This part of the documentation provides background information on the migration of SAP R/3 Gateway to a new platform architecture within the webMethods Integration Server environment.
The product SAP R/3 Gateway (product code: SRG) will be retired on January 31, 2016. The reason for this is that SAP has announced the retirement of its RfcSDK interface which the product is using. This part of the documentation provides background information on the migration of SAP R/3 Gateway to a new architecture based on the webMethods Integration Server Environment. Please do not hesitate to contact Software AG for more details on the migration or a cost estimate for the migration project.
The project steps required to execute the migration by using the webMethods Integration Server SAP and the EntireX Adapter are described in detail; in the context of the documentation the product SAP R/3 Gateway will be referred to as classic SAP R/3 Gateway.
The migration assets (software, documentation and license) are combined under the product code SRGRP.
The following points describe the motivation behind migrating the classic SAP R/3 Gateway to the new technology environment:
SAP's deprecation of the classic RfcSDK interface used in SRG
Availability of Unicode (previously not supported in SRG)
Support of asynchronous communication (IDocs and tRfc)
Extension of the limited point-to-point SRG architecture within the ESB
Reduced support efforts for customers because of using Java instead of a C-based product
Standard support of RFC data types such as String
Auditing and logging support
Use of caching features for distribution and big memory
Cluster support for high availability (HA) to avoid single point of failure with active/active nodes
The new architecture with its combination of webMethods Integration Server, EntireX Adapter and SAP Adapter based on Java replaces the classic SAP R/3 Gateway technology based on native C-programmed ERX and RFC interfaces.
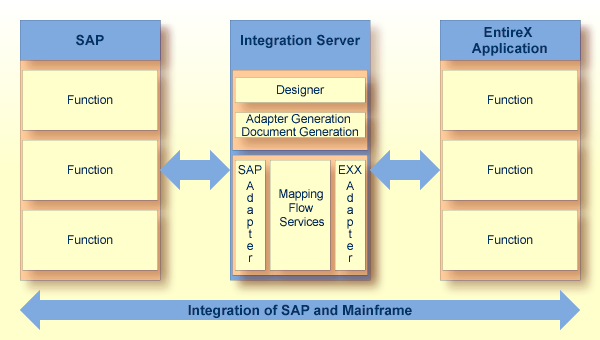
The Designer is a prerequisite for developing the data transfer between the adapters.
The migration project lays great value on preserving all existing interfaces on the client or server side. No Rpc2Rpc Server clients (in most cases Natural RPC clients) or SAP clients (in the case of Rfc2Rpc) should require any changes. The existing middleware will be replaced with running Rpc2Rfc and Rfc2Rpc servers.
To achieve this goal, the IDLs of all implemented directions are used in the migration project. Ensure that the following prerequisites are met:
Have the SRGRP license key of the webMethods Integration Server available.
Set up the webMethods ESB environment with Integration Server, EntireX Adapter, SAP Adapter and Designer for development.
Make IDLs available.
(Re-) activate the test scenarios, know-how and environment of interfaces implemented with classic SAP R/3 Gateway. For example, if you have implemented unit tests, re-use these assets. If you have not used them in the past, plan for interface testing scenarios.
Set up the webMethods ESB environment with Integration Server, EntireX Adapter, SAP Adapter for testing.
The EntireX Adapter inside Integration Server requires RPC protocol version 2000 or higher.
For Migrating the Rpc2Rfc Server, check your Natural (generated stubs) or EntireX RPC client environment to support this requirement.
For Migrating the Rfc2Rpc Server, check your Natural or EntireX RPC Server environment to support this requirement.
See the EntireX Release Notes for more about Supported RPC protocols.
Since the new architecture uses a different adapter technology, the following points must be taken into consideration for any existing or new testing scenarios when data is moved from one adapter to another.
There are usually two possibilities for the transport or mapping of data between interfaces. For functions or procedures, you can process the parameter data via calling conventions:
Call by reference or
call by value
When using call by reference, the sequence of the
parameter types in the source must be identical to that in the target. When
using call by value, the parameter name in the source must be
identical to that in the target.
The classic SAP R/3 Gateway handled data processing in the following way:
On data level 1, call by value was used because the
importing, exporting or table name had to be identical.
On data level 2, call by referencewas used because the
size of the data structure and types had to be identical.
In the Integration Server, the mapping of
data is part of the pipeline handling. The implicit mapping works on call
by value and the EntireX Adapter and
SAP Adapter data is generated from IDL - the
interface definition. In an ideal scenario all parameter names in IDL remain
unchanged for client and server and the implicit data mapping works perfectly.
This means that no explicit data mapping needs to be defined.
If one or more parameter names differ, you have to apply the flow
service data mapping with call by value.
If the mapping was thus changed from call by reference to
call by value, tests must then be carried out to ensure that all
data parameters have been passed from client to server.
![]() To set up the development environment
To set up the development environment
Install webMethods Integration Server with its license key.
Install Designer.
Import WxSRG package into Integration Server.
