The first thing you need to do when working with Tamino is to create a database. To do so, you use the command line . The command line is a user interface with which you can perform administration functions like starting, stopping, renaming, deleting, and restoring databases. When you create a database, you define a database name, a database location, and database specifics like size and properties. You can either accept the defaults or enter your own preferences according to your specific database needs.
On Windows, the runs in the folder "<INSTALL_ROOT>/Tamino/v101/bin". To set up the administration environment first run the command "ino_setenv".
On UNIX, use the shell script
inoadmin.sh, which is located in a directory that is
included in the search path after the Tamino installation.
Databases are created using .
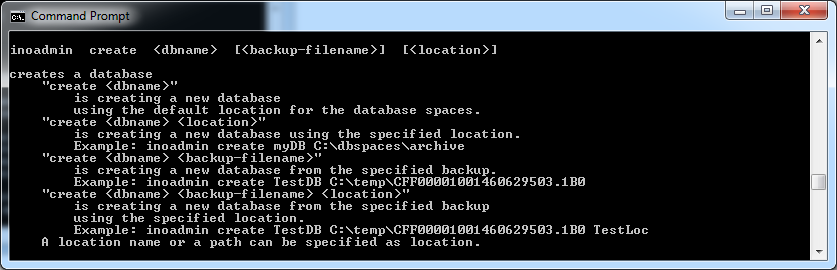
When only providing the name of the database to-be with the call, database specifics are assigned with default values. The database name can be up to a maximum of 32 characters in length. The following characters may not be used: SPACE , ; ! \ = # . [ ] " % ' / ^ ` ? *
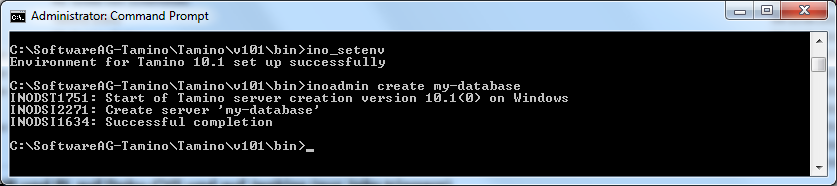
That's all there is to creating a database. If you want to learn more about creating databases, refer to the documentation for the Tamino Manager.