This documentation describes the installation of the Open Print Option (OPO) component of Entire Output Management on a Windows or Linux platform.
OPO is installed using the Software AG Installer, which you download from the Software AG Empower website at https://empower.softwareag.com/.
This documentation provides product-specific instructions for installing OPO. It is intended for use with Using the Software AG Installer. That guide explains how to prepare your machine to use the Software AG Installer, and how to use the Software AG Installer and Software AG Uninstaller to install and uninstall your products. The most up-to-date version of Using the Software AG Installer is always available at http://documentation.softwareag.com/ (Empower login required).
This documentation is organized under the following headings:
Before you install OPO, make sure that the desired EntireX broker is accessible.
In the EntireX broker, the appropriate RPC server parameters must be defined.
The person performing the installation must have administrator rights.
During the installation, you are asked to specify an installation
directory. Specify the installation directory in which to install your Software
AG products. We recommend that you use the SoftwareAG directory as
the location for OPO. But any other directory is also possible.
Important:
It is recommended that you do not install into a
directory which is a subdirectory of a previous installation. Such a previous
installation may have been created either with the Software AG Installer or by
an installation tool that was used in the past.
For information regarding side-by-side installations, see Installation in the Natural for UNIX documentation. What is said there about Natural also applies to OPO.
By default, the OPO installation procedure uses the following log files for additional information during the installation/uninstallation, especially in case of errors:
installLog.txt and uninstallLog.txt
in the directory install/logs below the installation
directory;
the Windows event log on Windows.
 To install OPO:
To install OPO:
Start the Software AG Installer GUI as described in Using the Software AG Installer.
When the first page of the Software AG Installer GUI (the so-called Welcome panel) is shown, choose the button repeatedly (and specify all required information on the shown panels as described in Using the Software AG Installer) until the panel containing the product selection tree appears. This tree lists the products you have licensed and which can be installed on the operating system of the machine on which you are installing.
To install OPO with all of its product components, expand the Natural Products node and select Entire Systems Management > Entire Output Management Open Print Option.
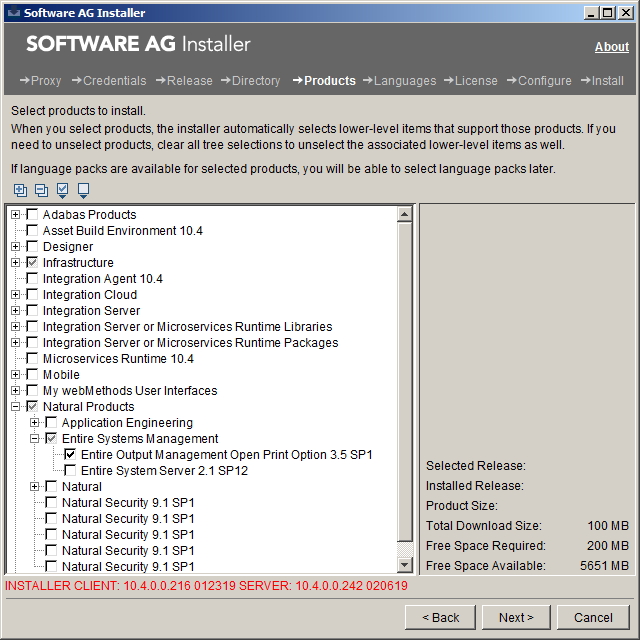
The installer automatically selects any additional components which are also required. This includes EntireX Libraries, if not already installed.
Note:
If an instance of EntireX is already installed on your
machine, you can use this instance by specifying the path to its 32-bit
libraries in the environment variable OPO_EXX_LIB_PATH. Please
note that even on 64-bit platforms the OPO executable nomrpt.exe
is only available as a 32-bit application.
Choose the button.
Read the license agreement, select the check box to agree to the terms of the license agreement, and choose the button.
Note:
If you are installing other products together with OPO,
several panels may appear that are not explained in this documentation. See the
documentation for these products for more information.
On the last panel, review the list of products and items you have selected for installation. If the list is correct, choose the button to start the installation process.
In the case of a first-time installation, then proceed as described under Configuration below.
The directory of the Open Print Option you have installed contains
the configuration file nomrptConf.xml. Adjust this file in
accordance with your environment. It contains the following parameters:
| Parameter | Explanation |
|---|---|
BlockName |
The name of the parameter block (see also below). |
EXX_Server |
The name of the broker. |
EXX_User
|
The user ID for the broker. |
EXX_Password
|
The password of this user. |
EXX_Ciphered_Password |
The encrypted password of this user.
