This section describes the dynamic and static SQL support provided by Natural.
The following topics are covered:
For a list of error messages that may be issued during static generation, see Static Generation Messages and Codes Issued under NDB in the Natural Messages and Codes documentation.
For information on Static SQL with Natural Security, see Integration with Natural Security.
The SQL support of Natural combines the flexibility of dynamic SQL support with the high performance of static SQL support.
In contrast to static SQL support, the Natural dynamic SQL support does
not require any special consideration with regard to the operation of the SQL
interface. All SQL statements required to execute an application request are
generated automatically and can be executed immediately with the Natural
RUN
command. Before executing a program, you can look at the generated SQLCODE,
using the LISTSQL
command.
Access to DB2 through Natural has the same form whether dynamic or static SQL support is used. Thus, with static SQL support, the same SQL statements in a Natural program can be executed in either dynamic or static mode. An SQL statement can be coded within a Natural program and, for testing purposes, it can be executed using dynamic SQL. If the test is successful, the SQL statement remains unchanged and static SQL for this program can be generated.
Thus, during application development, the programmer works in dynamic mode and all SQL statements are executed dynamically, whereas static SQL is only created for applications that have been transferred to production status.
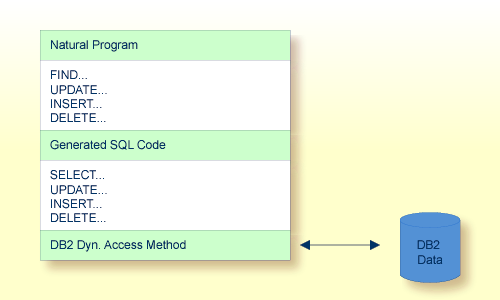
Natural automatically provides for the preparation and execution of each SQL statement and handles the opening and closing of cursors used for scanning a table.
The following topics are covered:
As each dynamic execution of an SQL statement requires a statically
defined DECLARE STATEMENT and DECLARE CURSOR
statement, a special I/O module named NDBIOMO is provided which
contains a fixed number of these statements and cursors. This number is
specified during the generation of the NDBIOMO module in the
course of the Natural for DB2 installation process.
If possible, an SQL statement is only prepared once and can then be
executed several times if required. For this purpose, Natural internally
maintains a table of all SQL statements that have been prepared and assigns
each of these statements to a DECLAREd STATEMENT in the module
NDBIOMO. In
addition, this table maintains the cursors used by the SQL statements
SELECT,
FETCH,
UPDATE
(positioned) and
DELETE
(positioned).
Each SQL statement is uniquely identified by:
the name of the Natural program that contains this SQL statement,
the line number of the SQL statement in this program,
the name of the Natural library into which this program was stowed,
the time stamp when this program was stowed.
Once a statement has been prepared, it can be executed several times
with different variable values, using the dynamic SQL statement EXECUTE
USING DESCRIPTOR or OPEN CURSOR USING DESCRIPTOR.
When the full capacity of the statement table is reached, the entry for the next prepared statement overwrites the entry for a free statement whose latest execution is the least recent one.
When a new SELECT statement is
requested, a free entry in the statement table with the corresponding cursor is
assigned to it and all subsequent FETCH,
UPDATE and
DELETE statements
referring to this SELECT statement will use
this cursor. Upon completion of the sequential scanning of the table, the
cursor is released and free for another assignment. While the cursor is open,
the entry in the statement table is marked as used and cannot be reused by
another statement.
If the number of nested FIND (SELECT)
statements reaches the number of entries available in the statement table, any
further SQL statement is rejected at execution time and a Natural error message
is returned.
The size of the statement table depends on the size specified for the
module NDBIOMO. Since
the statement table is contained in the DB2 buffer area, the setting of Natural
profile parameter DB2SIZE (see also
Natural Parameter Modifications for Natural for DB2 in
Installing
Natural for DB2 on z/OS in the
Installation documentation) may not be sufficient and may
need to be increased.
The embedded SQL uses cursor logic to handle
SELECT statements.
