods:
Removes the BPEL objects of the process flow indicated in the specified BPEL file.
public boolean remove (String bpelFile)
Specifies the BPEL file whose objects are to be removed. This could be the file in the CentraSite repository.
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| true | The BPEL objects were successfully removed. |
| false | The BPEL objects could not be removed. |
Removes the BPEL objects of the process flow indicated by the BPELProcess name and its namespace.
public boolean removeProcess(String bpelProcessName, String bpelNamespace
The process name of the BPEL objects to be removed.
The namespace of the BPEL objects to be removed.
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| true | The BPEL objects were successfully removed. |
| false | The BPEL objects could not be removed. |
The XPDL importer imports a process definition from an XPDL file. From the XPDL file, the importer produces a Process object and related components (e.g., Process Steps, Process Pools and Process Swimlanes). If the XPDL process references a Web service, the importer will add the Web service to the registry if it is not already present and associate it with the Process object.
The following example demonstrates how to import an XPDL file into CentraSite using the CentraSite Java API:
import com.centrasite.jaxr.JAXRAccessor;
import com.centrasite.jaxr.xpdl.ImportXPDL;
// Set URL for CentraSite Registry/Repository
String dbURL = "http://localhost:53307/CentraSite/CentraSite";
// Specify the location of the XPDL file.
String xpdlFile = "c:/temp/MyXPDL.xpdl";
// Specify the user account and password that the importer will use to log on to CentraSite
String user = "ctambrose";
String password = "jm6A1999";
// Build the connection to CentraSite
JAXRAccessor jaxr = new JAXRAccessor(dbURL, user, password);
try
{
// Instantiate XPDL importer object with specified XPDL file and connection info
// and then execute the import method.
ImportXPDL xpdl = new ImportXPDL(xpdlFile, jaxr);
xpdl.doImport();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
// Handle error
...
}
finally
{
// Close connection to CentraSite Registry/Repository
jaxr.close();
}
The ImportXPDL class provides the following
optional setter methods that you can use to specify certain properties in the
Process object. If you want to use these setter methods, you must call them
before you call the doImport() method.
Specifies the organization to which the Process object is to be added.
public void setOrganization (Organization org)
The organization to which the importer will add the Process object. Note that this method takes an Organization object as input. You can obtain the Organization object for a specified organization using the BusinessQueryManager.getRegistryObject() method.
Optional. If you do not set the organization parameter, the importer will add the Process object to the organization that the user specified in the JAXRAccessor belongs.
Specifies the filename to be assigned to the XPDL file in CentraSite's repository.
public void setOriginalFilename (String originalFilename)
The filename that is to be given to the XPDL file in the CentraSite repository.
Note:
A valid filename can consist of letters, numbers, and the
underscore character. It must not contain spaces or other special
characters.
Optional.
Specifies the category from the Product taxonomy by which the Process object is to be classified.
public void setProductConcept(Concept product)
The Product category (concept) that is to be assigned to the Process object. This classification is generally used to identify the product from which the Process was published.
The following are some of the predefined categories in the Product taxonomy in CentraSite. (For other categories, examine the Product taxonomy on the instance of CentraSite to which you are importing the XPDL file.)
CentraSite
webMethods ApplinX
webMethods EntireX
webMethods Composite Application Framework
webMethods Product Suite
webMethods BPM
webMethods Trading Networks
Optional.
Specifies the version identifier that is to be assigned to the Process object that the importer adds to the registry. (This methods specifies the user-defined version identifier. The Process object will also have a version number, which is automatically assigned and maintained by CentraSite.)
public void setVersion(String version)
The version identifier to be assigned to the Process object.
Optional.