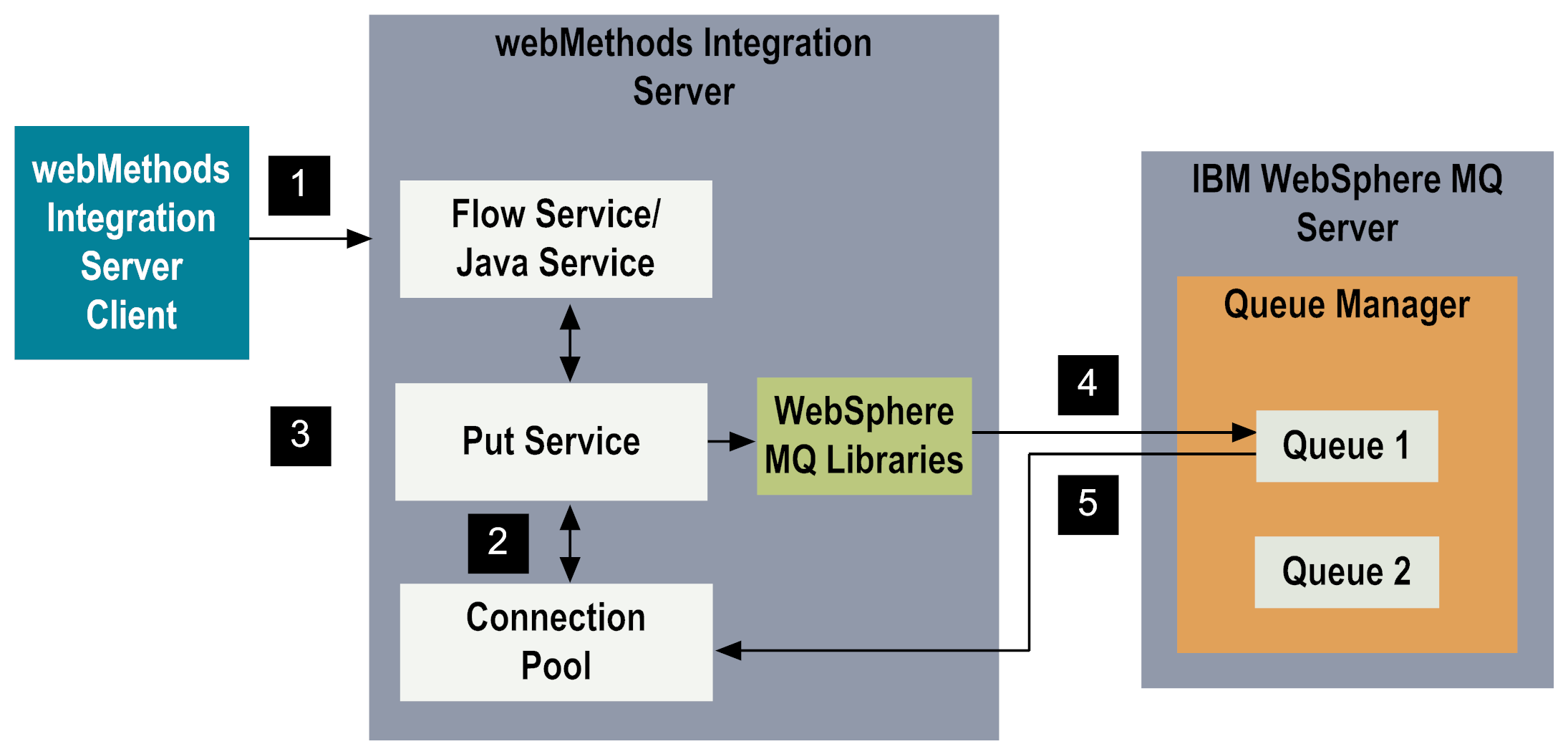

Step | Description |
1 | A flow or Java service, typically invoked by an Integration Server client, initiates the Put service on Integration Server. You configure the Put service and the wrapping flow or Java service, using Designer. |
2 | The Put service retrieves a connection from the service's associated connection pool. You configure and enable the adapter connection using Integration Server Administrator. For more information about connection pooling, including the runtime behavior of connection pools, see
Connection Pools. |
3 | WebSphere MQ Adapter uses the Put service's input document, or the msgHeader properties from the Put service's input signature, to create an MQMessage object. You define the Put service's input signature when you configure the service. Using Designer, the fields that you select on the MQMD Header tab and the JMS