To enable Natural to access a DB2 table, a logical Natural data
definition module (DDM) of the table must be generated. This is done either
with Predict (see the relevant Predict documentation for details) or with the
Natural utility SYSDDM; see also
SYSDDM
Utility in the Natural Editors
documentation.
If you do not have Predict installed, use the SYSDDM
function SQL
Services to generate Natural DDMs from DB2 tables. This
function is invoked from the main menu of SYSDDM and is described
on the following pages.
For further information on Natural DDMs, see Data Definition Modules - DDMs in the Natural Programming Guide.
This section covers the following topics:
The SQL Services (NDB) function of the Natural
SYSDDM utility (see Using SYSDDM Maintenance and
Service Functions in the Natural
Editors documentation) is used to access DB2 tables. You
access the catalog of the DB2 server to which you are connected, for example,
by using the Environment
Setting function as described in Natural Tools
for DB2, or by entering the name of a server in the Server
Name field on the SQL Services Menu. The name
of the DB2 server to which you are connected is then displayed in the top
left-hand corner of the screen SQL Services Menu. You can
access any DB2 server that is located on either a mainframe (z/OS) or a UNIX platform if the servers have been
connected via DRDA (Distributed Relational Database Architecture). For further
details on connecting DB2 servers and for information on binding the
application package (SYSDDM uses I/O module
NDBIOMO) to
access data on remote servers, refer to the relevant IBM literature.
The SQL Services function determines whether you are connected to a mainframe DB2 (z/OS) or a UNIX DB2, access the appropriate DB2 catalog and performs the functions listed below.
Note:
If you use SYSDDM SQL Services in a
CICS environment without file server, specify
CONVERS=ON
in the NTDB2
macro; otherwise you might get SQLCODE -518.
 To invoke the SQL Services function
To invoke the SQL Services function
In the command line, enter the Natural system command
SYSDDM and press ENTER.
Or:
From the Natural main menu, choose Maintenance and Transfer Utilities to display the Maintenance and Transfer Utilities menu.
From the Maintenance and Transfer Utilities menu, choose Maintain DDMs.
The menu of the SYSDDM utility is displayed. The fields
and functions provided on the SYSDDM utility menu are explained in
the section Using
SYSDDM Maintenance and Service Functions.
In the Code field of the Natural
SYSDDM utility Menu, enter code
B and press ENTER.
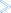
The SQL Services Menu is displayed.
11:31:39 ***** NATURAL SYSDDM UTILITY ***** 2009-11-27
Server DAEFDB29 - SQL Services: Menu -
Code Function
S Select SQL Table from a List
G Generate DDM from an SQL Table
L List Columns of an SQL Table
? Help
. Exit
Code ... _
Table name ... ________________________________
Creator ...... ________________________________
Replace ...... N (Y,N) DDM Name with Creator .. Y (Y/N)
Server name .. DAEFDB29__________
Remark ....... O (Overwrite/SQL/Comment)
Command ===>
Enter-PF1---PF2---PF3---PF4---PF5---PF6---PF7---PF8---PF9---PF10--PF11--PF12---
Help Exit Canc |
The functions available on this screen are described in the corresponding sections.
This function is used to select a DB2 table from a list for further processing.
 To invoke the Select SQL Table from a List function
To invoke the Select SQL Table from a List function
On the SQL Services Menu, enter function code S.
If you enter the function code only, you obtain a list of all tables defined to the DB2 catalog.
If you do not want a list of all tables but would like only a certain range of tables to be listed, you can, in addition to the function code, specify a value in the Table Name and/or Creator fields. You can use asterisk notation (*) or the greater-than character (>) for a start value.
Press ENTER.
The Select SQL Table From A List screen is invoked displaying a list of all DB2 tables requested. On the list, you can mark a DB2 table with a function code:
| Code | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| G | Generate DDM from an SQL Table | This function can be used to generate a Natural DDM from a DB2 table, based on the definitions in the DB2 catalog. |
| L | List Columns of an SQL Table | This function lists all columns of a specific DB2 table. |
This function is used to generate a Natural DDM from a DB2 table, based on the definitions in the DB2 catalog.