The preparation and execution of a SELECT statement is done as
follows:
The typical SELECT statement is prepared by a program
flow which contains the following embedded SQL statements (note that
X and
SQLOBJ are SQL variables, not program
labels):
DECLARE SQLOBJ STATEMENT DECLARE X CURSOR FOR SQLOBJ INCLUDE SQLDA (copy SQL control block)
Then, the following statement is moved into
SQLSOURCE:
SELECT PERSONNEL_ID, NAME, AGE
FROM EMPLOYEES
WHERE NAME IN (?, ?)
AND AGE BETWEEN ? AND ?
Note:
The question marks (?) above are parameter markers which indicate
where values are to be inserted at execution time.
PREPARE SQLOBJ FROM SQLSOURCE
Then, the SELECT statement is executed as follows:
OPEN X USING DESCRIPTOR SQLDA FETCH X USING DESCRIPTOR SQLDA
The descriptor SQLDA is used to indicate a variable
list of program areas. When the OPEN statement is executed, it
contains the address, length and type of each value which replaces a parameter
marker in the WHERE clause of the SELECT statement.
When the FETCH
statement is executed, it contains the address, length and type of all program
areas which receive fields read from the table.
When the FETCH statement is executed for the first
time, it sets the Natural system variable
*NUMBER
to a non-zero value if at least one record is found that meets the search
criteria. Then, all records satisfying the search criteria are read by repeated
execution of the FETCH statement.
To help improve performance, especially when using distributed
databases, the DB2-specific FOR FETCH ONLY clause can be used.
This clause is generated and executed if rows are to be retrieved only; that
is, if no updating is to take place.
Once all records have been read, the cursor is released by executing the following statement:
CLOSE X
This section describes how to prepare Natural programs for static execution.
The following topics are covered:
For an explanation of the symbols used in this section to describe the syntax of Natural statements, see Syntax Symbols in the Statements documentation.
Static SQL is generated in Natural batch mode for one or more Natural applications which can consist of one or more Natural object programs. The number of programs that can be modified for static execution in one run of the generation procedure is limited to 999.
During the generation procedure, the database access statements contained in the specified Natural objects are extracted, written to work files, and transformed into a temporary Assembler program. If no Natural program is found that contains SQL access or if any error occurs during static SQL generation, batch Natural terminates and condition code 40 is returned, which means that all further JCL steps must no longer be executed.
The Natural modules NDBCHNK and NDBSTAT must
reside in a steplib of the generation step. Both are loaded dynamically during
the execution of the generation step.
The temporary Assembler program is written to a temporary file (the
Natural work file CMWKF06) and precompiled. The size of the
workfile is proportional to the maximum number of programs, the number of SQL
statements and the number of variables used in the SQL statements. During the
precompilation step, a database request module (DBRM) is created, and after the
precompilation step, the precompiler output is extracted from the Assembler
program and written to the corresponding Natural objects, which means that the
Natural objects are modified (prepared) for static execution. The temporary
Assembler program is no longer used and deleted.
A static database request module is created by using either the sample job provided on the installation medium or an appropriate job created with the Create DBRM function.
The following topics are covered:
 To generate static SQL for Natural programs
To generate static SQL for Natural programs
Logon to the Natural system library SYSDB2.
Since a new SYSDB2 library has been created when
installing Natural for DB2, ensure that it contains all Predict interface
programs necessary to run the static SQL generation. These programs are loaded
into SYSDB2 at Predict installation time (see the relevant
Predict product documentation).
Specify the CMD CREATE command and the
Natural input necessary for the static SQL generation process; the
CMD CREATE command has the following syntax:
CMD
CREATE DBRM
static-name
USING
using-clause |
{application-name,object-name,excluded-object} |
:
|
:
|
The generation procedure reads but does not modify the specified Natural objects. If one of the specified programs was not found or had no SQL access, return code 4 is returned at the end of the generation step.
If the PREDICT
DOCUMENTATION option is to be used, a corresponding Predict
static SQL entry must be available and the
static-name must correspond to the name
of this entry. In addition, the
static-name must correspond to the name
of the DBRM to be created during precompilation. The
static-name can be up to 8 characters
long and must conform to Assembler naming conventions.