The encrypted password can be generated with the
executable If both |
RPC_Server
|
The name of the Entire Output Management RPC server which logs on the broker as RPC server. |
RPC_User
|
The user ID for the Natural logon to the RPC server. This user ID must also be specified in the *USER field under Natural Attributes in the definition of any report to be printed via OPO. Further Natural Attributes are not required. If Natural Security is installed, this user ID must be a valid Natural Security user ID. See Report Identification for Natural in the User's Guide. |
RPC_Password
|
The password for this user. |
RPC_Ciphered_Password |
The encrypted password of this user.
The encrypted password can be generated with the
executable If both |
Nat_Library
|
The Natural library to which the logon is performed (SYSSAT). |
Trace_Level |
0 = no trace; For |
Input_Format
|
Possible values:
If you use For binary data, see also Transferring Binary Data below. |
Input_Codepage |
The name of the code page which contains the text
data. This has to be specified only if Input_Format X is used.
The name of the code page must be made known to Natural on the server, as described in the section SYSCP Utility - Code Page Administration of the Natural documentation. |
Container_DB
|
The database ID of the container file used. |
Container_FNR
|
The file number of the container file used. |
Block_Size |
The OPO block size in bytes related to the RPC
MAXBUFF value. The recommended maximum is: 4000000.
|
Compression_Level |
The compression level value according to zlib/DEFLATE data compression. Possible values are from 0 (do not attempt compression) to 9 (representing the maximum capability). The recommended value is 6. |
Run_Mode |
Optional. If this parameter is set to B,
error messages will not be output in GUI windows/message boxes on Windows
platforms, but in stdout instead. This is useful if
nomrpt.exe is invoked via a batch script to avoid stopping at the
error box and waiting for user confirmation.
|
When invoking nomrpt.exe, you can use
Parameter 2 to specify which parameter block within nomrptConf.xml
is to be used. If Parameter 2 is empty, the block DEFAULT will be
used.
If you invoke nomrpt as follows:
nomrpt.exe nomrpt.xml
NOMvrSRV
the file nomrpt.xml will be used as the
meta data file, and NOMvrSRV will be
used as the block name to select the predefined parameters in the configuration
file nomrptConf.xml.
When you invoke nomrpto.exe, no meta data
file has to be specified. You can use Parameter 1 to specify which parameter
block within nomrptConf.xml is to be used. If
Parameter 1 is empty, the block DEFAULT will be used. According to
above example, invoke nomrpto as follows:
nomrpto.exe NOMvrSRV
You can use the Software AG Installer to create an installation package which can then be distributed automatically to any number of computers in your environment. You can use any third-party distribution tool for this purpose.
For details, see the section Using Software Distribution Tools to Install Natural in the Natural Installation documentation. What is said there, also applies to OPO.
In the section To adapt the script, an example of using environment variables as part of the path specification for OPO would be:
imageFile=$IMAGEDIR$\\OPO34.zip
If the RPC server environment has not been used for a long time, Adabas will issue return code 9 (Natural error NAT3009) to the Natural RPC server. To avoid this error, you activate the RPC user exit 39 (NATRPC39), which is provided in the library SYSRPC. See the Natural RPC documentation for details.
The following Natural parameters have to be specified for XML processing:
XML=(ON,PARSE=ON),CP=ON,CFICU=ON
Natural has to be relinked using the option sax2.
The server has to perform a logon to the library
SYSNOM, and the Entire Output Management libraries have to be
defined as steplibs of the library SYSSAT in Natural Security.
In an environment without Natural Security, the server has to
perform a logon to the library SYSSAT and the steplibs should be
defined with the module SATSLS-P; for example:
STACK=(LOGON SYSSAT;SATSLS-P)
For the RPC communication, it may in some cases be necessary to open a TCP port in the Firewall.
Invoke Entire Output Management > System Defaults (menu 8.1) > Trigger Container File and User Exits (menu item 10) to activate the trigger queue, by specifying the database ID and file number of the installed container file in the appropriate fields.
It is highly recommended to install a separate Entire Output
Management data file to serve as a container file for documents transferred via
the Open Print Option. Do not use the Entire Output Management data
file (NOMvrs-SYSF) for transferring
data.