The following topics are covered below:
 To invoke the function
To invoke the function
On the SQL Services Menu, enter function code G along with the name and creator of the table for which you wish a DDM to be generated.
If you do not know the table name/creator, you can use the function Select SQL Table from a List to choose the table you want.
If you do not want the creator of the table to be part of the DDM
name, enter an N (No) in the field DDM Name with
Creator. The default setting is is Y (Yes).
If you wish to generate a DDM for a table for which a DDM already
exists and you want the existing one to be replaced by the newly generated one,
enter a Y (Yes) in the Replace field.
By default, Replace is set to N
(No) to prevent an existing DDM from being replaced accidentally.
In the Remark field you can specify the contents of the DDM Remark column. Enter:
O (Overwrite)
|
for SQL column remarks if defined, overwritten by field information generated by Natural if available. This is the default setting; |
S (SQL)
|
for SQL column remarks if defined and blank otherwise; |
C (Comment)
|
for field information generated by Natural if available. SQL column remarks will be copied to a separate DDM comment line. |
By default, Remark is set to O
(Overwrite).
To define or alter a default value for the fields
Code, Table Name,
Creator, Replace, DDM Name
with Creator or Remark use user exit
NDBDDM-2 and its data area NDBDDM-L provided in
library SYSDB2. See
Making a User Exit
Routine Available. For detailed information on how to
handle NDBDDM-2, refer to the remarks in its source.
Important:
Since the specification of any special characters as part
of a field or DDM name does not comply with Natural naming conventions, any
special characters allowed within DB2 must be avoided. DB2 delimited
identifiers must be avoided, too.
To avoid user interaction popup windows during DDM field generation,
the user exit NDBDDM-1 and its data area NDBDDM-L
provided in library SYSDB2 can be used. For detailed information
on how to handle NDBDDM-1, refer to the remarks in its source. See
also Making a User
Exit Routine Available.
When the Generate DDM from an SQL Table function is invoked for a table for which a DDM is to be generated for the first time, the DBID/FNR Assignment screen is displayed. If a DDM is to be generated for a table for which a DDM already exists, the existing DBID and FNR are used and the DBID/FNR Assignment screen is suppressed.
On the DBID/FNR Assignment screen, enter one of the database IDs (DBIDs) chosen at Natural installation time, and the file number (FNR) to be assigned to the DB2 table. Natural requires these specifications for identification purposes only.
The range of DBIDs which is reserved for DB2 tables is specified in
the NTDB
macro of the Natural parameter module (see the Natural Parameter
Reference documentation) for the database type DB2. Any DBID not
within this range is not accepted. The FNR can be any valid file number within
the database (between 1 and 65535).
After a valid DBID and FNR have been assigned, a DDM is automatically generated from the specified table.
The maximum field length supported by Natural is 1 GB-1 (1073741823 bytes). If a DB2 table contains a column which is longer than 253 bytes or if a DB2 column is defined as a DB2 LOB field, the pop-up window Long Field Generation will be invoked automatically. A DB2 LOB field may be defined as a simple Natural variable with a maximum length of 1GB-1, or as a dynamic Natural variable.
A field which is longer than 253 bytes and which is not a DB2 LOB field may be defined as a simple Natural field with a maximum length of 1GB-1, or as an array. In the DDM, such an array is represented as a multiple-value variable.
If, for example, a DB2 column has a length of 2000 bytes, you can specify an array element length of 200 bytes, and you receive a multiple-value field with 10 occurrences, each occurrence with a length of 200 bytes.
Since generated long fields are not multiple-value fields in the sense of Natural, the Natural C* notation makes no sense here and is therefore not supported.
When such a generated long field is defined in a Natural view to be referenced by Natural SQL statements (that is, by host variables which represent multiple-value fields), both when defined and when referenced, the specified range of occurrences (index range) must always start with occurrence 1. If not, a Natural syntax error is returned.
UPDATE table SET varchar = #arr(*) SELECT ... INTO #arr(1:5)
Note:
When such a generated long field is updated with the Natural DML
UPDATE
statement, care must be taken to update each occurrence appropriately.