The using-clause specifies the
Natural objects to be contained in the DBRM. These objects can either be
specified explicitly as INPUT DATA in the JCL or obtained as
PREDICT
DOCUMENTATION from Predict.
|
|
|
|
WITH
XREF
|
|
|
|
|
|
FS
|
|
|
|
|
[LIB lib-name
] |
If the parameters to be specified do not fit in one line, specify the
command identifier (CMD) and the various parameters in separate
lines and use both the input delimiter (as specified with the Natural
profile/session parameter ID - default is a comma
(,) - and the continuation character indicator - as specified with the Natural
profile/session parameter CF; default is a
percent (%) - as shown in the following example:
Example:
CMD CREATE,DBRM,static,USING,PREDICT,DOCUMENTATION,WITH,XREF,NO,% LIB,library
Alternatively, you can also use abbreviations as shown in the following example:
Example:
CMD CRE DBRM static US IN DA W XR Y FS OFF LIB library
The sequence of the parameters USING,
WITH, FS and
LIB is optional.
As input data, the applications and names of the Natural objects to be
included in the DBRM must be specified in the subsequent lines of the job
stream ( application-name,object-name).
A subset of these objects can also be excluded again
(excluded-objects). Objects in
libraries whose names begin with SYS can be used for static
generation, too.
The applications and names of Natural objects must be separated by the
input delimiter - as specified with the Natural profile parameter
ID; default
is a comma (,). If you wish to specify all objects whose names begin with a
specific string of characters, use an
object-name or
excluded-objects name that ends with
asterisk notation (*). To specify all objects in an application, use asterisk
notation only.
Example:
LIB1,ABC* LIB2,A*,AB* LIB2,* : .
The specification of applications/objects must be terminated by a line that contains a period (.) only.
Since Predict supports static SQL for DB2, you can also have Predict
supply the input data for creating static SQL by using already existing
PREDICT DOCUMENTATION.
Since Predict Active References supports static SQL for DB2, the generated static DBRM can be documented in Predict, and the documentation can be used and updated with Natural.
WITH XREF is the option which enables you to store
cross-reference data for a static SQL entry in Predict each time a static DBRM
is created (YES). You can instead specify that no cross-reference
data are stored (NO) or that a check is made to determine whether
a Predict static SQL entry for this static DBRM already exists
(FORCE). If so, cross-reference data are stored; if not, the
creation of the static DBRM is not allowed. For more detailed information on
Predict Active References, refer to the relevant Predict documentation.
When WITH XREF (YES/FORCE) is specified,
XREF data are written for both the Predict static SQL entry (if
defined in Predict) and each generated static Natural program. However, static
generation with WITH XREF (YES/FORCE) is possible only if the
corresponding Natural programs have been cataloged with XREF
ON.
WITH XREF FORCE only applies to the USING INPUT
DATA option.
Note:
If you do not use Predict, the XREF option must be
omitted or set to NO and the module NATXRF2 need not
be linked to the Natural nucleus.
If the FS (file server) option is set to ON,
a second SELECT is generated for the
Natural file server for DB2.
ON is the default setting.
If the FS option is set to OFF, no second
SELECT is generated, which results in less SQL statements being
generated in your static DBRM and thus in a smaller DBRM.
With the LIB (library) option, a Predict library other
than the default library (*SYSSTA*) can be specified to contain
the Predict static SQL entry and XREF data. The name of the
library can be up to eight characters long.
In this step, the precompiler is invoked to precompile the generated temporary Assembler program. The precompiler output consists of the DBRM and a precompiled temporary Assembler program which contains all the database access statements transformed from SQL into Assembler statements.
Later, the DBRM serves as input for the BIND step and the
Assembler program as input for the modification step.
The modification procedure modifies the Natural objects involved by
writing precompiler information into the object and by marking the object
header with the static-name as
specified with the CMD CREATE command.
In addition, any existing copies of these objects in the Natural global
buffer pool (if available) are deleted and XREF data are written
to Predict (if specified during the generation procedure).
