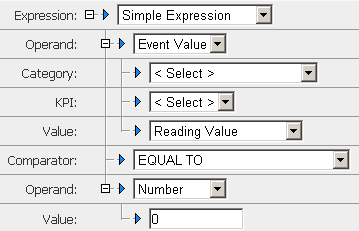
Defining Event Text or Event Value as the First Operand
The two Operand options Event Text and Event Value are available only for Event rule types. The specific steps for defining each of the two operands in a simple rule expression depend on your choice of operand types. The operand type determines the fields that appear in the Rule Expression panel on the Edit Rule Expression page. A specific set of fields is associated with each operand type, and whenever you change an operand type, the displayed fields change automatically. If you choose either Event Text or Event Value as the operand type for the first operand in a simple rule expression, Optimize displays the fields shown in the following figure and described in the subsequent task.
The following task assumes that you have already chosen either Event Text or Event Value as the first operand type in the Rule Expression panel on the Edit Rule Expression page.

To define Event Text or Event Value as the first operand in a simple rule expression
1. In the Category list (in the Rule Expression panel on the Edit Rule Expression page), click the category of the event you want to compare.
In addition to values supplied by categories that your system administrator created, the list could include the options that are described in the following table.
Category | Description |
Analytic Engine | Provides data about the Analytic Engines, such as JVM memory consumed and thread count. |
Intrinsic Process Metrics | Provides generic data about your processes as identified on the Problems page. For example, process cycle time (how long an instance takes to run) and step count (how many steps have completed successfully). Note:
When creating a rule against the intrinsic process metrics Cycle Time by Process or Process Time against a Reading Value, the unit of measure is in milliseconds. |
Additional options that might appear in the Category list: |  GarbageCollectionType  PersistenceQualifier  Queue  Router  WebService  Process names |
On the Edit Rule Expression page, the options for Event rule types are the same as the options for KPI rule types, with the following two exceptions:

If you choose
Event Text as the first operand, the second operand must be either
Text or
Event Text.

If you choose
Event Value as the first operand, the second operand must be either
Number or
Event Value.
2. In the Comparator list, click the logical comparator (such as Equal To) to compare the two operands in the simple rule expression (also known as a Boolean expression).
3. In the second Operand list, select an appropriate operand to complete the expression. If you select Number as the second operand, then in the related Value field, you would type the numeric constant that you want to compare to the first operand. If your first operand is of type KPI Value, for example, the unit of measure of your numeric constant must be the same as the unit of measure used by the selected KPI (shown to the right of the KPI's Value selection). For example, if the unit of measure used by the selected KPI is megabytes, Optimize interprets the literal in megabytes.
4. Click Save to save the rule expression.