This section describes the dynamic SQL support provided by Natural SQL Gateway. Natural SQL Gateway does not support static SQL.
The SQL support of Natural SQL Gateway provides the flexibility of dynamic SQL support.
In contrast to static SQL support, the Natural dynamic SQL support does
not require any special consideration with regard to the operation of the SQL
interface. All SQL statements required to execute an application request are
generated automatically and can be executed immediately with the Natural
RUN command. Before executing a program, you can
look at the generated SQLCODE, using the LISTSQL
command.
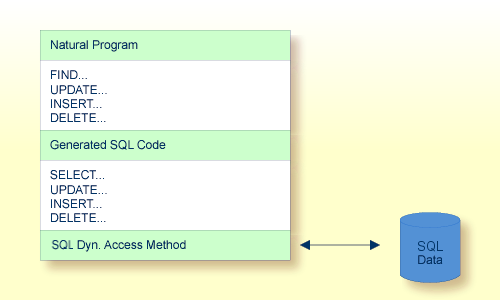
Natural automatically provides for the preparation and execution of each SQL statement and handles the opening and closing of cursors used for scanning a table.
If possible, an SQL statement is only prepared once and can then be
executed several times if required. For this purpose, Natural internally
maintains a table of all SQL statements that have been prepared. In addition,
this table maintains the cursors used by the SQL statements
SELECT,
FETCH,
UPDATE
(positioned), and DELETE (positioned).
Each SQL statement is uniquely identified by:
the name of the Natural program that contains this SQL statement,
the line number of the SQL statement in this program,
the name of the Natural library, into which this program was stowed,
the time stamp when this program was stowed.
Once a statement has been prepared, it can be executed several times
with different variable values, using the dynamic SQL statement EXECUTE
USING DESCRIPTOR or OPEN CURSOR USING DESCRIPTOR
respectively.
When the full capacity of the statement table is reached, the entry for the next prepared statement overwrites the entry for a free statement whose latest execution is the least recent one.
When a new SELECT statement is requested, a free entry in
the statement table with the corresponding cursor is assigned to it and all
subsequent FETCH, UPDATE, and DELETE
statements referring to this SELECT statement will use this
cursor. Upon completion of the sequential scanning of the table, the cursor is
released and free for another assignment. While the cursor is open, the entry
in the statement table is marked as used and cannot be reused by another
statement.
If the number of nested FIND (SELECT)
statements reaches the number of entries available in the statement table, any
further SQL statement is rejected at execution time and a Natural error message
is returned.
Since the statement table is contained in the SQL buffer area, the
DB2SIZE
parameter may not be sufficient and may need to be increased.