Server mapping enables the RPC server to correctly support special COBOL syntax such as
REDEFINEs, SIGN LEADING and OCCURS DEPENDING ON clauses,
LEVEL-88 fields, etc.
If one of these elements is used, the IDL Extractor for COBOL automatically extracts a
server mapping file in
addition to the IDL file (interface definition language).
Also, the COBOL Wrapper may generate a server mapping file for RPC server generation.
The server mapping is used at runtime to marshal and unmarshal the RPC data stream.
There are client-side mapping files (Designer files with extension .cvm) and server-side mapping files
(Designer files with extension .svm).
If you have not used server-side mapping, we recommend you use client-side mapping.
This document describes the handling of server mapping files (Designer files with extension .cvm or .svm) for COBOL and covers the following topics:
See also Server-side Mapping Files in the RPC server documentation for z/OS (CICS, Batch, IMS) | Micro Focus | CICS ECI | IMS Connect | BS2000 | z/VSE (CICS, Batch).
This section covers the following topics:
The following rules apply to a server mapping file for COBOL in the Designer:
The mapping file is of type client-side or server-side. We recommend using client-side mapping files, which is the default. You cannot use both types in the same Eclipse workspace. See How to Set the Type of Server Mapping Files.
Mapping files have the extension .cvm (client-side) or .svm (server-side).
The mapping file has to relate to an appropriate IDL file. Always keep the IDL file and the mapping file together in the same folder.
The mapping file is created if required by the COBOL Wrapper | Extractor. See When is a Server Mapping File Required?.
If an IDL file has a corresponding mapping file, at least one of the IDL programs in the IDL file requires server-mapping information to correctly call the target server. For those IDL programs, there is a server mapping (corresponding to a line) in the server mapping file.
If there is an IDL file but no corresponding mapping file, there is no IDL program that requires server mapping information.
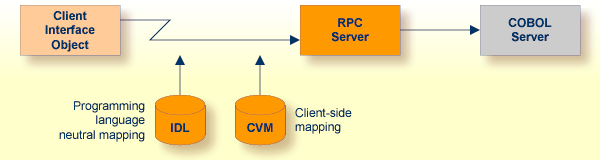
The following rules apply to client-side mapping:
Client-side mapping files have the extension .cvm in the Designer.
The mapping files are generated when the Designer is in client-side mapping mode, see How to Set the Type of Server Mapping Files.
Handling of client-side mapping is easier than server-side mapping. This can be an important criterion, for example if the RPC server is hosted in a mainframe environment and you do not have access to mainframe development resources. The following tasks are not required:
deploying the server mapping files to the RPC server
setting up a server-side mapping container in the mainframe environment
change management of server-side mapping files in the mainframe environment
The mapping is wrapped into the client interface objects when an RPC client is generated. The client-side mapping must available before you create any RPC client component, that is, the COBOL server program must be extracted or generated first.
The mapping is sent during runtime to the target RPC server with the RPC request.
Only point-to-point connections are allowed. The RPC client with the client-side mapping in its client interface object can only call one specific target COBOL server program. If you want to replace the COBOL server program by another implementation, for example Java, you need to rebuild all the RPC clients without the client-side mapping wrapped into their client interface object.
Client-side mapping files are not supported by RPC clients generated with the DCOM Wrapper and COBOL Wrapper. Use server-side mapping files instead. See Server-side Mapping.
To use client-side mapping, all EntireX components involved must be version 9.7 or higher.
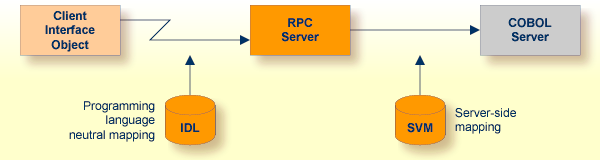
The following rules apply to server-side mapping:
Server-side mapping files have the extension .svm in the Designer.
The files are generated when the Designer is in server-side mapping mode, see How to Set the Type of Server Mapping Files.
The files have to be deployed to the RPC server. See Deploying Server-side Mapping Files in the RPC server documentation for z/OS (CICS, Batch, IMS) | Micro Focus | CICS ECI | IMS Connect | BS2000 | z/VSE (CICS | Batch).
