This document describes how to set up Super Natural to suit your environment and covers the following topics:
 To initialize Super Natural
To initialize Super Natural
Execute the Super Natural initialization function with:
LOGON SYSSN SNINIT
The user DBA and the default user
******* are defined and the Super
Natural Administration Application is invoked.
The administrator is defined as an authorized user who may use the Super Natural Administration Application.
 To add / link users and files
To add / link users and files
Add/link additional users and files to Super Natural using the Super Natural Administration Application as described in the following instruction.
 To define files and users
To define files and users
When Natural Security is not installed, the following sequence is recommended when defining files and users to Super Natural:
Define files to Super Natural using the
Add Files function.
Note:
For DL/I files, the options Physical Read
Allowed, Display Values for Key Fields and
Adabas Sorting Allowed must be set to
N.
Set default user options by modifying the default user
*******.
Note:
The user options of the default user
******* are used as a basis when adding
Super Natural users.
Define users to Super Natural using the
Add User function, and create a file list for them
using either the Modify User >Files function or
the Modify File >Users function.
Now files are defined to Super Natural, users
are defined to Super Natural with default user
option settings, and each user definition includes an associated file list. You
can now modify users and files further using the Modify
User and Modify File functions.
The hierarchy of the specific file and user option settings is discussed in the Administration documentation.
When Natural Security is installed, the
application SYSSN must be defined (without protection) to the
Natural Security system before it can be used.
Note:
If Super Natural replaces an existing
older version running with Natural Security, remove
the startup program MENU from the library profile
SYSSN (this prevents installation errors when loading help texts
with SNLOAD). After the installation is completed, set the startup
program again to MENU.
SYSSN must be installed with Programming Mode
Reporting.
 To define mandatory command processors to Natural Security
To define mandatory command processors to Natural Security
Link the following command processor to the application
SYSSN using Additional Options in Functional Security:
MNSPCMD1 |
Super Natural Maintenance |
Set the Keyword defaults to ALLOWED.
Link the following command processors to the library
SYSLIB using Additional Options in Functional Security:
NRMNSNS1 |
Natural Report Manager - Maintenance |
NRM-CMD1 |
Natural Report Manager - Testing |
Set the Keyword defaults to ALLOWED.
 To define language-dependent command processors to Natural
Security
To define language-dependent command processors to Natural
Security
Link the following command processor to the application
SYSSN using Additional Options in Functional Security:
NSP-CMDn |
Super Natural Processor Where n is replaced by the language code number of the language you want to install. |
Set the Keyword defaults to ALLOWED.
Link the following command processors to the library
SYSLIB using Additional Options in
Functional Security:
NRMNSN0n |
Natural Report Manager - Processor |
NRM-CMDn |
Natural Report
Manager - Testing (not necessary if installing English version) Where n is replaced by the language code number of the language you want to install. |
Set the Keyword defaults to ALLOWED.
 To initialize Super Natural
To initialize Super Natural
Execute the Super Natural initialization function with:
LOGON SYSSN
SNINIT
The administrator is defined as an authorized user who may use the
Super Natural Maintenance System.
The
user DBA and the default user
******* are defined and the Super
Natural Maintenance System is invoked.
The Super Natural administrator should now define additional authorized Super Natural users and files as described below.
 To modify the application
To modify the application SYSSN
Once SNINIT has been executed successfully, do
the following:
Modify the application SYSSN to people
protected.
Allow command mode.
Set the startup and restart programs to MENU.
Set the error program to SNRTE.
 To link users and files
To link users and files
Link at least one user to the application.
Link private files to be used to library SYSSN.
Add/link users and files to Super Natural using the Super Natural Administration Application as described in the following instruction.
 To define files and users
To define files and users
When Natural Security is installed, it is recommend that the following sequence be followed when defining files and users to Super Natural:
Set default user options by modifying the default user
*******.
Note:
The user options of the default user
*******are used as a basis when
addingSuper Natural users.
Import users and their associated private files to Super
Natural by using the Import User
function.
Only private files that are linked to application SYSSN
are available for this function.
Note:
For DL/I files, the options Physical Read
Allowed, Display Values for Key Fields and
Adabas Sorting Allowed must be set to
N.
Import public files to Super Natural by
using the Import File function.
Note:
For DL/1 files, the options Physical Read
Allowed, Display Values for Key Fields and
Adabas Sorting Allowed must be set
toN.
Modify users' file lists by using the Modify User
>Files function to add public files to their file lists, or
modify the public files' users list by using the Modify File
>Users function.
Now files are defined to Super Natural, users
are defined to Super Natural with default user
option settings, and each user definition includes an associated file list with
private and public files that can be used through Super
Natural. At this point, individual option settings may be changed
for files and users using the Modify User and
Modify File functions.
