With the Web Services Stack Configuration Editor, an Eclipse plug-in, you can configure individual web services or groups of web services in the services.xml file that is part of a web service archive (Designer file with extension .aar). Using an external configuration file of the Listener for XML/SOAP allows you later to override settings of a web service archive for different Web server environments without modifying the archive itself. See also Configuring Web Services.
This document covers the following topics:
For more information on the Configuration Editor see the separate Web Services Stack documentation in the Software AG Infrastructure Administrator's Guide under Software AG Suite & Cross-Product Guides.
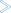 To invoke the Web Services Stack Configuration Editor
To invoke the Web Services Stack Configuration Editor
Use the context menu of a web service archive (Designer file with extension .aar) that was generated with the Designer to open the Web Services Stack Configuration Editor:
The following pages are provided to configure different aspects of the web service:
Archive Page
Displays the contents of the web service archive (Designer files with extension .aar). In general it allows you to add additional
files to the archive or remove files from the archive. Specifically you can add additional EntireX files (Designer files with
extension .idl, and .xmm) to the web service.
Services Page
See Services Page. Allows you to update and provide further configuration settings that apply to a web service contained in the web service
archive (Designer file with extension .aar).
Operations Page
Allows you to provide additional configuration settings that apply to an operation of a web service contained in the web service
archive.
services.xml Page
Allows you to view the web services archive's configuration file in text form (XML format).
EntireX Settings Page
See EntireX Settings Page. Provides configuration and settings for the Listener for XML/SOAP. See Listener for XML/SOAP.
Notes:
ServiceLifecycle class: com.softwareag.entirex.xml.rt.WSSServiceLifeCycle
Session Scope: Application
MessageReceiver class: com.softwareag.entirex.xml.rt.EntireXMessageReceiver
Do not modify these settings.
This section covers the following topics:
Web services can be configured to be accessible over multiple transport protocols. The default transport is HTTP.
HTTP
No additional configuration is required.
HTTPS
This requires that HTTPS is configured for the servlet engine that is running the Web Services Stack.
TCP
Additional configuration of the Web Services Stack in axis2.xml is necessary to enable support of this transport.
For more details see the Web Services Stack documentation in the Software AG Infrastructure Administrator's Guide under Software AG Suite & Cross-Product Guides.
To enable WS-Addressing headers for a web service, check the Enable WS-Addressing check box in section Modules. This inserts a WS-Addressing policy into services.xml and enables the addressing module of the Web Services Stack that processes addressing SOAP headers.
<wsp:Policy wsu:Id="User defined"
xmlns:wsp=http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2004/09/policy
xmlns:wsu="http://docs.oasis-open.org/.../...wssecurity-utility-1.0.xsd">
<wsp:ExactlyOne>
<wsp:All>
<wsaws:UsingAddressing
xmlns:wsaws="http://www.w3.org/2006/05/addressing/wsdl"/>
</wsp:All>
</wsp:ExactlyOne>
</wsp:Policy>
<module ref="addressing"/>
WS-Security can be configured to ensure integrity, confidentiality and allow authentication of messages exchanged between web services clients and web services. To enable WS-Security for a web service, check the check box in section Modules. This enables further configuration options in section Security on the Services page. This section covers the following topics:
WS-Security policy assertions can be defined for a service to accept and enforce SOAP messages containing a WS-Security SOAP header. With WS-Security the message exchange between a web service client and a service can be secured in the following aspects:
confidentiality: messages (or parts of messages) are encrypted on transport or on message level
integrity: messages (or parts of messages) are signed on transport or on message level
authentication: the sender of a message supplied authentication information on transport or on message level that allows the service to perform authentication
The following security policies are supported:
Security bindings
TransportBinding, SymmetricBinding and AsymmetricBinding, which
specify the mechanism used to ensure confidentiality and integrity.
TransportBinding
The message exchange is secured on
transport level (HTTPS). As a prerequisite, the secure transport needs to be
enabled and configured for the servlet engine that hosts the Web Services Stack service
runtime.
SymmetricBinding
The confidentiality of the message
exchange is achieved on message level, using a symmetric encryption key that is
shared between web service client and service.
AsymmetricBinding
The confidentiality of the message
exchange is achieved on message level using, an asymmetric encryption key (that is,
client and service use different private/public key pairs for encryption and
decryption).
Timestamps
A service can have a policy that requires that timestamps
are added to messages.
Authentication
Policies can be defined that require messages
exchanged contain authentication information such that receivers can
authenticate the sender. The following authentication methods are
supported:
HTTP basic authentication
client certificates for the HTTPS transport
user-name token contained in the message
digital signatures and X509 tokens contained in the message
Message exchange can be secured either on transport level or on message level. You can configure three different "bindings" for secure message exchange:
No Binding
Message exchange is not secured.
