This section describes the attributes which are part of a report definition:
Default values for report attributes can be set by the system administrator in Report Defaults.
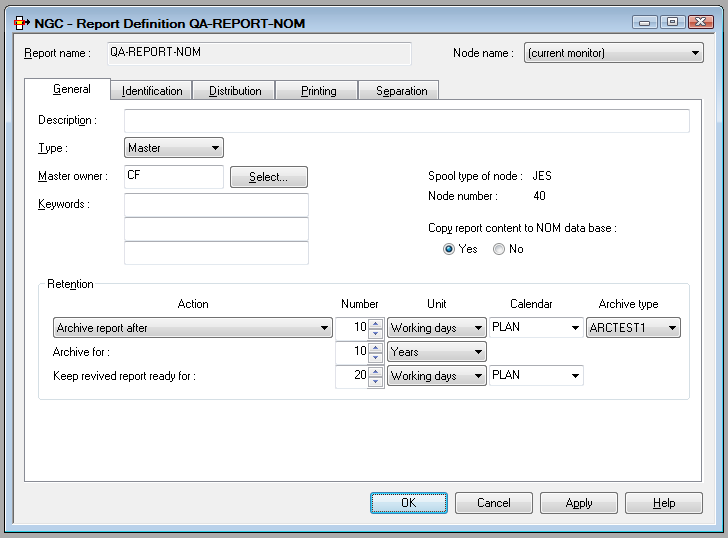
On this screen you define the general attributes of a report.
| Field | Explanation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Report name | Enter a report name before any other data when creating a new report. This field is write-protected when you modify an existing report. | |||
| Node name | Select the node name the report definition is to be associated with. This node determines the environment in which the data source for the report is to be identified. | |||
| Description | Enter a short description for the report. | |||
| Type | Created | A definition created automatically
by separation definitions during the processing of a master report or default
definition or copied from another created definition. Next to the
Type field, the name of the originating report definition
is displayed.
The type "Created" cannot be set or changed manually. |
||
| Default | A definition containing
identification and processing rules used to process spool data not identified
by a suitable master report definition.
To have a default definition for all jobs for which no suitable
master definition exists, you create a default definition with the name
|
|||
| Master | A definition containing identification and processing rules used to process one or more spool files. | |||
| Suspended | Use this type for a definition which is currently not to be used. | |||
| Master owner |
The user ID specified here is used to initialize the Master owner field in the General Attributes of the resulting active report. It determines who may delete the active report. The monitor also takes this user ID to submit print jobs for reports to be scheduled for automatic printing. This field is initialized with the ID of the user who creates the report. If you wish, you can select a different user ID. |
|||
| Keywords | Enter up to 3 keywords which will later help you select reports. | |||
| Copy report content to NOM database | Select Yes
to take the report contents from the spool and store them in the Entire Output
Management active-data file for later viewing or archiving. Otherwise, select
No.
If you do not specify a storage location, the report stays in the spool. |
|||
|
Retention
The retention period determines how long the active report is available online for viewing and printing. When this retention period expires, the active report is archived/deleted depending on the selected Action. |
||||
| Action | Purge report after | The report will be deleted when the retention period expires. It will not be archived. | ||
| Archive report after | The report will be archived when the retention period expires. | |||
| Archive report directly and keep online for | The report will be archived the next time the archive job runs, but is still available online until the retention period expires. | |||
| Archive report directly, purge online immediately | The report will be archived the next time the archive job runs, and deleted from the spool when its processing is completed. | |||
| When an active report is archived, it is no longer available online. After this, it exists only in the archive data set. The active report has to be revived before it can be viewed or printed again. | ||||
| Number / Unit / Calendar |
Specify the length of time (a number and a unit of time) for the selected Action. The unit of time can be: absolute days, working days, weeks or months. If you choose "working days", you also have to choose a calendar. For more information on calendars, see Calendars in the System Administration documentation. With the unit Generations you can specify the number of instances of the active report to be kept. If this number is exceeded, older active reports will be archived/deleted depending on the selected Action. |
|||
| Archive Type | If the report is to be archived in a user-defined archive, select the desired archive type. Select "none" to archive the report in a standard Entire Output Management archive file. | |||
| Archive for | Specify the length of time (a number and a unit of time: days, weeks, months or years) the active report is to be kept in the archive. When this period expires, the active report is deleted from the archive data set. An active report can be archived no matter where it is stored. | |||
| Keep revived report ready for | Specify the length of time (a
number and a unit of time) a revived active report is be available online for
viewing and printing. When this period expires, this "copy" of the archived
report is deleted automatically.
The unit of time can be: absolute days, working days, weeks or months. If you choose "working days", you also have to choose a calendar. For more information on calendars, see Calendars in the System Administration documentation. |
|||
A report can be identified by one of the following:
The following attributes determine how a job in the POWER spool is identified by the report definition.
| Field | Explanation | |
|---|---|---|
| Identifying attributes | You have to enter a value for at least one of these three attributes. A job is considered identified if it matches at least one of the specified attributes. | |
| Job name | If you want to identify the job by its name,
enter the job name here.