The hierarchy of the specific file and user option settings is discussed in the Administration documentation.
Note:
for BS2000/OSD users:
If you wish to run batch while
online, ETID parameters must not be generated (see the
Natural Security documentation).
The master DDM for the Super Natural personal database is cataloged on Database 0, File Number 90 in accordance with the following naming conventions:

It shows the compatibility format to former Super Natural versions and can be used if the DBID and FNR are in the following range.
| DBID | 0 - 254 |
| FNR | 1 - 255 |
The general format for the master DDM enabling even for a DBID greater than 255 and/or a FNR greater than 255 is as follows:
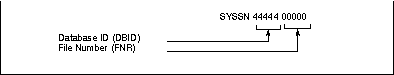
The DBID and FNR are in the following range:
| DBID | 0 - 65535 |
| FNR | 1 - 5000 |
The DBID and FNR must be renamed and recataloged to correspond to the actual DBID and FNR of the Adabas file installed in Step 2 of the installation procedure. This DBID and FNR must also be entered in the options User File Adabas Database ID and User File Adabas File Number (see User Options).
Note:SYSSN must not be renamed.
If there are inconsistencies in the user and default options, users receive one of the following error messages when invoking the File List screen:
| Adabas Response Code | Natural Error |
|---|---|
| 148 | NAT3148 |
| 017 | NAT3017 |
| 061 | NAT3061 |
It is also possible to have multiple Personal Databases (one physical Adabas file required per Personal Database). Use of these files is defined by these DBID and FNR option settings.
The field list may be restricted within the DDM, thus enabling the Super Natural administrator to control the use of the file.
Note:
The field with the Adabas short name AA
must never be changed.
If Natural Security is installed, note that
all user files created on the Personal Database will automatically be defined
as Natural Security private files and automatically
be linked to the application SYSSN.
The size of the Natural runtime buffer is determined by the Natural
profile parameter RUNSIZE, and the size of the
user-buffer extension area is determined by the profile parameter
ESIZE (see the Natural Parameter
Reference documentation). We recommend the following parameter
settings:
| Buffer | Size |
|---|---|
RUNSIZE |
20 |
ESIZE |
45 |
ESIZE is dependent on the size of the DDMs you
are dealing with and the number of fields used. Some transactions may need
larger values than those listed above.
For an example of the buffer sizes needed by the transactions SAMPLE2 and SAMPLE3 (described in the Tutorial), see Technical Information.
Super Natural uses the
Natural user system file (FUSER) to
store and maintain the following:
- Authorized Users
A record is maintained for each Super Natural user. The record contains the user's default options, a list of the files which the user is authorized to access and an entry for the user's authorization to the Super Natural Maintenance System.
Note:
The profiles of the Natural Report Manager are stored on the Natural system system fileFNAT.- Files
A record is maintained for each file on which Super Natural transactions are to be performed. These files must have a corresponding Natural DDM in the dictionary file (
FDIC).- Transaction Programs
When a user saves or runs a new transaction, a Natural program is generated from the transaction specification and this program is saved and cataloged like any other Natural program. The transaction specification information is stored as comment lines at the beginning of the generated Natural program to facilitate transaction modification.
The Natural library name used for transaction programs is generated as follows:
The first character is the private library prefix (defaultY).
The second through eighth characters are the User ID of the user.Super Natural also supports read-only public libraries which have corresponding Natural libraries where the first character is the public library prefix (default
Z). A transaction may be copied into a public library using the Super Natural Maintenance Application. The transaction program names in both private and public libraries are constructed as follows:
The first character is the transaction prefix (defaultI)
The second through eighth characters are the Transaction ID as specified by the user.- Common Libraries
List of common libraries.
- Help Text
Super Natural help texts.
Note:
If you are using a new Natural system user
file (FUSER), use the utilities SNULD and SNLOAD to move
Super Natural data created in a former
Natural environment.
SYSSN is the Super
Natural system library. SYSSN is in the
Natural system system file (FNAT) and
is used to store and maintain the following:
The Natural programs comprising the
Super Natural system are provided in INPL object
form for loading (using the Natural INPL facility) into the
Natural library SYSSN.
The system exit programs SPRJEU, SPPARM,
EXIT, SNERRU and ENTRY are provided in
source form which you can modify. For further information, see
Customizing Super
Natural.
The batch utilities SNULD, SNLOAD and SNDELUF are provided in object form. For further information, see Batch Utilities.
- SNELOG
Service program for reviewing the error protocol. You can use the error protocol to see whether errors are environment-specific, for example, size problems, or printer or work file assignment problems. For further information on error logging, see Error Logging.