Note:
For IMS Connect and CICS ECI connections with the webMethods EntireX Adapter for Integration Server,
server-side mapping files are not deployed. They are wrapped into the Integration Server connection - the same as client-side
mapping files.
For RPC connections, the server-side mapping files must be deployed to the target RPC server.
See the EntireX and your webMethods Integration Server Applications.
Server-side mapping is read at runtime by the RPC server from the server-side mapping container, see Server-side Mapping Files in the RPC server documentation for z/OS (CICS, Batch, IMS) | Micro Focus | CICS ECI | IMS Connect | BS2000 | z/VSE (CICS, Batch)
Flexible connections are possible: the RPC client can call any target server program as long as the IDL interface matches. You do not need to rebuild the RPC clients when replacing the COBOL server program by a different implementation, for example Java, as required with client-side mapping files.
Server-side mapping files can be migrated to client-side mapping files, see Migrating Server Mapping Files.
Every Designer (Eclipse) workspace is either in client-side mapping mode (generating Designer server mapping files with extension .cvm) or server-side mapping mode (generating Designer server mapping files with extension .svm) for COBOL mapping. The default mode is client-side mapping and can be changed on the preferences page :
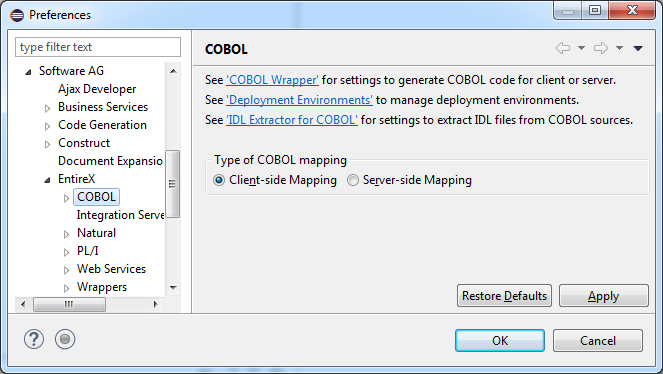
For more information on handling the different types of COBOL mapping, see Server Mapping Files in the Designer.
In client-side mapping mode, it is not possible to modify server-side mapping files (Designer files with extension .svm). This means that if there is a related server-side mapping file available for an IDL file, you cannot use the
IDL Extractor for COBOL to extract an additional interface or modify an existing one
COBOL Wrapper to generate an RPC Server
You have to migrate the server-side mapping files first. See Migrating Server Mapping Files.
In server-side mapping mode, it is not possible to modify client-side mapping files (Designer files with extension .cvm). This means that if there is a related client-side mapping file available for an IDL file, you cannot use the
IDL Extractor for COBOL to extract an additional interface or modify an existing one
COBOL Wrapper to generate an RPC Server
Later on, you can readjust the mode in the Preferences of the respective tool. See COBOL Preferences or Generation Settings - Preferences in the COBOL Wrapper documentation.
A server mapping file (Designer file with extension .cvm or .svm) is generated by the IDL Extractor for COBOL if the COBOL server program is of a specific interface type, contains specific COBOL syntax, or the IDL interface is redesigned (Suppress, Set constant, etc.) in the COBOL Mapping Editor. The type of server mapping (server-side with extension .svm or client-side with extension .cvm) is defined in a preference that applies to the entire Designer (Eclipse) workspace. See How to Set the Type of Server Mapping Files.