You can use an asterisk notation (*) for the job name. For
example, to identify all jobs whose names begin with "IEE", you enter
|
|
| Destination | If you want to identify the job by its
DEST parameter, enter the destination here.
|
|
| Form | If you want to identify the job by its
FORM parameter, enter the form here.
|
|
| Filter for spool files and sequential files |
Use these fields to select the files whose contents are to be used as print data for the active report. For an active report to be created, at least one file of the job has to match these filter criteria. You specify the spool files in the identified jobs which are to be assigned to the report. You specify them as follows:
The following special characters can be used to create a file-name pattern:
Example: |
|
| Code page |
By default, Entire Output Management uses the code page defined for the respective node and applies it to all report definitions associated with that node. If you want to use a different code page for a particular report, select the desired code page here. If you do not want to use a report-specific page, select "none". For the definition of code pages, see Default Code Pages. |
|
Note:
The processing of sequential files is also triggered by spool
queue entries. The corresponding spool file does not contain print data, but an
entry with a link pointing to the sequential file. This entry can be created
with any utility (for example, a Natural program) and must have the following
attributes:
NOM DSN=data-set-name VOL=volser NOM RECFM=recform RECSIZE=record-length NOM BLKSIZE=block-size CC=carriage-control
data-set-name may have a
maximum length of 22 characters.
carriage-control may be
ASA, MACHINE or NONE.
Before processing, the file name is extended with a time stamp to make it unique.
The following attributes determine how a job in the BS2000 spool is identified by the report definition.
| Field | Explanation | |
|---|---|---|
| Identifying attributes | You have to enter a value for at least one of these three attributes. A job is considered identified if it matches at least one of the specified attributes. | |
| Pname | If you want to identify the job by the
PNAME option of the BS2000 print command (/Print
...,PNAME=ADAREP), enter the PNAME here.
You can use asterisk notation (*) to for the job name. For
example, to identify all jobs whose names begin with "ADA", you enter
|
|
| User ID | If you want to identify the job by the BS2000
user ID under which the print command was entered, enter this user ID here (for
example: PROD01).
|
|
| Form | If you want to identify the job by its
FORM parameter, enter the form here.
|
|
| Filter for spool files and sequential files |
Use these fields to select the files whose contents are to be used as print data for the active report. For an active report to be created, at least one file of the job has to match these filter criteria. You specify a completely or partially qualified file name which identifies the report. A report definition is considered identified if, in addition to one of the identifying attributes, one of the files from the file list matches. The following special characters can be used to create a file name pattern:
For example, if you enter |
|
| Code page |
By default, Entire Output Management uses the code page defined for the respective node and applies it to all report definitions associated with that node. If you want to use a different code page for a particular report, select the desired code page here. If you do not want to use a report-specific page, select "none". For the definition of code pages, see Default Code Pages. |
|
The RECFORM parameter of the file allows you to determine
whether the print file contains carriage control characters and which ones. It
is specified as follows:
RECFORM=(x,y)
where:
x = F for fixed
record length, or V for variable record length.
y determines the type of
carriage control characters:
A = ASA carriage control characters,
M = machine-code carriage control characters,
N = no carriage control characters.
It is recommended that files with a fixed record length be used, because positioning within them is easier than within files with a variable record length.
Note:
Files with fixed record length that were expanded with OPEN-EXTENT
are not supported.
The following attributes determine how a job in the JES spool is identified by the report definition.
| Field | Explanation | |
|---|---|---|
| Identifying attributes | You have to enter a value for at least one of these four attributes. A job is considered identified if it matches at least one of the specified attributes. | |
| Job name |
To identify the job by its name, enter a job name here. You can use asterisk notation (*) for the job name. For example,
to identify all jobs whose names begin with "IEE", you enter |
|
| Destination | To identify the job by the
Destination parameter, enter the destination here.
|
|
| Writer | To identify the job by the External
Writer parameter, enter the writer name. This links the report to the
spool file assigned to this writer name. If you use an external writer similar
to the report name, it makes identification easier.
|
|
| Form | To identify the job by the FORMS
parameter, enter the form here.
|
|
| Filter for spool files and sequential files |
Use these fields to select the files whose contents are to be used as print data for the active report. For an active report to be created, at least one file of the job has to match these filter criteria. You can specify which spool files (data sets) in the identified jobs are to be assigned to the report. See Spool Files and Sequential Files below. |
|
| Code page |
By default, Entire Output Management uses the code page defined for the respective node and applies it to all report definitions associated with that node. If you want to use a different code page for a particular report, select the desired code page here. If you do not want to use a report-specific page, select "none". For the definition of code pages, see Default Code Pages. |
|
To specify the spool files in the selected jobs, you use one of the following three possibilities:
Specify: file-type
file-sequence-number
where file-type can be:
JL = JCL statements, SI = system input,
SM = system messages, SO = system output.
Examples:
Specify SO 1 for the first SYSOUT file.
Specify SO 1:4 for the first to fourth SYSOUT files.
Specify a list of full DDNAME qualifiers in the format:
proc-name.step-name.ddname
proc-name and
step-name are not mandatory, and if
omitted are assumed to be * (any). You can use an asterisk (*) to enter
selection criteria for the file names.
Examples:
PROC1.STEP1.DDN1 is a full qualifier.
*.STEP1.DDN1 refers to a spool file with
STEPNAME=STEP1, DDNAME=DDN1 and any procedure
name.