The new implementation in Integration Server will create a large number of assets such as connection, adapter, listener, document types and flow services, which have to be organized. The Integration Server supports the grouping of assets with packages in which the assets have a namespace. You can use the following statements to create packages and namespace.
![]() To create packages and namespace
To create packages and namespace
Create an Integration Server package for
each IDL of Rpc2Rfc or Rfc2Rpc and give it the identical name in camel case. If
you have multiple IDLs of the same type (e.g. Rpc2Rfc), add a postfix to
identify the business case (for example SD for sales and
distribution).
In a package, create a top folder and name it with the package name in lower case letters.
In the top folder, create the following subfolders:
a folder with the name docs for all document
types;
a folder with the name adapter for all RFC or RPC
functions and the connections;
a folder with the name listener for all RFC or RPC
services acting as listener and for the connections.
The WxSRG package contains flow as well as java services for development and runtime:
Services are available for generating Integration Server assets, e.g., document types during development.
At runtime, services are available for handling functionalities of the classic SAP R/3 Gateway.
The development part is contained in the namespace
wx.srg.dev.
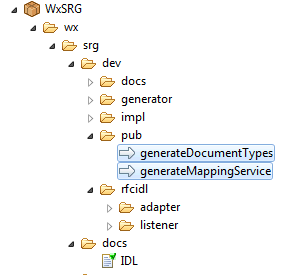
There are 2 public services for generating Integration Server assets from IDL:
wx.srg.dev.pub:generateDocumentTypes: Generates all
required document types from IDL. One document type is generated for each group
on level 1, another for all input parameters and another for the output
parameters.
wx.srg.dev.pub:generateMappingService: Generates one
mapping flow service for each function in IDL.
Both services have input parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| filename | Sets the path and filename of the input IDL in the local filesystem or URL with HTTP Get protocol. |
| packageName | Sets the target package name of the generated output. |
| ns | Sets the namespace inside the package of generated output. |
| ns_of_docs | Sets the namespace of generated document types.
This parameter is used on calling
wx.srg.dev.pub:generateMappingService and the value comes from the
ns parameter off calling
wx.srg.dev.pub:generateDocumentTypes .
|
The services used during runtime are contained in the namespace
wx.srg.run.
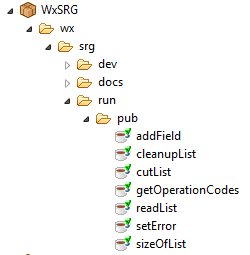
Note:
Neither of the two services can overwrite flow-services or document
types that have already been generated. If you want to regenerate the assets,
you must delete them first.
The content for handling RFC tables is stored in the
Integration Server cache. The SAP R/3
Gateway supports the cursor concept to read partial RFC tables;
to set up this feature, you have to configure a Cache Manager named
SRG in Integration Server.
![]() To configure the cache manager
To configure the cache manager
In the Administrator, go to > .
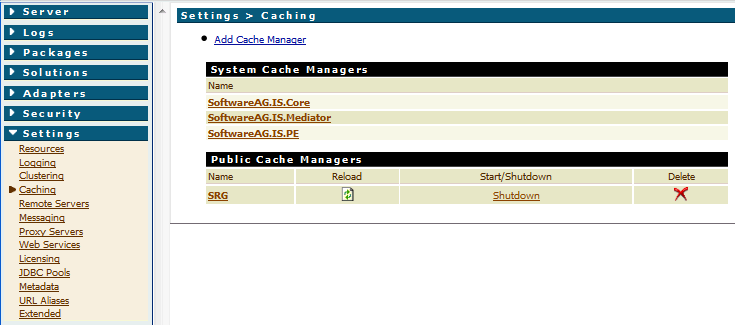
Inside SRG Cache Manager, add a cache named
Rpc2RfcTableContent.
This results in
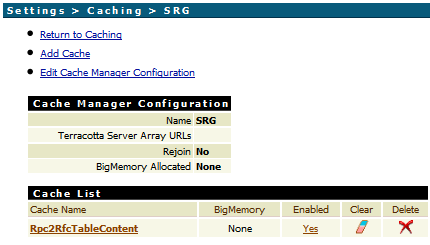
The cache contains the two required parameters Maximum
Elements in Memory and Time to Live.
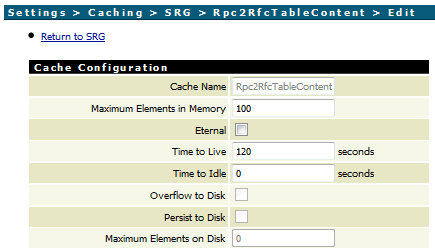
Maximum Elements in Memory: Calculate the number of
elements as the number of parallel sessions multiplied by the maximum number of
tables in one RFC function. One element in the cache is one RFC table in one
session. For example, if you have 10 parallel user sessions each calling an RFC
function with 5 tables, you should set this value higher than 50.
Time to Live: Set the no activity expiration
time.
Tip:
You can set the same value of parameter Connection
Pool Time Limit in Rpc2Rfc Server.
Set the other parameters to the default value or leave them blank for the Terracotta Server Array if you have no TSA.