| Interface Type | COBOL Syntax | COBOL Mapping Editor | Server Mapping Required |
More Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CICS DFHCOMMAREA and In different to Out | all | yes | CICS with DFHCOMMAREA Calling Convention - In different to Out under COBOL Mapping Editor in the IDL Extractor for COBOL documentation (1) and the following COBOL server examples for CICS input message different to the CICS output message:
|
|
| CICS Channel Container | all | yes | CICS with Channel Container Calling Convention | |
| CICS Large Buffer | all | yes | CICS with DFHCOMMAREA Large Buffer Interface |
|
| COBOL Converter and In different to Out | all | yes | COBOL Converter (2) | |
| IMS MPP (IMS Connect) | all | yes | IMS MPP Message Interface (IMS Connect) | |
| IMS BMP | all | yes | IMS BMP with Standard Linkage Calling Convention | |
| Micro Focus | BINARY clause, see COBOL Data Type to Software AG IDL Mapping under COBOL to IDL Mapping in the IDL Extractor for COBOL documentation
|
yes | Micro Focus with Standard Linkage Calling Convention | |
| CICS DFHCOMMAREA, CICS Channel Container, CICS Large Buffer, IMS MPP (IMS Connect), COBOL Converter | OCCURS clause, see COBOL Tables with Fixed Size |
Set Arrays (Fixed <-> Unbounded) | yes | See Set Array Mapping (fixed <-> unbounded) for interface type DFHCOMMAREA (In same as Out, In different to Out) | Large Buffer (In same as Out, In different to Out) | Channel Container | IMS Connect | COBOL Converter (In same as Out, In different to Out) (1, 2) |
| all | OCCURS clause, see COBOL Tables with Fixed Size |
Map to | no | See Map to for interface type DFHCOMMAREA (In different to Out) | Large Buffer (In different to Out) | Channel Container | IMS Connect | COBOL Converter (In different to Out) (1,2) |
| Map to In, Out, InOut | See Map to In, Out, InOut for interface type DFHCOMMAREA (In same as Out) | Large Buffer (In same as Out) | Batch | IMS BMP | Micro Focus | COBOL Converter (In same as Out) (1,2) | |||
| CICS DFHCOMMAREA, CICS Channel Container, CICS Large Buffer, IMS MPP (IMS Connect), COBOL Converter | COBOL group data items used in optional manner, see Optional COBOL Group Data Items | Set multiple possible output structures (MPO) | yes | See Set Multiple Possible Output (MPO) Structures for interface type DFHCOMMAREA (In same as Out, In different to Out) | Large Buffer (In same as Out, In different to Out) | Channel Container | IMS Connect | COBOL Converter (In same as Out, In different to Out) (1,2) |
| all | COBOL group data items | Map to | no | See Map to for interface type DFHCOMMAREA (In different to Out) | Large Buffer (In different to Out) | Channel Container | IMS Connect | COBOL Converter (In different to Out) (1,2) |
| Map to In, Out, InOut | See Map to In, Out, InOut for interface type DFHCOMMAREA (In same as Out) | Large Buffer (In same as Out) | Batch | IMS BMP | Micro Focus | COBOL Converter (In same as Out) (1,2) | |||
| all | OCCURS DEPENDING ON clause, see COBOL Tables with Variable Size - DEPENDING ON Clause |
Map to | yes | See Map OCCURS DEPENDING ON for interface type DFHCOMMAREA (In different to Out) | Large Buffer (In different to Out) | Channel Container | IMS Connect | COBOL Converter (In different to Out) (1,2) |
| Map to In, Out, InOut | See Map OCCURS DEPENDING ON for interface type DFHCOMMAREA (In same as Out) | Large Buffer (In same as Out) | Batch | IMS BMP | Micro Focus | COBOL Converter (In same as Out) (1,2) |
|||
| CICS DFHCOMMAREA, CICS Channel Container, CICS Large Buffer, IMS MPP (IMS Connect), COBOL Converter | REDEFINES clause, see REDEFINES Clause |
Set multiple possible output (MPO) structures | yes | Set Multiple Possible Output (MPO) Structures for interface type DFHCOMMAREA (In same as Out, In different to Out) | Large Buffer (In same as Out, In different to Out) | Channel Container | IMS Connect (1,2) |
| Map to | COBOL REDEFINES can be used in several ways:
|
|||
| Map to In, Out, InOut | COBOL REDEFINES can be used in several ways:
|
|||
| Batch, IMS BMP, Micro Focus | REDEFINES clause, see REDEFINES Clause |
Map to In, Out, InOut | yes | COBOL REDEFINES can be used in serveral ways:
|
| all | SIGN LEADING [SEPARATE] clause, see SIGN LEADING and TRAILING SEPARATE Clauses |
yes | ||
| all | SIGN TRAILING [SEPARATE] clause, see SIGN LEADING and TRAILING SEPARATE Clauses |
yes | ||
| all | SYNCHRONIZED clause, see SYNCHRONIZED Clause |
yes | ||
| all | all | Rename of program | yes | See Map to Multiple IDL Interfaces for interface type DFHCOMMAREA (In same as Out, In different to Out) | Large Buffer (In same as Out, In different to Out) | Channel Container | Batch | IMS BMP | Micro Focus | IMS Connect | COBOL Converter (In same as Out, In different to Out) (1,2) |
| all | Set to constant | yes | See Set COBOL Data Items to Constants for interface type DFHCOMMAREA (In same as Out, In different to Out) | Large Buffer (In same as Out, In different to Out) | Channel Container | Batch | IMS BMP | Micro Focus | IMS Connect | COBOL Converter (In same as Out, In different to Out) (1,2) | |
| all | See Unneeded COBOL Data Items | Suppress | yes | Suppress Unneeded COBOL Data Items for interface type DFHCOMMAREA (In same as Out, In different to Out) | Large Buffer (In same as Out, In different to Out) | Channel Container | Batch | IMS BMP | Micro Focus | IMS Connect | COBOL Converter (In same as Out, In different to Out) (1,2) |
| other combinations | no | |||
Notes:
A server mapping file (Designer file with extension .cvm or .svm) is generated by the COBOL Wrapper if an RPC server is generated (1,2) and at least one IDL program meets the criteria in the table below. The type of server mapping (server-side with extension .svm or client-side with extension .cvm) is defined in a preference that applies to the entire Designer (Eclipse) workspace. See How to Set the Type of Server Mapping Files.