 To perform the modification procedure
To perform the modification procedure
Logon to the Natural system library SYSDB2.
Specify the CMD MODIFY command which has the following
syntax:
CMD
MODIFY [XREF]
|
The input for the modify step is the precompiler output which must
reside on a data set defined as the Natural work file CMWKF01.
The output consists of precompiler information which is written to the corresponding Natural objects. In addition, a message is returned telling you whether it was the first time an object was modified for static execution (modified) or whether it had been modified before (re-modified).
If you specify the XREF option of the CMD
MODIFY command, an output listing is created on the work file
CMWKF02, which contains the DBRM name and the Assembler statement
number of each statically generated SQL statement together with the
corresponding Natural source code line number, program name, library name,
database ID and file number.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------....
DBRMNAME STMTNO LINE NATPROG NATLIB DB FNR COMMENT ....
-------------------------------------------------------------------------....
TESTDBRM 000627 0390 TESTPROG SAG 010 042 INSERT ....
000641 0430 INSERT ....
000652 0510 SELECT ....
000674 0570 SELECT ....
000698 0570 SELECT 2ND ....
000728 0650 UPD/DEL ....
000738 0650 UPD/DEL 2ND ....
000751 0700 SELECT ....
000775 0700 SELECT 2ND .... |
The columns in the output listing are explained below:
| Column | Explanation |
|---|---|
DBRMNAME |
Name of the DBRM which contains the static SQL statement. |
STMTNO |
Assembler statement number of the static SQL statement. |
LINE |
Corresponding Natural source code line number. |
NATPROG |
Name of the Natural program that contains the static SQL statement. |
NATLIB |
Name of the Natural library that contains the Natural program. |
DB / FNR |
Natural database ID and file number. |
COMMENT |
Type of SQL statement, where 2ND indicates that
the corresponding statement is used for a reselection; see also the
Concept of the File
Server.
|
We recommend that you execute the DB2 BIND command
after the CMD
MODIFY command.
The DB2 BIND command binds the DBRM into a DB2 package.
You can bind one or more DB2 packages into a DB2 application plan. In addition
to the packages of static DBRMs created with the
CMD
CREATE command, this application plan can also contain the
package of the DBRM of the NDBIOMO module
Natural provides for dynamic SQL execution.
A DBRM can be bound into any number of packages and the packages can be bound into any number of application plans where required. A plan is physically independent of the environment where the program is to be run. However, you can group your packages logically into plans which are to be used for either batch or online processing, where the same package can be part of both a batch plan and an online plan.
Unless you are using plan switching, only one plan can be executed per
Natural session. Thus, you must ensure that the plan name specified in the
BIND step is the same as the one used to execute Natural.
To be able to execute Natural in static mode, all users of Natural must
have the DB2 EXECUTE PLAN/PACKAGE privilege for the plan created
in the BIND step.
To execute static SQL, start Natural and execute the corresponding Natural program. Internally, the Natural runtime interface evaluates the precompiler data written to the Natural object and then performs the static accesses.
To the user there is no difference between dynamic and static execution.
It is possible to operate Natural in a mixed static and dynamic mode where for some programs static SQL is generated and for some not.
The mode in which a program is run is determined by the Natural object program itself. If a static DBRM is referenced in the executing program, all statements in this program are executed in static mode.
Note:
Natural programs which return a runtime error do not automatically
execute in dynamic mode. Instead, either the error must be corrected or, as a
temporary solution, the Natural program must be recataloged to be able to
execute in dynamic mode.
Within the same Natural session, static and dynamic programs can be mixed without any further specifications. The decision which mode to use is made by each individual Natural program.
For a list of error messages that may be issued during static generation, refer to Static Generation Messages and Codes Issued under NDB in the Natural Messages and Codes documentation.
This section describes how to switch application plans within the same Natural session in different TP-monitor environments or in batch mode.
The following topics are covered:
When using application plan switching, you can switch to a different application plan within the same Natural session.