To support Call by value, the RfcIdl generator tool has a
new option webMethods SAP Adapter Calling Convention, which allows
printing the original SAP field names on level 2 into IDL.
![]() To update the RfcIdl Generator Tool
To update the RfcIdl Generator Tool
Install the new option.
Upload the latest fix update into the SAP R/3 Gateway
development environment.
Compile the RfcIdl tool: > > Compile EntireX RfcIdl Tool.
The new option webMethods SAP Adapter Calling
Convention is now available in >
.
Note:
The new option with value yes is now the
default setting. To switch back to using camel case field names on level 2, you
must select no.
Each function inside the IDL must be implemented as a flow service, which is called from EntireX Adapter Listener for incoming requests. The incoming data is passed to the SAP Adapter function as a request document; the output is returned to the EntireX Adapter Listener as a response document.
Before using the generators to generate Integration Server assets, the IDL should be revised. The RfcIdl generator tool supports the exchange of parameter names on level 2. If the parameter names in the EntireX Adapter Listener and the SAP Adapter function are identical, the flow mapping service works with implicit data mapping. If the parameter names are not identical, explicit data mapping is required:
Use the function to print a report about differences between the original parameter names in the SAP Repository and the IDL.
Use the function to replace the current function in IDL with the interface definition from the SAP Repository.
Notes:
_ character as postfix in front of the following field names:
program, library, parameter,
structure and version.
Generate the EntireX Listener.
Generate the SAP functions.
Generate the document types using
wx.srg.dev.pub:generateDocumentTypes described in
WxSRG.
Generate the mapping services using
wx.srg.dev.pub:generateMappingService described in
WxSRG.
One mapping services is generated for every function in the IDL; the
mapping services are generated from template
wx.srg.dev.generator:templateMappingRpc2Rfc; see the following
figure:
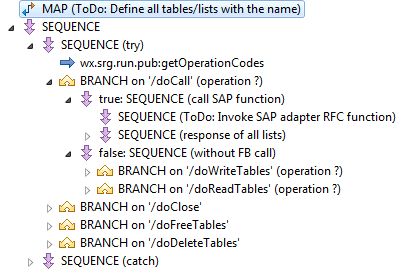
Check the EntireX Listener interface for input and output document
types. The document types are generated with services
wx.srg.dev.pub:generateDocumentTypes and have the suffix
Request or Response. For Input,
set document type Request, for Output, set
document type Response. If the referenced document type is found,
all input and output parameters are displaced. If not, check the parameter
ns_of_docs on generation with
wx.srg.dev.pub:generateMappingService.
Work through the generated mapping services and rework all steps that
are commented with ToDo:
Enter the list of tables in the Map step ToDo: Define all
tables/lists with the name. The table names of this SAP function must be
set in the pipeline variable DocumentNames as
String List.
In the Sequence step ToDo: Invoke SAP adapter RFC
function, insert the SAP Adapter function generated from the SAP
Repository.
Tip:
See the flow services
wx.srg.dev.rfcidl.listener:RFCINTFB or
wx.srg.dev.rfcidl.listener:RFCINTPA in the
package WxSRG for a sample
implementation.
wx.srg.run.pub:addFieldIn case of different field names in the SAP Repository and the IDL on
level 2, this helper service enables you to implement explicit mapping via
call by value. The services adds a field with specific name and
value into the document list.
The following example explains the use of the helper service:
The multiple group (RFC table) on level 2 has a field with the name
library; however, the use of the parameter name
library is not permitted because it is a reserved name in the IDL
syntax and the field must be renamed to _library (for example).
Implement an explicit data mapping from field content
_library to library; use the service by adding a
field library in the target group.
Note:
Removal of _library in the source is not required.
Each function inside the IDL must be implemented as a flow service, which is called from the SAP Listener Notification for incoming requests. The incoming data is passed to the EntireX RPC function as a request document; the output is returned to the SAP Listener Notification as a response document.
For each IDL of the Rfc2Rpc server, generate the EntireX RPC adapter function.
For each function inside the IDL, generate a SAP listener notification.
One flow service exists for each generated SAP listener notification; inside this flow service, the generated EntireX RPC Adapter function is called.
All differences between the IDL and the SAP Repository must be implemented in explicit data mapping services.
Notes:
The following table lists the unsupported features of classic
SAP R/3 Gateway and the error messages in the IS
package WxSRG.
| Exception | Description |
|---|---|
| 'write' only operation is not supported | The classic SAP R/3
Gateway supports the 'write' only operation (using operation code
OP_WRITE_TABLES without
OP_CALL) to transport data (content of RFC tables)
to SAP without calling the RFC function in the first step. After the transport,
the client can call the function in a second step with the operation code
OP_CALL. This operation allows the sending of data
(table items) from client to SAP server before the RFC function is called. This
operation is not supported in the migration product. The preferred solution is
to change the IDL to a variable array of this table.
|
| No valid context handle created or handle is not available | If you call a query function in SAP that returns
a large number of RFC table rows, the data are stored in the
cache under a key (or called as
context handle). To access the data, you must set the field handle
with the last returned value. This error message is displayed if the value of
handle is invalid.
|