Generate a Natural RPC server by starting Natural in batch mode with the following parameters (sample):
RCA=BROKER,RCALIAS=(BROKER,BKIMBTSO), RPC=(SERVER=ON,ACIVERS=9,SIZE=32,SRVNODE='BKR034:3800:TCP', RPCSIZE=4100,TIMEOUT=30,TRACE=0,MAXBUFF=4096,NTASKS=2,SRVUSER='*NSC', SRVNAME=NOMvrSRV,LOGONRQ=ON)
The above sample assumes the broker name to be
BKR034, listening on port 3800, the RPC server name to be
NOMvrSRV, and that the server is
started with 2 replicas. However, you can choose your own values for these
parameters. Be sure to configure a maximum buffer size of at least 4096 KB and
the TCP transport mechanism.
The following parameters of the Broker must be adapated in the Broker attribute file:
| Parameter | Value for OPO |
|---|---|
MAX-MSG or
MAX-MESSAGE-LENGTH |
16000000 |
NUM-COMBUF |
3000 |
NUM-LONG-BUFFER |
5000 |
The Open Print Option redirects data from a print driver to Entire
Output Management. The data are redirected to
nomrpt.exe, which receives binary data from
stdin, are then converted to BASE64 and via the RPC
server written to an Entire Output Management container file.
The type of data is irrelevant for
nomrpt.exe. In fact, the data need not necessarily be
print data from a Windows printer driver. If you specify in
nomrptConf.xml that the data are text data (with the
parameter Input_Format=T), it is even possible to send print data
to a predefined report (as identified by the report name and the report
identification attribute for Natural *USER) within Entire Output Management with a simple Windows
echo command:
echo "Hello, world."|nomrpt.exe
nomrpt.exe can be invoked with the
following parameters:
| Parameter | Meaning |
|---|---|
-m
file-id |
With this parameter, you specify the XML file which is to be passed to Entire Output Management via the XML tags as described below. This file is primarily intended to supply meta data, but can also be used to supply print data. |
-b block-id |
With this parameter, you specify the
section (block) of the configuration file nomrptConf.xml which is
to be used to build up the connection to Entire Output Management via a defined
RPC server.
|
-h |
This parameter can be specified to
invoke command-line help on nomrpt.exe and information on further
parameter options available.
|
The echo command could then look as follows:
echo "Hello, world."|nomrpt.exe -m c:\test\nomrpt.xml -b
MYSECTION
The possible return codes issued by
nomrpt.exe are:
| Return Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 1 | Sending source name failed. |
| 2 | Sending sender name failed. |
| 3 | Sending user name failed. |
| 4 | Loading key from meta data failed. |
| 5 | Sending meta data in first put failed. |
| 6 | Sending document name failed. |
| 7 | Invalid meta data tag ignored. |
| 8 | Sending CLOSE call failed. |
| 51 | Locating NomrptConf.xml
failed.
|
| 52 | Loading of configuration file failed. |
| 53 | Loading of ERX DLLs failed. |
| 54 | Loading of input file failed. |
| 55 | Logon to ERX failed. |
| 56 | Start of conversation failed. |
| 57 | Close of conversation failed. |
| 58 | Opening ERX failed. |
| 59 | Loading of meta data failed. |
| 60 | Reading meta data file from
nomrpt.so failed.
|
| 61 | Sending print data failed. |
| 62 | Sending meta data failed. |
| 63 | Sending data failed. |
| 66 | Invalid trace level. |
nomrpt.exe converts the print and meta
data passed to the program via the first parameter of the
nomrpt.exe call into an XML data stream and sends them
to the Entire Output Management RPC server as defined in the configuration file
(RPC_Server). The print data stream (stdin) itself
cannot contain any XML data. This XML file is always evaluated before the print
data stream is read, as meta data for the print data stream are expected to be
supplied from there.
If the configuration parameter (see
nomrptConf.xml) Input_Format is set to
"B" or not at all, the print data are converted into the format BASE64. If
Input_Format is set to "T", the text - which then must not contain
any non-printable characters - will be passed in text lines, as shown in the
above "Hello, world" example.
They are read from the file via Parameter 1 of the
nomrpt.exe call. This XML file is always evaluated
before the print data stream is read, as meta data for the print data stream
are expected to be supplied from there.
The XML tags are evaluated as explained in the table below.