If a second application plan is to be used, this can be specified by
executing the Natural program NATPLAN. NATPLAN is
contained in the Natural system library SYSDB2 and can be invoked
either from within a Natural program or dynamically by entering the command
NATPLAN at the NEXT prompt. The only
input value required for NATPLAN is an eight-character plan name.
If no plan name is specified, you are prompted by the system to do so.
Before executing NATPLAN, ensure that any open DB2
recovery units are closed.
Since the NATPLAN program is also provided in source form,
user-written plan switching programs can be created using similar logic.
The actual switch from one plan to another differs in the various environments supported. The feature is available under Com-plete, CICS, and IMS TM MPP. When using the Call Attachment Facility (CAF) or Resource Recovery Services Attachment Facility (RRSAF), it is also available in TSO and batch environments.
In some of these environments, a transaction ID or code must be specified instead of a plan name.
Under CICS, you have the option of using either plan switching by
transaction ID (default) or dynamic plan selection exit routines. Thus, by
setting the field #SWITCH-BY- TRANSACTION-ID in the
NATPLAN program to either TRUE or FALSE,
either the subroutine CMTRNSET or the desired plan name is written
to temporary storage queue.
For more information on activating plan switching under CICS, see Installation Steps Specific to CICS in the Installing Natural for DB2 on z/OS documentation.
Below is information on:
If #SWITCH-BY-TRANSACTION-ID is set to
FALSE, the desired plan name is written to a temporary storage
queue for a CICS/DB2 exit routine specified as PLANExit attribute of a DB2ENTRY
or of the DB2CONN definition, the NATPLAN program must be invoked
before the first DB2 access. Natural for DB2 provides NDBUEXT as
CICS DB2 plan selection exit program. For additional information on CICS/DB2
exit routines, refer to the relevant IBM literature.
The name of the temporary storage queue is
PLANsssstttt, where
ssss is the remote or local CICS system
identifier and tttt the CICS terminal
identifier.
When running in a CICSplex environment, the CICS temporary storage
queue PLANsssstttt containing the plan
name must be defined with TYPE=SHARED or TYPE=REMOTE
in a CICS TST.
For each new DB2 unit of recovery, the appropriate plan selection exit routine is automatically invoked. This exit routine reads the temporary storage record and uses the contained plan name for plan selection.
When no temporary storage record exists for the Natural session, a default plan name, contained in the plan exit, can be used. If no plan name is specified by the exit, the name of the plan used is the same as the name of the static program (DBRM) issuing the SQL call. If no such plan name exists, an SQL error results.
In Com-plete environments, plan switching is accomplished by using the Call Attachment Facility (CAF), which releases the thread in use and attaches another one that has a different plan name.
Once the DB2 connection has been established, the same plan name
continues to be used until the plan is explicitly changed with IBM's call
attachment language interface (DSNALI). For additional information
on the CAF interface, refer to the relevant IBM literature.
Under Com-plete, the NATPLAN program first issues an
END TRANSACTION
statement and then invokes an Assembler routine by using
DB2SERV.
The assembler routine performs the actual switching. It issues a
CLOSE request to DSNALI to terminate
the DB2 connection (if one exists). It then issues an
OPEN request to re-establish the DB2 connection and
to allocate the resources needed to execute the specified plan.
If NATPLAN has not been executed before the first SQL
call, the default plan used is the one defined in the Com-plete startup
parameters. Once a plan has been changed using NDBPLAN, it remains
scheduled until another plan is scheduled by NDBPLAN or until the
end of the Natural session.
In an IMS MPP environment, the switch is accomplished by using direct or deferred message switching. As a different application plan is associated with each IMS application program, message switching from one transaction code to another automatically switches the application plan being used.
Since Natural applications can perform direct or deferred message
switches by calling the appropriate supplied routines, use of the
NATPLAN program for plan switching is optional.
NATPLAN calls the Assembler routine CMDEFSW,
which sets the new transaction code to be used with the next following terminal
I/O operation.
In the TSO and batch environments, plan switching is accomplished by using the Call Attachment Facility (CAF) or the Resource Recovery Services Attachment Facility (RRSAF). Either facility releases the thread in use and attaches another one that has a different plan name.