Transport Security with SSL
Message exchange is secured on transport level using HTTPS transport (SSL/TLS). To be able to configure transport security,
the servlet engine must have HTTPS configured and enabled as a prerequisite. In addition, HTTPS must be configured for the
Web Services Stack in the global configuration file axis2.xml. This is not configured by default. As an option you can specify
whether a client certificate has to be provided on the transport.
Message-level Security with Symmetric Binding
Message exchange is secured using a symmetric key. Additional keystore configuration is required for symmetric binding, see
Encryption/Signing. See Encryption/Signing.
Message level Security with Asymmetric Binding
Message exchange is secured using an asymmetric key. Additional keystore configuration is required for asymmetric binding
see Encryption/Signing. See Encryption/Signing.
Encrypt body
The message body must be encrypted.
Sign body
The message body must be signed.
Sign entire headers and body
The message headers and body must be signed
Username Token
The web service requires a username token in the message header.
Secure Conversation
The web service provides secure communication over one or more messages.
Xpath expressions can be specified to identify parts of a message that are signed and/or encrypted.
User
The alias of the public key in the keystore that is used for encryption. For decryption, a private key is required.
The password for accessing the private key is queried at runtime, using the Password Callback Class.
Password Callback Class
This is the name of a class that implements a password callback handler that is called by the Web Services Stack Runtime to
query a password for accessing a private key in the keystore for signing, or decrypting or a password for username token authentication.
The password callback handler class implementation needs to be provided by the application writer. See Password Callback Class.
Certificate Alias
The alias of the private key in the keystore that is used for signing outgoing messages.
The alias name is also used as the username that is used for authentication. The password for accessing the private key is
queried at runtime using the Password Callback Class.
To verify a signature, a corresponding public key is used.
Keystore
The location of a Java keystore. This can be a relative path to a Java keystore contained in the web service archive (Designer
file with extension .aar), or an absolute path to a keystore located in the file system.
Keystore Password
The password required to access keys in the keystore.
Truststore
The location of a Java truststore. This can be a relative path to a Java truststore contained in the web service archive (Designer
file with extension .aar), or an absolute path to a truststore located in the file system.
Truststore Password
The password required to access keys in the truststore.
Include Timestamp
The web service requires a (signed) timestamp in the message header.
A WS-ReliableMessaging policy assertion can be defined for a service. This service then only accepts SOAP requests using the WS-ReliableMessaging protocol.
Example: WS-ReliableMessaging policy assertion
<wsp:Policy wsu:Id="ReliableMessaging" xmlns:wsp="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2004/09/policy"
xmlns:wsu="http://docs.oasis-open.org/wss/2004/01/oasis-200401-wss-wssecurity-utility-1.0.xsd">
<wsp:ExactlyOne>
<wsp:All>
<wsrm:RMAssertion xmlns:wsrm= "http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/02/rm/policy">
<wsrm:InactivityTimeout Milliseconds="600000"/>
</wsrm:RMAssertion>
</wsp:All>
</wsp:ExactlyOne>
</wsp:Policy>
The EntireX Settings page allows you to specify EntireX specific settings of the Web Services archive (Designer file with extension .aar). The page contains two sections:
Under Configuration, a combo box is available with general settings for all XMM/SOAP mapping files in the web service archive (Designer file with extension .aar); Specific settings for an XMM/SOAP mapping file supersede the general settings.
| Parameter | Description | More Information |
|---|---|---|
Broker ID |
The broker ID to be used. | |
User ID |
The user ID for access to the broker. | Using the Broker and RPC User ID/Password |
Password |
The password for secured access to the broker. | |
Compression Level |
Sets the compression level. | Using Compression under Writing Advanced Applications - EntireX Java ACI |
Use Codepage |
Determines the translation processing of the broker. Valid values: true|false|<character encoding>. If a character encoding is set, this character encoding is used for the RPC message.
|
Method setCharacterEncoding of class BrokerService (EntireX Java ACI).
|
Use Security |
Possible values: true|false.
|
|
Server Address |
This is the triplet of server class/server name/service. | |
RPC User ID |
The RPC user ID sent to the RPC server. | Using the Broker and RPC User ID/Password |
RPC Password |
The RPC password sent to the RPC server. | |
Natural Library |
By default the library name sent to the RPC server is retrieved from the IDL file (see library-definition under Software AG IDL Grammar in the IDL Editor documentation). The library name can be overwritten. This is useful if communicating with a Natural RPC
server.
|
|
Natural Logon |
Enable to send RPC user ID/password pair. Possible values: true|false.
|
Using the Broker and RPC User ID/Password |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Default Wait Time | Sets the value of the default wait time field to the argument (see setDefaultWaittime of class BrokerService).