Properties tab in the adapter service become the service's input signature. The following diagram illustrates the Put service's input signature, or input document, where the msgBody value is copied to the MQMessage payload: 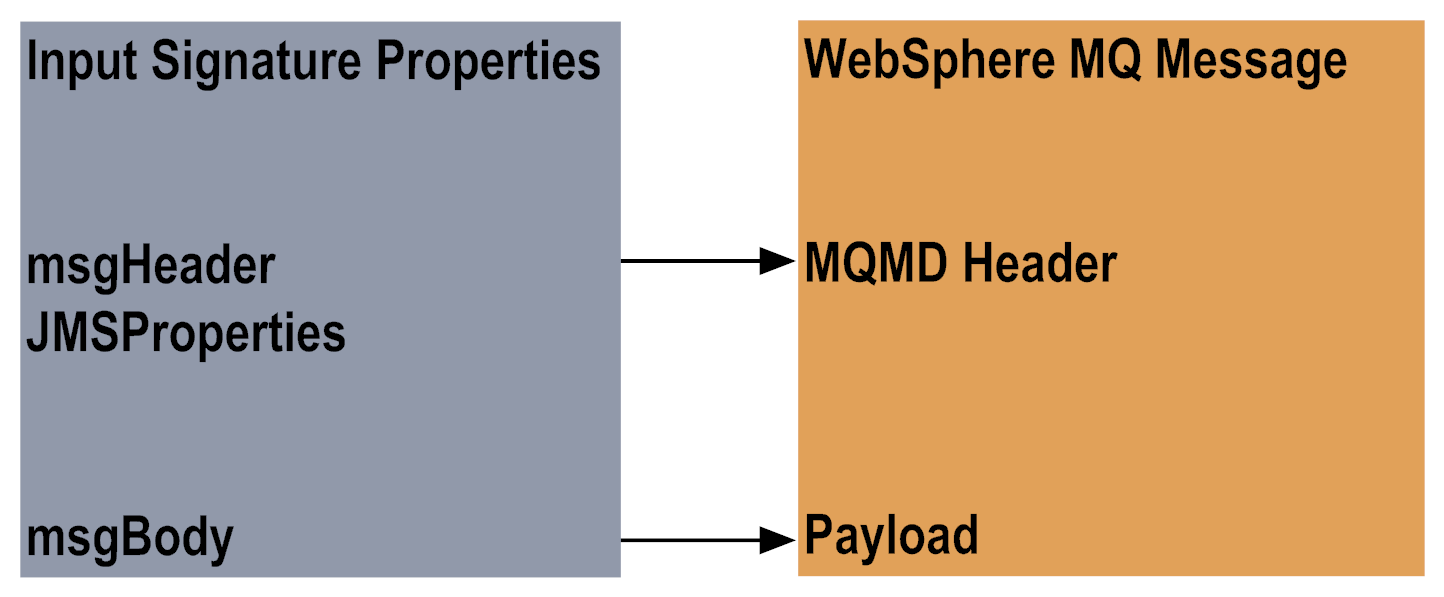 |
4 | WebSphere MQ Adapter puts the MQMessage object on the WebSphere MQ queue. |
5 | The Put service returns a document that contains the msgHeader fields. You define the Put service's output signature, or output document, when you configure the service. The fields that you select on the MQMD Header tab become the service's output signature. The reasonCode, conditionCode, and errorMsg properties are also returned in the output signature's document. The following diagram illustrates the Put service's output signature where the MQMD fields are copied back to the msgHeader document: 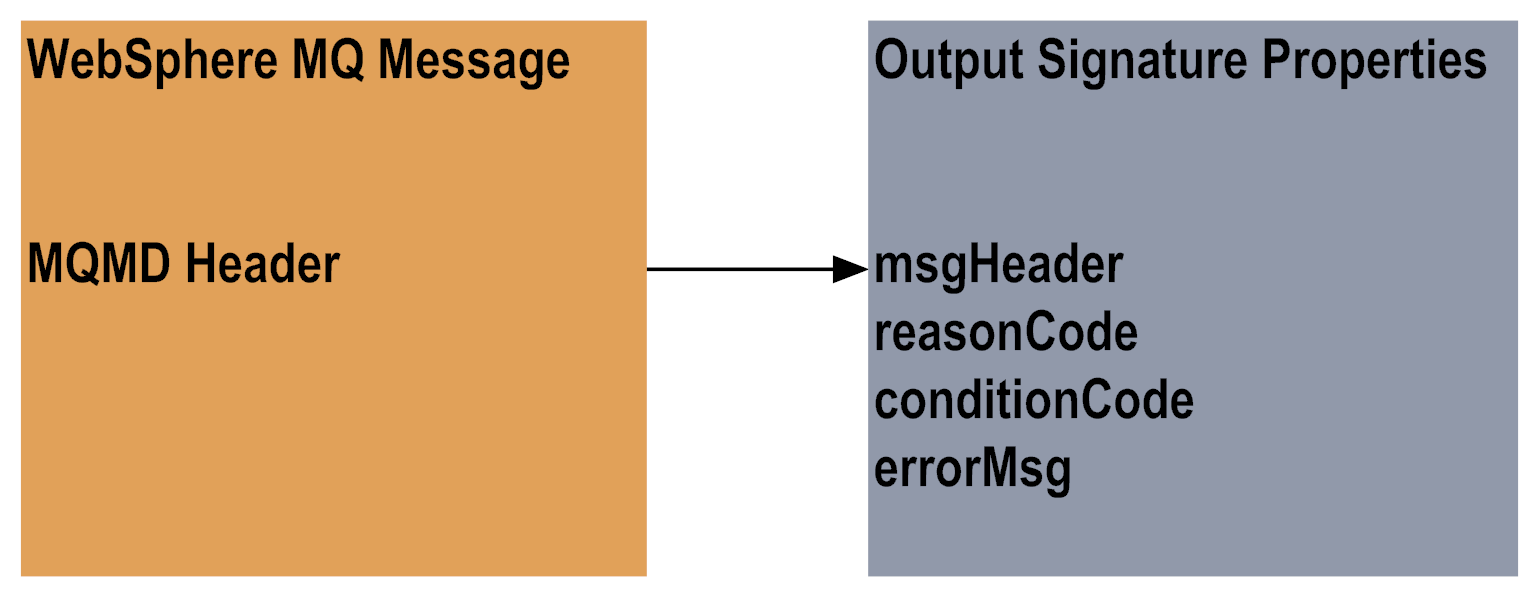 |