Using Natural Business Services, you can create all the components of a business service, including Natural object subprograms that perform maintenance and browse functions and GUI dialogs or web pages that communicate with the object subprograms. Communication between server and client components of an application is performed by a combination of EntireX and Entire Net-Work (or EntireX configured to use TCP/IP), as well as Natural Business Services middleware components: the business service client proxy and Natural Business Services servers. The middleware components encapsulate calls to EntireX on the client and server. The following diagram shows the architecture of character-based Natural applications and business service components:
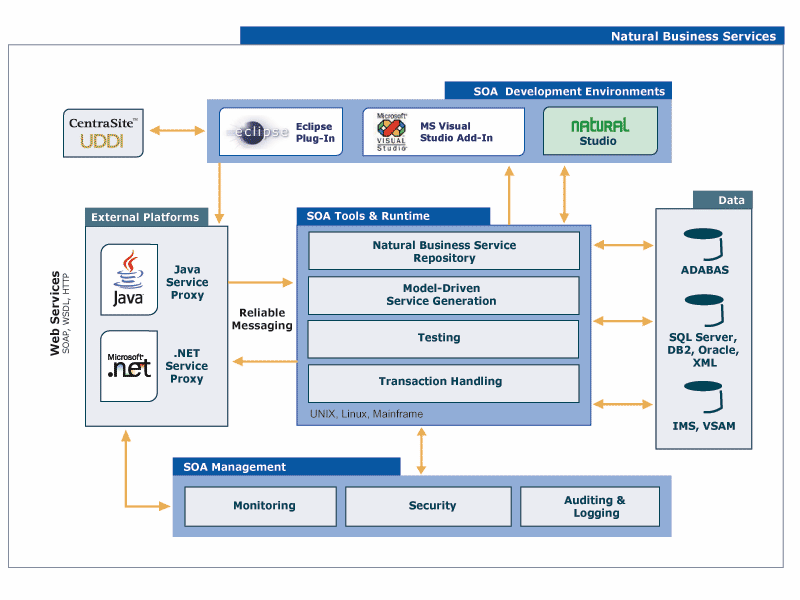
This section describes these components according to the platforms on which the components run.
This section describes the server components for Natural Business Services. The following topics are covered:
The following table lists the components required for development purposes:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Natural subprograms | Subprograms written in
Natural that do not contain user interface code (for
example, WRITE, DISPLAY, PRINT, INPUT, and REINPUT statements) or navigation
code (for example, PF-key processing). They can be existing
Natural subprograms or they can be wizard-generated
in Natural for Windows. Existing subprograms can be
wrapped together so one server subprogram accesses more than one subprogram.
The Business Service wizard can wrap the subprograms it generates, as well as
use Natural Construct models internally to generate
subprograms that perform maintenance and browse functions on the server. The
wizard chooses the appropriate model based on criteria the user has selected.
These models are: Object-Browse-Subp, Object-Maint-Subp,
Object-Browse-Select-Subp, and Object-Generic-Subp.
Notes:
The same set of business objects can be accessed from character-based Natural applications, client/server applications, and web applications. This ensures that the integrity of business data is preserved, independent of the presentation layer, and existing code can be preserved. |
| Character user interface (optional; only used at sites that access the business service from a 3270 client) | Non-distributed Natural applications created with Natural Construct accessing subprograms directly (for example, subprograms generated by the Object-Maint-Dialog model). |
| Subprogram proxy | Link between a specific subprogram and the
Natural Business Services dispatch server. The
subprogram proxy:
|
The following table lists the components required for runtime purposes:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Business Service Administration subsystem | Server subsystem that allows system
administrators, application administrators, and developers to set up and manage
system and application environments.
Note: |
| EntireX | Runtime component that transfers messages
between Windows or the web server and the Natural
environment. EntireX can be configured to use either
native TCP/IP or Entire Net-Work as the transport
layer.
EntireX performs the following runtime functions:
Notes:
|
| Natural Business Services dispatch server | Server that provides a common interface and
EntireX services for
Natural subprograms in the application. The main
functions of the Natural Business Services dispatch
server are to:
Note: |
| Dispatch server data | Information that is defined and maintained in the Business Service Administration subsystem and accessed by Natural Business Services dispatch servers anywhere on the network using EntireX. |
| Security server | Server used to check security settings in the Business Service Administration subsystem to determine whether to grant client requests. This stand-alone server operates independently of any one Natural Business Services dispatch server, which allows the server to centrally process the requests of several dispatch servers located on nodes throughout the network. |
| Attach server | Server that determines which dispatcher to use and whether other dispatchers are required. If other dispatchers are required, the attach server will start them. |
| Business Service repository | Directory structure containing the business service metadata, such as domains, subprogram proxies, descriptions, methods, method descriptions, as well as security access to these services and methods. |
All Natural Business Services dispatch servers defined in the Business Service Administration subsystem have access to the following common system functions:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Return debugging information | Ensures that all requested debugging information is generated into the source area. Debugging information is requested by setting a trace option in the subprogram proxy. The debugging information is stored as a source member that can be examined or used to initiate the request locally on the server, thereby removing the client and the network from the test. |
| Handle errors | Captures runtime errors and returns the errors to the client. If possible, this function also restarts the server that ended with the runtime error. |
| Handle messages | Returns a message string based on a message number and substitution values. This function accepts and updates the data used by the Natural Business Services dispatch server to return the message. |
The client components for Natural Business Services are:
The Natural for Windows components on the client are:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Program generation plug-in | Interface into Natural Construct. |
| Business Service plug-in/add-in | Interface into the Business Service repository. This interface also provides a wizard to generate business services. |
| Natural Development Server (NDV) | Middleware component used to connect the client to a Natural server. EntireX is not required in a Natural for Windows environment. |
| Business Service repository explorer | Tree view of the business repository. Using the
repository explorer, you can:
|
| Business Service wizard | Wizard used to create business services from existing Natural subprograms and/or generate new subprograms. Internally, the wizard generates Natural subprogram proxies and Natural Construct objects and populates the Business Service repository. |
You can create business services in the Visual Studio and Eclipse development environments, as well as consume the services. Use the Natural Business Services Visual Studio add-in or Eclipse plug-in to create classes and Web services from business services.
The business service consumer components on the client are:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Business Service add-in or plug-in | Link to Natural Business Services from Visual Studio or Eclipse. Using the add-in or plug-in, you can configure the business service connections, search for business services, and invoke the client proxy and/or Web Service wizard to generate classes and/or Web services ( .NET or C# in Visual Studio or Java in Eclipse). |
| Business Service menu | Menu used to perform the following tasks:
|
| Business Service repository explorer | Tree view of the business repository. Using the
repository explorer, you can:
|
| Client Class wizard | Wizard used to generate client proxies and/or Web services (depending on the context) that are specific to a particular business service. |
| Web Service wizard | Wizard used to generate Web services that use
IIS (Internet Information Server) and a .NET runtime component. This wizard is
invoked from the Web Services node in the explorer window.
After generating the Web service, open the context menu for the Web service and select to submit SOAP messages and test these services. |
| Web Application wizard | Wizard used to generate a web application based
on previously generated Web services. This wizard is invoked from the Web
Applications node in the explorer window. During generation, the wizard sets up
folders for the web application and creates the support files.
After generating the web application, you can open the Web Applications node and select the context menu for Pages to generate a web page or select the context menu for Menu to generate a menu for the web application. |
| Configuration utility | Utility used to define configuration settings
for Web services and applications.
Note: |