*.*.DDN1 or *.DDN1 or DDN1
are equivalent and refer to a spool file with DDNAME=DDN1 in any
step name or procedure name in the job.
Specify TYPE=AL to create an active report containing
all System Message and SYSOUT files for a job matching the specified JES
attributes. The job must have at least one spool file in one of Entire Output
Management's managed classes. TYPE=AL must be the only file
criterion.
Note:
If more than one JES2 spool file of a job is to be processed by
Entire Output Management, the job's spool files which are to be processed must
all have the same group ID and all be together in a class reserved for Entire
Output Management. If this is not achieved by the DD statements, but, for
example, by a program via Entire System Server functions, the view
SPOOL-UPDATE should be used as follows:
PROCESS SPOOL-UPDATE
USING FUNCTION = 'CHANGE'
USING JOB-NAME = #JOB-NAME
USING JOB-NUMBER = #JOB-NUMBER
USING GROUP-ID = #GROUP-ID
USING CLASS = #NOM-CLASS
USING NODE = #NODE
GIVING ERROR-CODE
ERROR-TEXTIf the report data reside in a sequential file, enter the file name in
the form DSN=file-name.
The following special characters can be used to create a file-name pattern:
? (question mark) or _ (underscore) to indicate a single position not to be checked.
* (asterisk) to indicate any number of positions not to be checked.
Example: DSN=NATURAL.*EMPL_YEE*
Note:
The processing of sequential files is also triggered by spool queue
entries. The corresponding spool file does not contain print data, but points
to the sequential file. The pointer can be created with any utility and must
have the following attributes:
NOM DSN=data-set-name
data-set-name may have a
maximum length of 22 characters.
The STEPNAME to create the spool file must be
NOMDSN.
//JOB 1 JOB...
......
//NOMDSN EXEC PGM=IEBGENER
//SYSPRINT DD SYSOUT=*
//SYSUT2 DD SYSOUT=3
//SYSIN DD DUMMY
//SYSUT1 DD *
NOM DSN=OUTPUT.LISTING
/*For the definition of reports that rely on a general, user-defined 3GL interface, all identifying attributes can be freely chosen.
These attributes determine how a job in the CA spool is identified by the report definition. A job can be identified by one of the following four attributes. You have to specify a value for at least one of these fields. A job is considered identified if it matches at least one of the specified attributes.
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| File name | To identify the job by the file name, enter the file name
here as it appears on the CA screen. The file name can contain the user ID of
the file creator, the job name or a parameter entered in the OWN
field in an OPEN request. See the CA Spool
documentation for details.
|
| User ID | To identify the job by the ID of the user who created the
list, enter the user ID here (UID field in OPEN
request).
|
| Writer | To identify the job by the Writer parameter,
enter the writer name here (WTR field in OPEN
request).
|
| Form | To identify the job by the FORM parameter, enter
the form here (FOR field in OPEN request).
|
You can use asterisk notation (*) for the file name. For example, to
identify all files whose names begin with "ADA", enter ADA*. Or,
to identify all files which were either created by the user "XYZ" or whose
names begin with "ADA", enter ADA* for File
name andXYZ for User ID.
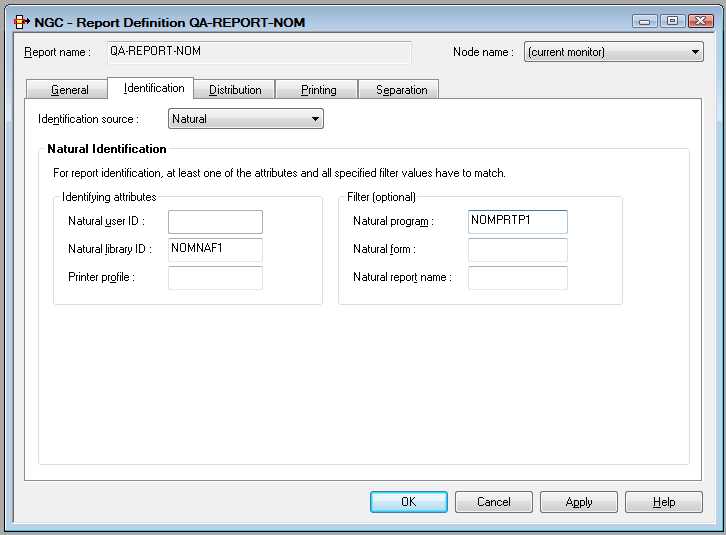
On this screen, you define how a report is identified which is created by Natural or its related products like Natural Advanced Facilities or Open Print Option.
Output from Natural is produced during the processing of a specific
Natural program, which is stored in a Natural library and executed by a Natural
user. The output can have various attributes defined in the program's
DEFINE PRINTER statement.
The Identifying attributes are used as selection criteria for output under Natural. A report is considered identified if it meets at least one of these criteria. You have to specify at least one identifying attribute.
In addition, you can specify one or more Filter criteria to further narrow down the selection. All specified filter criteria must be met for a successful identification.