| Interface Type | IDL Type | COBOL Wrapper | Server Mapping Required |
More Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CICS Large Buffer | all | yes | CICS with DFHCOMMAREA Large Buffer Interface under COBOL Server Interface Types in the COBOL Wrapper documentation
|
|
| CICS Channel Container | all | yes | CICS with Channel Container Calling Convention | |
| IMS BMP | all | yes | IMS BMP with Standard Linkage Calling Convention | |
| Micro Focus | I2 or I4 | yes | Micro Focus with Standard Linkage Calling Convention | IDL Data Types | |
| all | IDL unbounded array | yes | array-definition under Software AG IDL Grammar in the IDL Editor documentation
|
|
| all | IDL unbounded group | yes | group-parameter-definition |
|
| all | all | IDL program name is not a valid COBOL name and is therefore adapted, or the COBOL program name is customized | yes | Customize Automatically Generated Server Names under Generating COBOL Source Files from Software AG IDL Files in the COBOL Wrapper documentation |
| other combinations | no | |||
| (1) | Server mapping files are never generated for RPC clients. |
This section covers the following topics:
Server-side mapping files (Designer files with extension .svm) can be migrated to client-side mapping files (Designer files with extension .cvm).
Note:
Client-side mapping files are not supported by RPC clients generated with the DCOM Wrapper and COBOL Wrapper.
All EntireX components involved in the migration must be version 9.7 or higher:
the target RPC server z/OS (CICS | Batch | IMS), CICS ECI, IMS Connect, Micro Focus
the webMethods EntireX Adapter for Integration Server. See EntireX and your webMethods Integration Server Applications
the RPC client runtimes
Rename the extension .svm to .cvm in the Designer. This results in a client-side mapping file.
Remove the server-side mapping files in the server-side mapping container of the target RPC server. See Undeploying Server-side Mapping Files in the RPC server documentation for z/OS (CICS, Batch, IMS) | Micro Focus | CICS ECI | IMS Connect | BS2000 | z/VSE (CICS | Batch).
Note:
For IMS Connect and CICS ECI connections with webMethods EntireX Adapter for Integration Server, this step is not required.
Re-create (wrap, build, compile etc.) all involved RPC clients (1) using the related IDL file to wrap the client-side mapping files into the client interface objects. See EntireX Wrappers.
Test the RPC clients with client-side mapping files.
If necessary, re-deploy the RPC clients with client-side mapping files.
| (1) | This includes all variants of RPC connections of the webMethods EntireX Adapter for Integration Server. See webMethods Integration Server Wrapper. |
Because server mapping files (Designer files with extension .cvm or .svm) contain text data only, a server mapping file is text-based (although it is not intended for human consumption). Therefore, you can include it in your source control management together with the IDL file and the COBOL source(s) as a triplet that should always be kept in sync.
For server mapping files (Designer files with extension .cvm or .svm), you can use a third party file/text compare tool to check if two files are identical.
A server mapping entry (corresponding to a line in a server mapping file) contains a creation timestamp at offset 276 (decimal) in the format YYYYMMDDHHIISST. The precision is 1/10 of a second.