This document covers the following topics:
The following graphic shows how Unicode data and parameters are accessed.
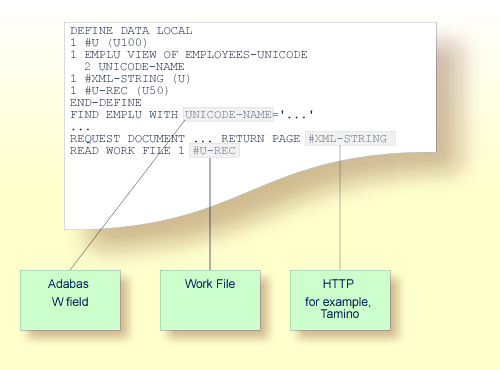
Natural enables users to access wide-character fields (format W) in an Adabas database.
- Data Definition Module
Adabas wide-character fields (W) are mapped to the Natural data format U (Unicode).
- Access Configuration
Natural receives data from Adabas and sends data to Adabas using UTF-16 as common encoding.
Before accesing unicode data in an Adabas database, you must set the correct
OPRBparameter innatparm. The currentOPRBparameter values are sent to Adabas with the open request. The values are used for wide-character fields and apply to the entire Adabas user session.
For detailed information, see Unicode Data in the Accessing Data in an Adabas Database part of the Programming Guide.
The following topics are covered below:
The information below applies for the statement WRITE WORK FILE. See the Statements
documentation for detailed information on this statement.
The following work file types write code page data:
ASCII and ASCII compressed
Unformatted
CSV
Entire Connection
The work file type and the code page must be defined in the Configuration Utility. For further information, see Work Files in the Configuration Utility documentation.
All Natural data defined with the operands A (alphanumeric) and U (Unicode) are
converted to the specified code page. If a code page has not been specified, all data
are converted to the default code page which is defined with the CP parameter.
Note
In the work file, all written A and U operand data are in code page format.
If U operand data are to be written into these work files and afterwards read from
these work files without loss of data, you have to define UTF-8 as the code page (in the
Configuration Utility). In this case, all A and U operand data are written in UTF-8
format. A subsequent READ WORK FILE statement where the work file is also
configured using code page UTF-8 reads the operand U data without loss of data.
Notes:
If one of the above-mentioned work file types is specified and the code page UTF-8 is
defined for the work file, the work file attributes BOM (write byte order
mark) and NOBOM (do not write byte order mark) take effect. These
attributes can be specified in the Work
Files category of the Configuration Utility and with the
DEFINE WORK FILE statement.
If the code page UTF-8 is defined for the work file and the work file attribute
BOM is specified, the UTF-8 byte order mark (hexadecimal representation:
H'EFBBBF') is written at the beginning of the work file, in front of the
work file data.
If a work file type other than the above-mentioned work file types is used for writing
the work file, or if a code page other than UTF-8 is defined for the work file, the
specification of the attribute BOM is ignored during runtime. The following
table shows the runtime behavior during the processing of the statements WRITE
WORK FILE and READ WORK FILE:
| Code Page and Attribute Setting | WRITE WORK FILE |
READ WORK FILE |
|---|---|---|
|
The code page UTF-8 is not specified for the work file (default). The work file attributes |
No UTF-8 byte order mark is written. No conversion to UTF-8. |
No check for UTF-8 byte order mark. No conversion from UTF-8. |
|
The code page UTF-8 is specified for the work file. The work file attribute |
UTF-8 byte order mark is written. A and U fields are converted to UTF-8. |
Check for UTF-8 byte order mark. If an UTF-8 byte order mark is found, it is removed from the work file data. A fields are converted from UTF-8 to the default code page. U fields are converted from UTF-8 to the Natural internal runtime representation UTF-16. |
|
The code page UTF-8 is specified for the work file. The work file attribute |
No UTF-8 byte order mark is written. A and U fields are converted to UTF-8. |
Check for UTF-8 byte order mark. If an UTF-8 byte order mark is found, it is removed from the work file data. A fields are converted from UTF-8 to the default code page. U fields are converted from UTF-8 to the Natural internal runtime representation UTF-16. |
The following work file types write binary data (for example, UTF-16 for operand format U):
SAG
Portable
Natural data defined with the operands A and U are not converted to code page. These data are written to the work file in binary format. For U operand data, this is done in UTF-16.
The information below applies for the statement READ WORK FILE. See the Statements
documentation for detailed information on this statement. Take note of the restrictions
that are listed for the RECORD option.
When the following work file types are used, the work file data that are read into Natural U (Unicode) operands are converted from the specified code page to UTF-16.
ASCII and ASCII compressed
Unformatted
CSV
Entire Connection
Data that are read into A (alphanumeric) operands are converted, if required, from the
specified code page to the default code page which has been defined with the parameter
CP.
If one of the above-mentioned work file types is specified and the code page UTF-8 is
defined for the work file, the READ WORK FILE statement automatically
checks the work file for an UTF-8 byte order mark. If an UTF-8 byte order mark is found
at the beginning of the work file, it is removed. The data that are read from the work
file are converted from UTF-8 to the default code page.
If data are read from another work file type, the check for a byte order mark is not performed and a byte order mark is therefore not removed.
For information on the runtime behavior during the processing of the statements
WRITE WORK FILE and READ WORK FILE, see the table in the
previous section.
When the following work file types are used, the work file data are read into the Natural operands A and U without conversion (that is: they are read in binary format):
SAG
Portable
The work file type Portable supports endian conversion for data of operand format U.
Operand format U is generally supported for the work file type Transfer. If Entire Connection is not able to read or write Unicode for the selected file type, a runtime error message is displayed.
The handling for Unicode data in print files depends on the selected logical device’s (LPT1 to LPT31) print method, currently either GUI (Windows only) or TTY.
Regardless of the print method, data are passed to the Natural printing services in UTF-16 format. That is, any format A field data will already have been converted to Unicode.
With this Windows-only print method, the data are passed to the Windows printer driver in Unicode (UTF-16) format. Because this is the standard method for printing data in Windows, the driver invariably handles this data appropriately. This is therefore the recommended print method under Windows if any characters that are not within the system code page are being used.
With this print method, the data are, by default, converted from the internal (UTF-16) format into the system code page. However, by using a printer profile, it is possible to specify that the data should instead either be converted into UTF-8 format, or be subjected to an additional conversion to an arbitrary external code page. For more information on these alternatives, see Printer Profiles in the Configuration Utility documentation.
The rationale behind the default behavior of converting the data into the system code page is based on the current lack of printers capable of directly accepting raw text files in UTF-8 format.