The output data of the program will be used as print data when an active report is created.
| Field | Explanation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Identifying attributes | |||
| Natural user ID | Enter a Natural user ID or a Natural library ID (but not both). | ||
| Natural library ID | |||
| Printer profile | Enter the name as defined in the
OUTPUT option of the DEFINE PRINTER
statement.
|
||
| Filter (optional) | |||
| Natural program | Enter the name of a Natural program. | ||
| Natural form | Enter the form as defined in the
FORMS option of the DEFINE PRINTER statement.
|
||
| Natural report name | Enter the name as defined in the
NAME option of the DEFINE PRINTER statement.
|
||
You can use asterisk notation (*) for all attributes, except
Printer Profile. For example, to select all programs
executed by users whose IDs begin with "MRS", you specify MRS* as
the user ID. Or, if you enter the user ID value ABC and the
printer profile value NOMPRT, all print files are identified which
were created either by the user "ABC" or with the printer profile "NOMPRT".
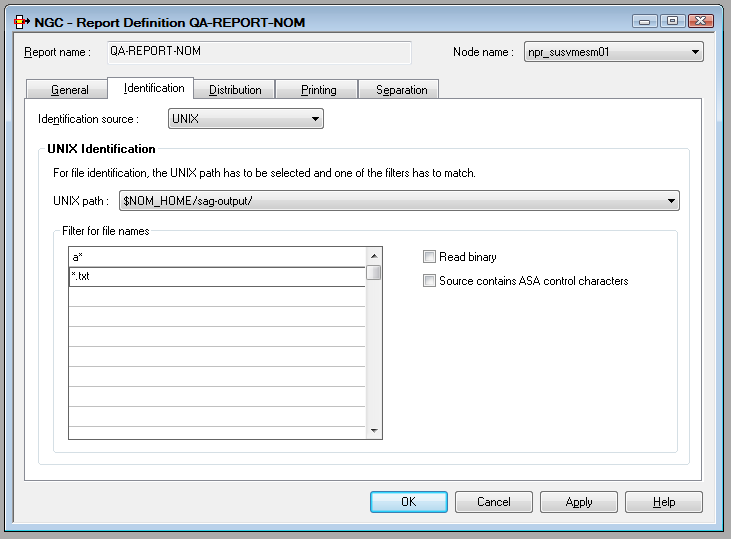
On this screen, you define how a report is identified on UNIX or Windows nodes.
The identification is done using the node name and path, and a file-name pattern. Entire Output Management will process any file found in this path, if it matches one of the specified file names or file-name patterns. Directories are not processed (no recursion).
For every matching file, an active report will be created. For this purpose, the file contents will be copied to the Entire Output Management container file. Then the file will be deleted from the path.
For any file not matching one of the criteria, Entire Output Management checks if an appropriate default report exists. If none exists, the file cannot be processed and will be moved to a temporary directory defined for this node in the Node Definitions instead.
ASCII files can contain line feeds, form feeds and tabulators; any other kind of control character will be ignored and set to blank.
Binary files can be of any format. They are stored in the container file in Base64 format. At the time of printing, they are re-converted to binary format.
In addition to the identified files, associated meta-data files can be
processed. If a pair of files such as
file-name.extension and
file-name.extension.nomxml is found,
the nomxml file is treated as a meta-data file in XML format.
Node names, path names and file names are case-sensitive. Node names and paths have to be defined in the Node Definitions first.
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Node name |
Select a node name. |
| Path |
Select a path. Path definitions must not contain any wildcard characters. |
|
Filter for file names |
Enter up to 10 files, or file-name patterns, without path entries. File extensions are treated as part of the file name. In a file-name pattern, you use an asterisk (*) as placeholder for several characters and a question mark (?) for a single character in the file name. |
| Read binary |
|
| Source contains ASA control characters | Mark this field if the report is to be created as a text file and the print data from the data source already contain ASA control characters. These will then be used, and additional ASA control characters will not be generated. |
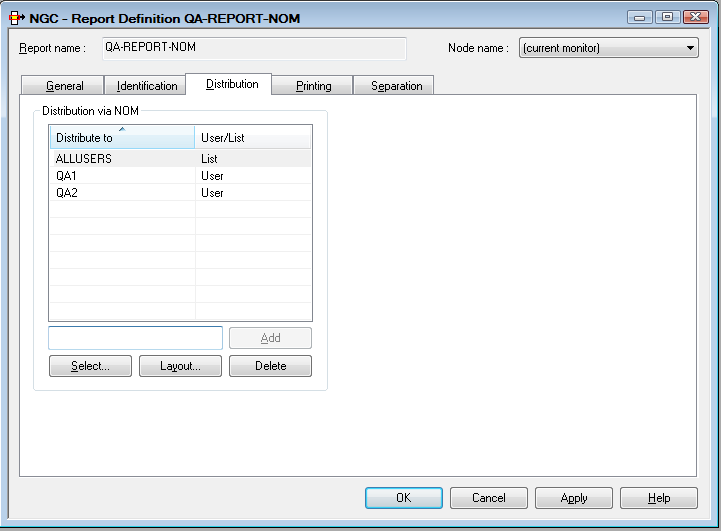
On this screen you can define the recipients of a report and the facilities used for distribution.
You can select up to 10 users or distribution lists. When the report is created, it is distributed to the Inbasket of the selected users. All users connected to IDs or lists entered here can browse and print the report.
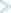 To select a user or distribution list for receiving a report:
To select a user or distribution list for receiving a report:
Choose the button under .
The window is displayed in the content pane:
Select a user/list from the list of Users or list of Distribution Lists.