Any unknowns tags will not be interpreted as print data, but as
"extended spool attributes" (meta data). They supply information which can be
evaluated via an Entire Output Management separation exit or the user exit
NOMEX014, if activated. The exit will receive the meta data in the
variable #SPOOL-ATTR-EXTENDED using the following format:
key(1)=value(1);key(2)=value(2);...;key(n)=value(n)
These meta data can be displayed in Entire Output Management via PF2 (Meta) on the Display Active Reports > Spool Attributes screen (PF10). When using the Entire Output Management GUI Client from a Windows front-end, select Control Functions > Folders > Active Reports and then select Spool from the pull-down menu of the appropriate active report. The meta data will be displayed in the Spool tab.
For extended spool attributes, 28,900 characters per document are available. The value of one tag plus its opening and closing tag must not exceed 248 characters. The meta data tags must not contain German umlauts or any other special characters.
The following meta-data tags are reserved and must not be used by the user application:
| Tag | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| During the OPEN command: | ||
parms |
The group tag which indicates the parameter block during the OPEN command. | <parms> |
rpc_user |
The user ID for the RPC login. | User |
rpc_server |
The RPC server name. | Server |
exx_user |
The user ID for the broker login. | User |
exx_server |
The name of the broker | Broker |
nat_lib |
The Natural library to log on to. | SYSNOM |
sender |
The ID of the user who initiated the print operation in OPO. | User |
domain |
The domain of the user ID.
With a local user ID and on Linux systems, the domain corresponds to the name of the source machine. |
Domain |
source |
The name of the source machine. | CLIENTPC |
| During PUT commands: | ||
document |
The group tag for document properties. | |
source |
The name of the source machine. | CLIENTPC |
sender |
The ID of the user who initiated the print operation in OPO. | User |
domain |
The domain of the user ID.
With a local user ID and on Linux systems, the domain corresponds to the name of the source machine. |
Domain |
title |
The title of the document being printed (for example, if the printing was initiated by Microsoft Word). | Document |
data |
Printout data, either in BASE64 (binary) or text format. | |
multi_data |
The group tag which contains several
<'data'> tags or any other tags treated as meta-data
tags.
|
|
Some special tags are interpreted and used to control further processing. The following table lists the tags which are evaluated:
| Tag | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
db |
This tag specifies the database number of the Entire Output Management container file, as defined in System Defaults > Trigger Container File and User Exits (menu 8.1 > menu item 10). The value specified with this tag overrides the
corresponding value in the configuration file
|
<db>9</db> |
fnr |
This tag specifies the file number of the Entire Output Management container file, as defined in System Defaults > Trigger Container File and User Exits (menu 8.1 > menu item 10). The value specified with this tag overrides the
corresponding value in the configuration file
|
<fnr>246</fnr> |
filename |
This tag specifies the file name to be associated with the print data stream. | <filename>document</filename> |
filetype |
This tag specifies the file type to be associated with the print data stream. | <filetype>pdf</filetype> |
path |
This tag specifies the path of the file to be associated with the print data stream. | <path>test/output</path> |
canceltag |
This tag can be used to simultaneously cancel several printouts which contain the same tag value. When a user selects a printout to be cancelled, and its
meta data contain the Example:
The OPO user selects for cancellation a printout whose
meta data contain
The selected printout will be scanned for the tag
The selected printout and all other printouts which
contain All of these printouts must have the status "ready to print"; if any of them has not, none of them will be deleted. This means that either all or none of these printouts will be deleted. If the meta data of the selected printout contain no
Each deletion will be logged in the Entire Output Management monitor log. In addition, a message will be issued indicating the tag value which caused the deletion. |
<canceltag>ordernumber</canceltag> |
showproperties |
This tag specifies the tags which are to be shown to the OPO user. Note: |
<showproperties>tag1,tag2,tag3</showproperties> |
encoding |
This tag specifies the encoding of the meta data. | utf-8 |
mime-type |
This tag specifies the mime type in the meta data. | application/pdf |
The print data stream is not automatically associated with a file
name. If the print data are to be written to a file when they are printed from
Entire Output Management, the file name and file type can be supplied via tags.
The examples in the table above create a PDF file
test/output/document.pdf if the binary data stream is written to a
target directory, or when the binary data are loaded into the Entire Output
Management GUI Client for browsing. In the latter case, because of the file
type, the Adobe Reader which interprets PDF files will be invoked as external
viewer.