|
| Behavior of Non-conversation Calls | The parameter indicates whether a non-conversational call is finalized with a logoff call to free Broker resource (default), or by means of timeout. The default value for this parameter is "nonConv-with-logoff", which defines that a non-conversational call will finish with an additional logoff call (two calls per message). Set to "nonConv-without-logoff" to specify that a non-conversational call will finish without logoff call (one call per message); Broker will clean up resources by means of timeout. |
| User Name Token: |
Use credentials retrieved from Username Token for EntireX server call. |
| Basic Authentication: |
Use credentials retrieved from Basic Authentication for EntireX server call. |
EntireX supports two user ID/password pairs: a broker user ID/password pair and an (optional) RPC user ID/password pair sent from RPC clients to RPC servers. With EntireX Security, the broker user ID/password pair can be checked for authentication and authorization.
The RPC user ID/password pair is designed to be used by the receiving RPC server. This component's configuration determines whether the pair is considered or not. Useful scenarios are:
Credentials for Natural Security
Web Service Transport Security with the RPC Server for XML/SOAP, see XML Mapping Files
Service execution with client credentials for EntireX Adapter Listeners, see Configuring Listeners
etc.
Sending the RPC user ID/password pair needs to be explicitly enabled by the RPC client. If it is enabled but no RPC user ID/password pair is provided, the broker user ID/password pair is inherited to the RPC user ID/password pair.
With the parameter Natural Logon (see Service Parameters)
sending the RPC user ID/password pair is enabled for the Web Services Wrapper.
If you do so, we strongly recommend using SSL/TLS. See SSL/TLS, HTTP(S), and Certificates with EntireX.
 To use the broker and RPC user ID/password
To use the broker and RPC user ID/password
Specify a broker user ID with parameter User ID.
Optional. Specify broker password with parameter Password.
Enable to send the RPC user ID/password pair with parameter Natural Logon set to true.
If different user IDs and/or passwords are used for broker and RPC, use the parameters RPC User ID and RPC Password to provide a different RPC user ID/password pair.
By default the library name sent to the RPC server is retrieved from the IDL file (see library-definition under Software AG IDL Grammar in the IDL Editor documentation). The library name can be overwritten. This is useful if communicating with a Natural RPC
server. Specify a library in parameter Library.
This section provides an example of a password callback handler.
/*
/*
* PasswordCallbackHandler.java -
* com.softwareag.wsstack.test.PasswordCallbackHandler class
*
* Server/Client Password Callback Handler, responsible for delivering
* passwords for accessing a private signing or decryption key from a
* keystore or a password for a username token.
*/
package com.softwareag.wsstack.test;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.security.auth.callback.Callback;
import javax.security.auth.callback.CallbackHandler;
import javax.security.auth.callback.UnsupportedCallbackException;
import org.apache.ws.security.WSPasswordCallback;
public class PasswordCallbackHandler implements CallbackHandler
{
/*
* Handles all supported callbacks
* @see javax.security.auth.callback.CallbackHandler#handle(
* javax.security.auth.callback.Callback[])
*/
public void handle(Callback[] callbacks) throws IOException,
UnsupportedCallbackException
{
try {
for (int i = 0; i < callbacks.length; i++) {
WSPasswordCallback pwcb = (WSPasswordCallback)callbacks[i];
//get the type of the callback: SIGNATURE, DECRYPT, USERNAME_TOKEN
int usage = pwcb.getUsage();
String id = pwcb.getIdentifer();
if (usage == WSPasswordCallback.SIGNATURE) {
//supply password for signing key
if ("client".equals(id)) pwcb.setPassword("apache"); else
if ("service".equals(id)) pwcb.setPassword("apache");
} else
if (usage == WSPasswordCallback.DECRYPT) {
//supply password for decryption key
if ("client".equals(id)) pwcb.setPassword("apache"); else
if ("service".equals(id)) pwcb.setPassword("apache");
} else
if (usage == WSPasswordCallback.USERNAME_TOKEN_UNKNOWN) {
// verify username token on the server side
if (id != null) {
//get the password from the request
String pass = pwcb.getPassword();
// authenticate the user
if (id.equals("client") && pass.equals("apache")) {
return;
} else {
throw new UnsupportedCallbackException(callbacks[i],
"authentication failed");
}
}
} else
if (usage == WSPasswordCallback.USERNAME_TOKEN) {
// supply password for username token on the client side
if (id != null) {
// supply the password
String pass = pwcb.getPassword();
if (pass == null) {
if ("client".equals(id)) pwcb.setPassword("apache"); else
if ("service".equals(id)) pwcb.setPassword("apache");
pass = pwcb.getPassword();
}
}
}
} // for
}
catch (Throwable e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return;
} // handle
}