Choose the down arrow on the right.
The selected user/list appears in the section at the bottom of the dialog:
Choose .
The selected user ID or list name now appears in the section of the Distribution Attributes.
 To remove a user or distribution list from the
list:
To remove a user or distribution list from the
list:
Select an entry on the list.
Choose the Delete button below the list.
The selected user/distribution list is removed from the list.
Note:
You cannot combine a report layout definition with
separation attributes. You
can only use either one or the other.
You can restrict a user's view of the report by defining a user-specific report layout. In this layout, you specify the parts of the layout which are to be visible to the user.
You can define a different layout for each addressee of the report. If the addressee is a distribution list, the specified layout is visible to all members of the list.
 To define a layout for a user or distribution list:
To define a layout for a user or distribution list:
Select the desired user/list.
Choose the button.
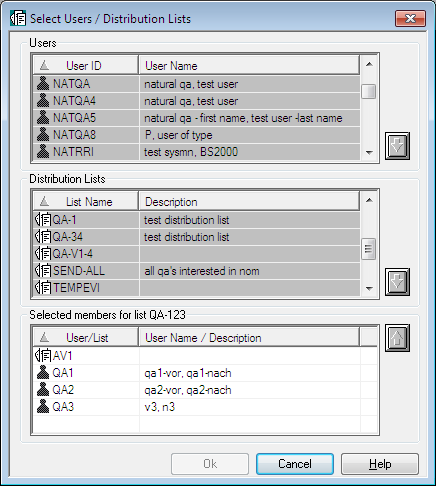
The Layout for User window is displayed:
You can define up to 10 columns of the report which are to be displayed to the selected user/list. The fields available to do this are described below. The user(s) will see only the specified columns.
In the field Start layout below report line, enter the line number (counting from the top of the page) below which the layout definition is to take effect.
Lines above and including this line remain in their original format.
For each column to be displayed, you specify the first and the last position to be displayed in the from position and to position fields.
The positions are counted from the beginning of a report line (not including ASA/machine codes).
The specified positions will be shown in the Select range for layout column field.
Or:
Click on a column number (1 to 10). Then mark the desired range of
positions in the field Select range for layout column with
the cursor, and select .
The positions thus selected will be shown in the from/to position fields for the column.
For easier orientation, you can copy text lines from the original report to the clipboard, and then select to paste them into the display area. You can copy several lines, but only line by line.
When you have specified all columns to be displayed, choose .
If a report is to be automatically printed with a special layout,
define AUTOPRNT as an addressee and attach the special layout to
that addressee (the report will not be distributed to AUTOPRNT).
To use this facility, you must also define a user AUTOPRNT.
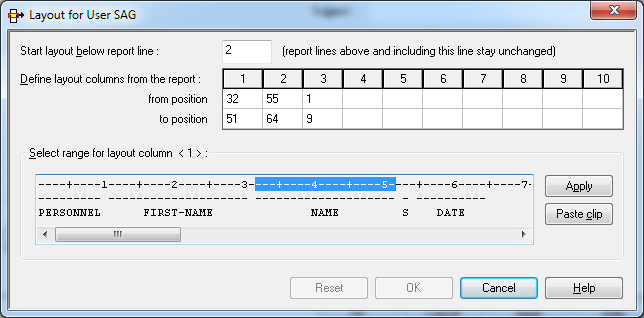
On this screen you can define how reports are printed automatically.
| Field | Explanation | |
|---|---|---|
| Hold Logic | This field controls how the report is queued for printing. Choose one of the following values from the drop-down list box: | |
| (none) | ||
| Release manually | The report is held in the printout queue until released manually. | |
| All users confirm | The report is held in the printout queue until manually confirmed by all recipients. A message requesting printing confirmation is displayed to each user in the distribution list. When all users have confirmed, the report is automatically released for printing. | |
| Release immediately | The report is printed immediately. | |
| Separator Pages | Start |
Enter the name of the separator page to be printed at the beginning of the report. To edit the corresponding text member, you use the button next to the field. |
| End |
Enter the name of the separator page to be printed at the end of the report. To edit the corresponding text member, you use the button next to the field. |
|
| Copies | Specify how many times each separator page is to be printed. | |
| Length | Enter a separator line length, if your separator line length is greater than your report length. The default length is the report length. | |
| See Separator Pages for further information. | ||
| Jobcards | Enter the job cards for printing
with batch jobs. The following substitution variables can be used:
§USER, §REPORT and §JOBNAME.
If you leave this field blank, the Jobcards specifications from the logical printer definition are used. |
|
| Printers | Printers |
The IDs of the printers on which the report will be printed. To add a printer to the list, see Selecting Printers for a Report below. |
| Copies | The number of copies of the report to be printed on this printer. | |
| Separator |
Determines whether or not the Separator Pages (see above) are printed on this printer. By default, they are printed on all printers listed (as indicated by an "X"). If this is not desired, you can change this specification for individual printers. |
|
| To change the Copies and Separator specifications, select a printer ID and choose the button. In the fields below the Printers list, you can then change them for the selected printer. | ||
 To select one or more printers for a report:
To select one or more printers for a report:
In the Printers section of the Printing Attributes screen, choose the button.