SNTALOGService routine for reviewing Status Reports written if the option
DDM Check on Modifyis set and deviations are detected in a transaction.SNTAONService routine which activates status reporting. The Status Reports are written to the Personal Database. If you invoke
SNTAONusing theNOUSERparameter, user IDs are not recorded in the status report.SNTAOFFService routine which deactivates status reporting. It deletes all Status Reports
In the library SYSSN, Super
Natural provides the following system exit programs in source
form, which may be modified to customize Super
Natural to the needs of your user site. At the beginning of each
program, there is a detailed program description.
- EXIT
Program invoked as exit routine when the Super Natural session is terminated.
SNERRUProgram invoked by error routine
SNRTE.SNERRUcan be modified to handle specific error conditions. For example, you can useSNERRUto give the user additional information or instructions when an error occurs.SPRJEUNatural subprogram which is executed once for every job card prior to the submission of a batch job.
SPPARMSubprogram to define environment specific parameter settings. Parameters include:
- The submission indicator for batch job submission (RJEorNPR)
- Com-plete hardcopy support - default printer number generation or prompting for destination (default)
- Common library prefix character
- Layout prefix characterENTRYProgram invoked as entry routine for the Super Natural session.
The Report function displays a list of errors showing date, time, error number, type of error, program, line and user (if not deactivated using theNOUSERparameter). If you move the cursor to an error line and press ENTER, you receive further information concerning the error.
The Delete function deletes the current list of errors.SHEXITProgram which takes over if the user presses CLEAR.
Using Super Natural inverse mode, you can display right-to-left languages (such as Arabic and Hebrew) provided that the appropriate hardware facilities are available. All input and output fields are displayed in inverse mode.
The Super Natural administrator defines which language code each user will use for inverse mode by setting the user option Language Code for Inverse Mode in that user's user profile. For further information, see Users. If the user selects this language code in his/her user profile, the terminal display is switched.
If the files Super Natural users are accessing in inverse mode contain only data in inverse format, no further set-up requirements need be considered.
If a file contains both fields with data in regular format (to be displayed from left to right) and fields with data in inverse format (to be displayed from right to left), the Super Natural administrator must prepare the Super Natural environment accordingly.
Super Natural must be able to distinguish between fields of regular and inverse format for all data maintenance and reporting functions. If this distinction is not made, both field types are treated alike and the resulting data is unusable. If the distinction between regular and inverse format data is made, Super Natural can display regular format fields from left to right when accessing the mixed file in inverse mode.
So that Super Natural can distinguish
between the two field types of a mixed file, fields with regular format must be
indicated by a prefix in the field name when the file is designed. For example,
you could define regular format fields with the prefix
reg-, as in REG-NAME,
REG-CITY, etc. This prefix must also be specified in the
mixed file's file option Prefix for Inverse Field
Output. Users do not need to distinguish between the two field
types when operating in inverse mode as Super
Natural adjusts the corresponding field formats automatically.
Users can maintain and display data of any field type regardless of field
format.
You must consider the following when operating Super Natural in inverse mode with mixed files:
Define all names of fields that are to contain data in regular format (from left to right) with a prefix when creating the file.
Use the same prefix for the file's option Prefix for Inverse Field Output.
Set the option Language Code for Inverse Mode to the appropriate code for each user who is to operate in inverse mode.
Advise users to only access mixed files in inverse mode.
If you proceed with the examples 9 to 11 of the Tutorial you have to provide the data you have selected with the transaction to your Natural for Windows environment for further processing.
The following steps describe how to load the example application from the Documentation CD and to set up your environment.
 To load the example application
To load the example application
If you want to set up your
Natural for Windows in order to use the
Super Natural RPC Service, set up the
NATPARM parameter module according to the recommondation. For
further information, see the Natural documentation
sectionRemote Procedure Call > Setting up a Natural
Client. Furthermore, ensure that your connections and servers are
active.
Open Natural for Windows.
Execute the Natural for Windows Unload Utility by selecting .
The Unload Utility window appears:
Enter L in theCode
field.
Press ENTER.
Select the button and enter the path of the workfile you want to load to your Natural for Windows environment: .
Press ENTER.
Enter A in the Code
field to determine that you want to load all data.
Press ENTER until you reach the screen of Step 7.
All data for the sample application is loaded.
Exit the Unload Utility by entering . in
the Code field.
 To set up your Natural environment for the tutorial example data
To set up your Natural environment for the tutorial example data
Go to the user library you expect the sample application (here
NSNSAMPL) and refresh it.
NSNSAMPL is placed in the user library
now.
Execute .
Select .
Add the library NSNSAMPL and the corresponding
subprograms RPCSMPL1, RPCSMPL2 and
RPCSMPL3.
Select OK.
Go to the library
and copy the subprogram NATCLTGS to the library NSNSAMPL
> Subprograms.
Your Natural environment is now ready to use for the tutorial RPC examples.