For each of the column types listed above, an additional length
indicator field (format/length I2 or I4 for LOB fields) is
generated in the DDM. The length is always measured in number of characters,
not in bytes. To obtain the number of bytes of a VARGRAPHIC,
LONG VARGRAPHIC or DBCLOB field, the length must be
multiplied by 2.
The name of a length indicator field begins with L@
followed by the name of the corresponding field. The value of the length
indicator field can be checked or updated by a Natural program.
If the length indicator field is not part of the Natural view and if
the corresponding field is a redefined long field, the length of this field
with UPDATE and STORE operations is calculated
without trailing blanks.
With Natural, it is possible to distinguish between a null value and the actual value zero (0) or blank in a DB2 column.
When a Natural DDM is generated from the DB2 catalog, an additional
NULL indicator field is generated for each column which can be
NULL; that is, which has neither NOT NULL nor
NOT NULL WITH DEFAULT specified.
The name of the NULL indicator field begins with
N@ followed by the name of the corresponding field.
When the column is read from the database, the corresponding indicator
field contains either zero (0) (if the column contains a value,
including the value 0 or blank) or -1 (if the column
contains no value).
The column NULLCOL CHAR(6) in a DB2 table definition
would result in the following view fields:
NULLCOL A 6.0 N@NULLCOL I 2.0
When the field NULLCOL is read from the database, the
additional field N@NULLCOL contains:
0 (zero) if NULLCOL contains a value
(including the value 0 or blank),
-1 (minus one) if NULLCOL contains no
value.
A null value can be stored in a database field by entering
-1 as input for the corresponding NULL indicator
field.
Note:
If a column is NULL, an implicit RESET
is performed on the corresponding Natural field.
For each LOB column, an additional locator field will be
generated in the I4 format.
A LOB locator may be used to reference a LOB
value in the DB2 database server, when a LOB value is not needed
locally in a program.
This function lists all columns of a specific DB2 table.
 To invoke the List Columns function
To invoke the List Columns function
On the SQL Services Menu, enter function code L along with the name and creator of the table whose columns you wish to be listed, and press ENTER.
The List Columns screen for this table is invoked, which lists all columns of the specified table and displays the following information for each column:
| Variable | Content | |
|---|---|---|
Name |
The DB2 name of the column. | |
Type |
The column type. | |
Length |
The length (or precision if
type is DECIMAL) of the column as defined in the DB2
catalog.
|
|
Scale |
The decimal scale of the column
(only applicable if type is DECIMAL).
|
|
Update |
Y
|
The column can be updated. |
N |
The column cannot be updated. | |
Nulls |
Y
|
The column can contain null values. |
N |
The column cannot contain null values. | |
Not |
A column whose scale length or whose type is not supported
by Natural is marked with an asterisk (*). For such a column, a view field
cannot be generated. The maximum scale length supported is 7 bytes. |
|
The data types DATE, TIME,
TIMESTAMP, FLOAT and ROWID are converted
into numeric or alphanumeric fields of various lengths: DATE is
converted into A10, TIME into A8, TIMESTAMP into A26,
FLOAT into F8 and ROWID into A40. DATE
and TIME could be mapped alternatively to Natural
DATE and Natural TIME respectively.
For DB2, Natural provides a DB2 TIMESTAMP column as an
alphanumeric field (A26) in the format
YYYY-MM-DD-HH.II.SS.MMMMMM.
Alternatively, you can generate the Natural TIME field (data
format T) as DB2 TIMESTAMP data type if the
DBTSTI
option of the COMPOPT system command is set to
ON (see the System Commands
documentation).
You can use the Natural subprogram
NDBSTMP to
compute TIMESTAMP (A26) fields.
You can customize the Generating Natural Data Definition
Modules (DDMs) map with user exit routine NDBDDM-1 or
NDBDDM-2.
 To make user exit routine
To make user exit routine NDBDDM-1 or
NDBDDM-1 available
Catalog the NDBDDM-num
source object under the name NDBDDMUnum
in library SYSDB2.
Note:
The names of the source object and the cataloged object of the
user exit routine must be different to ensure that the overwriting of the
source object during an update installation does not affect the cataloged
object.
Copy NDBDDMUnum to steplib
SYSLIBS.
A subprogram used by SYSDDM searches for
NDBDDMUnum in steplib
SYSLIBS.