Below is information on:
Initial connection and plan setting can be done using the
subparameters DB2PLAN
and DB2SSID of
the NTDB2
macro or of the DB2 profile parameter
without using the NATPLAN program. However, the initial settings
could be overwritten by using the NATPLAN program.
When using the Call Attachment Facility (CAF), plan selection is either implicit or explicit. If no DB2 connection has been made before the first SQL call, a plan name is selected by DB2. If so, the plan name used is the same as the name of the program (DBRM) issuing the SQL call.
Once the DB2 connection has been established, the plan name is
retained until explicitly changed by IBM's call attachment language interface
(DSNALI). For additional information on the CAF interface, refer
to the relevant IBM literature.
Under TSO and in batch mode, the NATPLAN program first
issues an END
TRANSACTION statement and then invokes an Assembler routine
by using DB2SERV.
Note:
Modify the NATPLAN program by setting the
#SSM field to the current DB2 subsystem name; the default name is
DB2.
The assembler routine performs the actual switching. It issues a
CLOSE request to DSNALI to terminate a
possible DB2 connection. It then issues an OPEN
request to re-establish the DB2 connection and to allocate the resources needed
to execute the specified plan.
If NATPLAN has not been executed before the first SQL
call, plan selection is done by DSNALI. If so, the plan name used
is the same as the name of the program issuing the SQL call. The subsystem ID
used is the one specified during the DB2 installation. If no such plan name or
subsystem ID exists, a Natural error message is returned.
If a static DBRM issues the SQL call, a plan name must exist with the same name as the one of the static DBRM.
If dynamic SQL is used, a DB2 plan must exist which contains a package
with the DBRM of the NDBIOMO module. If the name of the DB2 plan
has neither been defined in the NATPLAN program nor with the
DB2PLAN keyword subparameter, the DB2 Call Attachment
Facility (CAF) uses the name of the NDBIOMO DBRM as the default
plan name.
Note:
To avoid any confusion concerning the chosen plan name and/or
subsystem ID, always call NATPLAN before the first SQL
call.
Initial connection and plan setting can be done using the keyword
subparameters DB2COLL,
DB2GROV,
DB2PLAN,
DB2SSID
and DB2XID of
the NTDB2
macro or of the DB2 profile parameter
without using the NATPLAN program. However, the initial settings
can be overwritten by using the NATPLAN program.
When using the Resource Recovery Services Attachment Facility (RRSAF), plan selection is explicit.
RRSAF is used if IBM's DSNRLI interface module is linked
to Natural. Once the DB2 connection has been established, the plan name is
retained until explicitly changed with RRSAF. For additional information on
RRSAF, refer to the relevant IBM literature.
The NATPLAN program performs the actual switching. It
issues a TERMINATE IDENTIFY request to
DSNRLI to terminate a possible DB2 connection.
NATPLAN then issues an IDENTIFY request
to re-establish the DB2 connection. This request is followed by
SIGNON and CREATE THREAD
requests.
In an RRSAF environment, up to four of the following parameters can be
specified in NATPLAN where #PLAN is
mandatory:
| Parameter | Default Value | Format | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
#PLAN |
None | A8 | Name of the plan used for SQL processing in the thread created
(CREATE THREAD).
|
#SSM |
DB2 |
A4 | Subsystem ID of the DB2 server connected
(IDENTIFY).
|
#COLLID |
COLLID |
A18 |
Only used if the first character of #PLAN is a question mark (?). Collection ID used for SQL processing in the thread created
( |
#XID |
1 |
I4 |
Indicates that a global transaction ID is used. If set to0 (SIGNON), no global transaction ID is
used.
|
Example of Plan Selection with RRSAF under TSO
The example below demonstrates plan selection under TSO by using RRSAF.
NATPLAN
<Enter>
Please enter new plan name NDBPLAN4
,SUB SYSTEM ID DB27
,COLLECTION ID
,global XID (0/1) __________1
<Enter>
The example below demonstrates plan selection in batch mode by using RRSAF:
NATPLAN NDBPLAN4,DB27, ,1