The window is displayed:
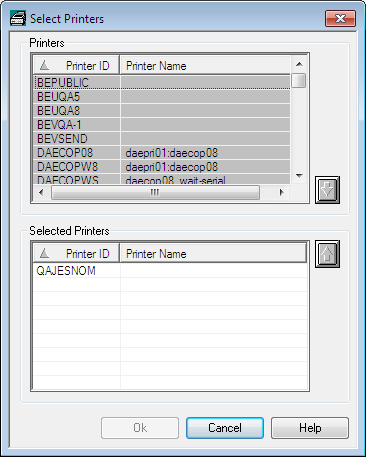
In the Printers section at the top, select a printer ID.
Choose the down arrow on the right.
The printer ID is written to the list of Selected Printers in the bottom section of the window.
Choose .
The selected printer now appears in the Printers section of the Printing Attributes screen.
Note:
You cannot combine separation attributes with a
report layout
definition. You can only use either one or the other.
For separation you can use one of the following:
The routines for standard separation are supplied by Software AG.
If no user routine or standard routine is specified, the whole identified spool file is contained in the report.
| Field | Explanation | |
|---|---|---|
| Separation Routine | Select the routine to be used. | |
| Create report definitions for active reports by separation. | By default, when active reports are
created dynamically during a separation process, the corresponding report
definitions are created automatically.
To suppress this automatic creation, select No. This may be useful if you create unique active reports. |
|
The spool file records can be filtered on a record-to-record basis by a supplied user routine. With various action codes, the user routine can control the separation process and positioning within the output and can determine the contents of the created reports.
For more information, see User Separation Routines in the System Administration documentation.
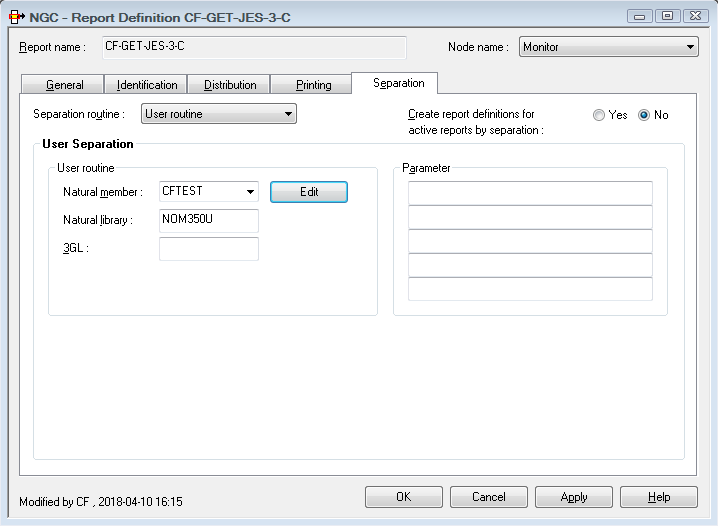
| Field | Explanation | |
|---|---|---|
| User routine | Natural member | Enter the name of the Natural subprogram
containing the user routine.
To edit the subprogram, you use the button next to the field. |
| Natural library | Enter the name of the Natural library which
contains the subprogram.
A library name beginning with |
|
| 3GL | If the user routine is written in a language
other than Natural, enter its name here. This user routine is invoked by a
CALL statement.
|
|
| Parameter | You can enter up to 5 parameters which are passed to the user routine at the start of report processing. | |
Standard Separation 1 separates spool data into several reports depending on the break of the specified suffix. The suffix need not appear in sorted order. This separation searches for a defined string in a defined line or anywhere on a page. If the string appears on a page, a suffix is evaluated (at break of the suffix value, a new report is opened). If the string is not found, the page is added to the currently open report. If no report is open, the page is rejected.
| Item | Explanation | |
|---|---|---|
| Search | Line |
Enter the line number, starting from the top of the page, where the string must appear. To determine this line number, you must also count lines containing only carriage control characters. If you do not specify a line number, the search string can appear anywhere on the page. |
| String |
Enter the string to be searched for. If this string appears on a page, the suffix is evaluated (at break of the suffix value, a new report is opened). If the string is not found, the page is added to the currently open report. If no report is open, the page is rejected. You can specify a search pattern like: *STRING1*STRING2*
or: *STRING1%STRING2*
where * stands for any string and % stands for any character. Note: |
|
| Suffix | Line |
Enter the line number, starting from the top of the page, where the report suffix appears. To determine this line number, you must also count lines containing only carriage control characters. If you leave this field empty, Entire Output Management assumes that the suffix is located in the Search Line. |
| Column from | Enter the position in the line where the report suffix starts (value from 1 to 251). To determine the position, you must also count carriage control codes and/or table reference characters. | |
| Column to | Enter the position in the line where the report suffix ends (value from 1 to 251). To determine the position, you must also count carriage control codes and/or table reference characters. | |