Transfer of text data is active if the configuration parameter
Input_Format is set to X or T. Binary
conversion is active if Input_Format is set to
B.
Defining the file type: The transfer of documents in other formats
than print formats can be achieved by using the command
type.
For example:
type TestOPO.doc |nomrpt.exe TestOPO-doc.xml
NOMvrSRV
The type of binary conversion depends on the file type (tag
<filetype>) which can be defined in the meta data file. An
example file of the meta data file (nomprt.xml) is delivered with
the product. If the file or tag are not available, an error message will be
displayed.
On mainframe platforms, output from Natural modules can be passed to Entire Output Management. On a Linux platform, this functionality is provided by an interface from Natural to OPO which passes the output to Entire Output Management.
In the Natural source code, it is only necessary to define a corresponding printer, write the output data this printer, and then close it.
Example:
DEFINE PRINTER (1) OUTPUT 'NOM' PROFILE 'NATOPO' FORMS 'FORM' PRTY 1 NAME 'LISTNAME' DISP 'D' CLASS 'X' COPIES 3 ... WRITE (1) *DATE *TIME ... CLOSE PRINTER (1) END
In Natural Configuration Utility you will need to declare the
printer profile in Configuration / Printer Profile … / Printer
Profiles by first creating a printer profile with the Method
NOM. Then you have to specify the parameters to call OPO in
Configuration / Printer Profiles … / NOM Printer Profiles.
For the example above, you may specify the parameters as:
Profile name: NATOPO
Config block: DEFAULT
Meta file: nomrpt.xml
After establishing a Natural RPC service, define
nomrptConf.xml as described above. In this example, it is assumed
that the BlockName in the nomrptConf.xml file is the
same as the RPC_Server name:
NOMvrSRV. A Natural user with access
rights to the Nat_Library logon library is to be defined as the
RPC_User.
Define a report in Entire Output Management (in this example named
OPO-Report), ensuring that the defined RPC_User is
defined in the Report Definitions >Identification
(PF7) under Natural Attributes (PF9)
as *USER.
Select a small Windows doc file, giving it the name
TestOPO.doc.
Use Notepad or another editor to create the following files:
1. Create the meta data file
TestOPO-doc.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" ?> <document> <filetype>doc</filetype> </document>
This example, which shows the minimum requirements for transferring
data, assumes that the values for the tags <db> and
<fnr> are defined in the configuration file
nomprtConf.xml (Container_DB and
Container_FNR) and that the default value "B" is used for the
configuration parameter Input_Format.
2. Create a command file TestOPO.cmd:
echo off echo start testing OPO echo TEST file type DOC echo Date: %DATE% Time: %TIME% REM the date and time values aids the tracing of REM this specific data transfer echo ******************************************** REM change to the Open Print Option directory REM ********************************************** cd "C:\Software AG\Open Print Option" echo on type TestOPO.doc |nomrpt.exe TestOPO-doc.xml NOMvrSRV echo after nomrpt.exe EOJ! pause
By using a command file, it is possible to control the output in case of any (typing) errors. By using the date and time values, the data transfer can be verified.
Start the command file TestOPO.cmd. Your file
TestOPO.doc can be viewed from an Entire Output Management GUI
Client by selecting the first active report OPO-Report and the the
Browse function.
If the required file (here TestOPO.doc) is not
delivered to the predefined report, verify that the user ID used to define the
OPO configuration parameter RPC_USER in the configuration file
nomrptConf.xml is also defined in the Entire Output Management
predefined report. If necessary, the Trace_Level option in
nomrptConf.xml can be set to "1". This will enable
the tracing of the transferred data within the SYSOUT files of the
RPC job of your RPC server.
You uninstall OPO using the Software AG Uninstaller. For detailed information on how to use the uninstaller, see the Using the Software AG Installer guide.
In short: to uninstall OPO, proceed as follows:
Open a command window and go to the bin directory of your main installation directory.
Run the command uninstall. This
starts the Software AG Uninstaller.
When you uninstall OPO, your customized OPO configuration files will not be deleted, but remain in the installation folder.
These configuration files may contain user-related authentification data such as user IDs and passwords added by your own administrator. The deletion of these data from the configuration files in compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), when applicable, is also your own administrator's responsibility.
If OPO is installed again in the same folder, these files will be re-used instead of the default configuration files delivered with the installation routine.