| Prefix | Reports | Enter the report prefix which is concatenated to the suffix to determine the report name. The suffix is concatenated suppressing leading and trailing blanks. |
| Bundles 1 to 5 |
(Optional) Enter the bundle prefix which is concatenated to the suffix to determine the bundle name. The suffix is concatenated suppressing leading and trailing blanks. Up to 5 bundles can be specified. To generate bundles with fixed names, fill in this field completely. No suffix is then appended. |
|
We have a salary report sorted by department number and want to separate it into the various departments. A standard routine could be defined as follows to perform an automatic separation:
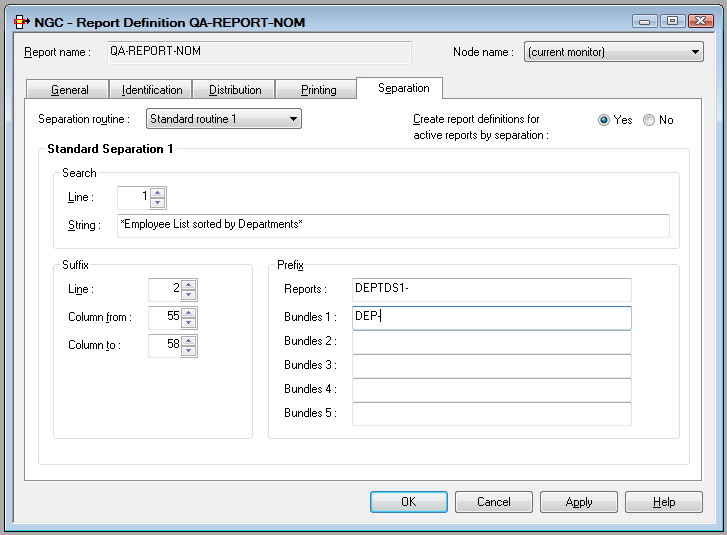
This standard routine separates the spool file on a page basis and
creates reports whose names begin with DEPTS1-. The report name is
created by adding the prefix DEPTS1- to the suffix found in the
spool file in the positions defined in the example above, for example:
DEPTS1-FINA.
Optionally, the report can be directed to a bundle with the prefix
DEP-. The bundle name is created by adding the prefix
DEP- to the suffix found in the spool file, for example:
DEP-FINA.
Note:
When the suffix and the identifier string are not on the same line,
the line parameters must be used. Enter the line numbers where the identifier
string and suffix are found. This must be the absolute line number as
counted from the top of the page.
Standard Separation 2 separates spool data into several reports depending on up to 5 break conditions. It searches for a defined string in a defined line or anywhere on a page. If the string appears on a page, up to 5 suffixes are evaluated (at the break of a suffix value, a new report is opened for that suffix). If no string is found, the page is added to the currently opened reports. If no report is opened, the page is rejected.
| Field | Explanation | |
|---|---|---|
| Search | ||
| Line | Same as described for Standard Separation 1. | |
| String | ||
| Suffix - Prefix (summary) - You can define parameters for up to 5 suffixes in these fields | ||
| Line |
Enter the line number, starting from the top of the page, where the report suffix appears. To determine this line number, you must also count lines containing only carriage control characters. If you leave this field empty, Entire Output Management assumes that the suffix is located in the Search Line. |
|
| Column from | Enter the position in the line where the report suffix starts (value from 1 to 251). To determine position, you must also count carriage control codes and/or table reference characters. | |
| Column to | Enter the position in the line where the report suffix ends (value from 1 to 251). To determine position, you must also count carriage control codes and/or table reference characters. | |
| Report Prefix | Enter the report prefix which is concatenated to the suffix to determine the report name. The suffix is concatenated suppressing leading and trailing blanks. | |
| Bundle Prefix 1 to 5 |
(Optional) Enter the bundle prefix which is concatenated to the suffix to determine the bundle name. The suffix is concatenated suppressing leading and trailing blanks. Up to 5 bundle prefixes can be specified for each suffix. To generate bundles with fixed names, fill in this field completely. No suffix is then appended. The number of the currently displayed prefix appears after the title Bundle Prefix. |
|
We have a salary report sorted by department number and want to separate it into the various main departments and sub-departments. A standard routine could be defined as follows to perform an automatic separation:
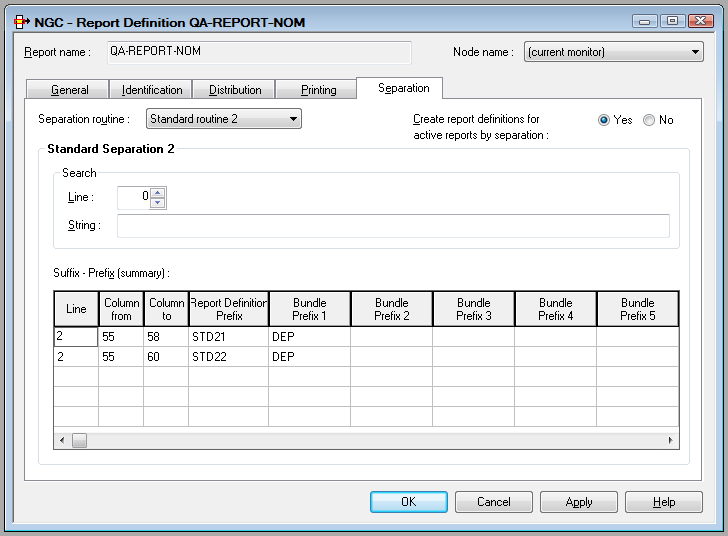
This standard routine separates the spool file on a page basis and
creates reports whose names begin with STD21- for the main
departments and STD22- for the sub-departments. The report name is
created by adding the prefix STD21- to the department name
(columns 55-58 in line 2) or by adding the prefix STD22- to the
sub-department name (columns 55-60 in line 2) found in the spool data.
Optionally, the report can be directed to a bundle with the prefix
DEP-. The bundle name is created by adding the prefix
DEP- to the department or sub-department name.
Note:
When the suffix and the identifier string are not on the same line,
the line parameters must be used. Enter the line numbers where the identifier
string and suffix are found. This must be the absolute line number as
counted from the top of the page.
Standard Separation 3 searches for a defined string in a defined line. If the string appears on a page, the lines of the page are analyzed regarding the defined logical expression. If not, the whole page is rejected.
From the Start line until end of page, the lines are added to the report, if they match the defined logical expression. Lines before the Start line are also rejected unless they are defined as Header lines.
| Field | Explanation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Search | Line | Same as described for Standard Separation 1. | |
| String | |||
| Header lines |
Enter the number of lines (0-20), starting from the top of the page, which are used as header lines. To determine this line number, you must also count lines containing only carriage control. If Header lines = 0, no header lines are added. Otherwise, if there is at least one line on a page which matches the separation's logical expression, the header lines are added. |
||
| Start line | Enter the line, starting from the top of the page, from which filter processing starts. The lines preceding the Start line are automatically excluded from the report, unless they are defined as Header lines. To determine this line number, you must also count lines containing only carriage control characters. | ||
| AND/OR | Concatenates two conditions. Possible values: | ||
| Operator | Meaning | ||
AND |
Concatenates with logical AND. | ||
OR |
Concatenates with logical OR. | ||
| (blank) | Concatenates the same variable with OR=. | ||
| Column from | Indicate the position of the operand. Enter positions in column from which to start and at which to end filter processing (value from 1 to 251). | ||
| Column to | |||
| Format | Variable type:
|
||
| Relational Expression | Possible values: | ||
| Operator | Meaning | ||
EQ or
= |
Equal to. | ||
GE or
>= |
Greater than or equal to. | ||
GT or
> |
Greater than. | ||
LE or
<= |
Less than or equal to. | ||
LT or
< |
Less than. | ||
NE or
! |
Not equal to. | ||
| Value | Enter a numeric or alphanumeric
value or a mask definition.
Note: |
||
We have a salary report sorted by department number and want to extract all employees with sex = M, personnel ID number >= 6000000 and birthday <= 50/01/01 (sub-department COMP12):
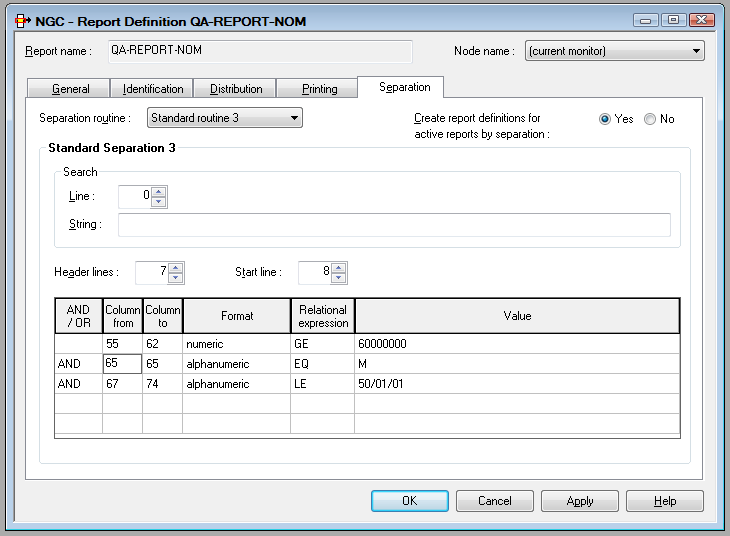
Lines 1 to 7 are taken as header lines. The filter starts in line 8.
We have a CATALL list and want to extract all lines with error number unequal to 0:
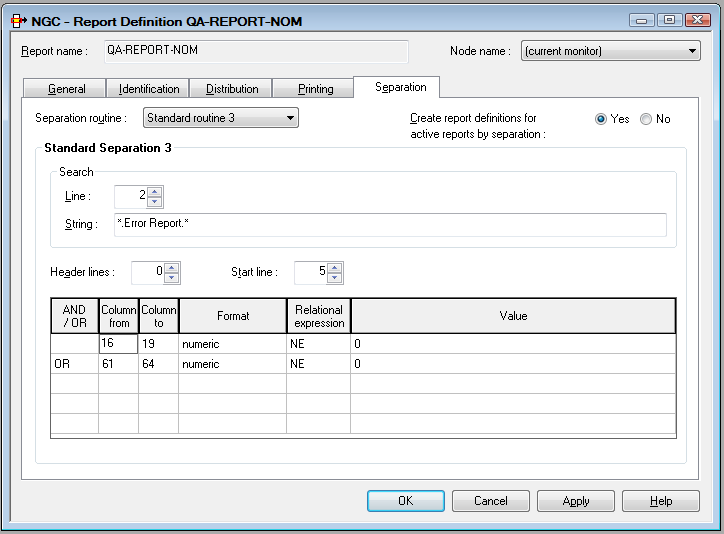
No header lines are added. The filter starts in line 5 on pages with
the string .Error Report. in line 2.