This document covers the following topics:
The development environment for Unicode applications is Natural Single Point of Development (SPoD).
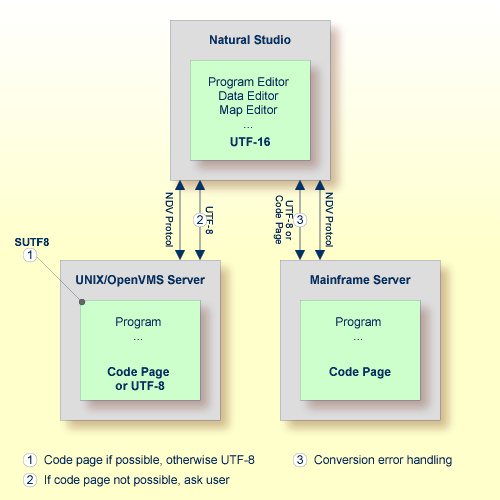
In a SPoD environment, the Natural objects of a Unicode application which are located on a Natural Development Server (NDV) can be modified using Natural Studio. If supported by the server, the sources are exchanged between client and server in UTF-8 format.
On NDV servers for UNIX and OpenVMS, the setting of the profile
parameter SUTF8 determines the format
that is used when storing the Natural object on the server. This is handled
just like the local Windows case.
On NDV servers for mainframes, the objects are stored with the default
or their original encoding, depending on the setting of the profile parameter
SRETAIN.
On Windows, UNIX and OpenVMS platforms, it is important that you define the correct default code page for your environment before changing any Natural code. For more information, see Migrating Existing Applications.
If you want to store characters from different languages in your
sources, you have to save the sources in UTF-8 format on Windows, UNIX or
OpenVMS platforms, or you have to use hexadecimal UH constants in the sources.
With the profile parameters SUTF8 and
SRETAIN you can control in
which format sources are saved. The following table lists some situations and
the recommended settings.
Note:
On UNIX and OpenVMS, the parameter SUTF8 can
only be used in a SPoD environment.
| Situation | Settings | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Sources are located on Windows; U constants are needed. |
SUTF8=ON, SRETAIN=OFF |
All sources are saved in UTF-8 format when saving them with Natural 6.2 or above. New sources are created in UTF-8 format. All characters can be stored in a source. |
| Sources are located on Windows, UNIX and/or OpenVMS; U constants are needed and SPoD is used for development. |
SUTF8=ON, SRETAIN=ON |
All sources are saved in UTF-8 format when a conversion to the original code page is no longer possible; if it is possible, the code page of a source will not be changed. New sources are created in UTF-8 format. All characters can be stored in a source. A source with UTF-8 format can only be changed with SPoD; it can no longer be handled with the Natural for UNIX or Natural for OpenVMS editors. |
| Sources are located on Windows; UNIX and/or OpenVMS; no U constants are needed. |
SUTF8=OFF, SRETAIN=ON |
All sources are saved with the original code page. New sources are saved with the default code page (of server). Only characters from the source code page can be stored in a source. The sources can further be handled with the Natural for UNIX or Natural for OpenVMS editors. |
| Sources are located on Windows, UNIX, OpenVMS and/or mainframe; U constants are needed and SPoD is used for development. |
SUTF8=OFF, SRETAIN=ON |
All sources are saved with the original code page. New sources are saved with the default code page (of the server). Only characters from the source code page can be stored in a source. The sources can further be handled with the Natural for UNIX, Natural for OpenVMS and Natural for Mainframes editors. All Unicode constants have to be defined as hexadecimal constants (UH). |
If the parameter SUTF8 is set to OFF
and you stow a source which contains characters from different character sets,
but which was not yet saved in UTF-8 format, it is possible that the generated
program is created, but that the source cannot be saved and thus remains
unchanged. This happens if characters from different character sets are used in
a comment or in a U constant. For this reason, it is recommended that you set
the parameter SUTF8 to ON if you want to
create sources with characters from different character sets and if your
sources do not need to be distributed to mainframe platforms.
If the parameter SRETAIN is set to
OFF, all sources are saved with the default code page. You have to
be careful with this setting because it may lead to improper code page
information if you have sources which were created with an earlier Natural
version. In this case, the encoding information of the source is unassigned and
the source is always opened with the default code page (value of the system
variable *CODEPAGE).
This will often work even if the default code page is not the correct encoding
of the source. Some language-specific characters will be displayed incorrectly
in this case. If such a source is opened with the wrong code page and is saved
with SRETAIN being set to ON, no encoding
will be stored for the source; the source can later be opened correctly if
Natural is started with the correct default code page. However, once you have
saved the source with SRETAIN being set to
OFF, the default code page will be saved as the encoding of the
source; from this time on, the source will only be opened with this code page.
For this reason, you should use this setting only if you are certain that all
of your Natural sources are encoded in the default code page.
See also: Regional Settings in the Configuration Utility documentation.
The Natural for Windows editors are fully Unicode-enabled. Via SPoD they can also be used for mainframe, UNIX and OpenVMS sources. The editors provided with Natural for Mainframes, Natural for UNIX and Natural for OpenVMS are not Unicode-enabled.
Note:
The editors provided with Natural for Mainframes provide code
page support. See Code Page
Support for Editors, System Commands and Utilities on the
Mainframe.
When a source is opened with an editor in Natural Studio (Natural for Windows), the content of the source will be converted from the corresponding code page to Unicode before it is loaded into the editor. This will guarantee that all characters can be displayed correctly even if the source contains characters which are not included in the system code page. If the conversion from the source's code page to Unicode fails, an error will be displayed and the editor is not opened. In this case, the user has to define the correct encoding of the source. The source encoding can be changed in the Properties dialog box (see Properties for the Nodes in the Using Natural Studio documentation).
For Windows, UNIX and OpenVMS sources, the Natural for Windows editors allow saving sources which contain characters from different languages in UTF-8 format. On mainframes, it will not be possible to save UTF-8 sources.
Note:
If you save a UNIX or OpenVMS source in UTF-8 format or with a code
page which differs from the default code page, the source can no longer be
opened with the native Natural for UNIX or Natural for OpenVMS editor.
Mainframe sources can be saved with a different code page and can be edited
with the native Natural for Mainframes editors.
Even if you do not want to use Unicode strings in your programs and sources, the Unicode-enabled editors have the advantage that you can write sources in all code pages, no matter which system code page is installed. For example, if you have installed the "windows-1252" (Latin 1) code page, you can write a program containing Cyrillic characters and save this program with the "windows-1251" (Cyrillic) code page. You only have to select code page "windows-1251" in the Save As dialog box (see Saving an Object with a New Name in the Using Natural Studio documentation).
Using the Natural for Windows program editor, you can convert text constants into their hexadecimal Unicode representations (see Converting to Hexadecimal Format in the Program Editor section of the Natural for Windows Editors documentation). If you are developing for a platform where UTF-8 sources are not preferred, you can thus enter all characters for a Unicode constant, select all the characters of the constant, convert them to their hexadecimal representation and then add the "UH" prefix for Unicode hexadecimal constants. Furthermore, when you hover the mouse pointer over a character or a selected character range of a text constant, a tool tip shows the corresponding hexadecimal Unicode representation.
A byte order mark (BOM) consists of the character code "U+FEFF" at the beginning of a data stream where it can be used as a signature defining the byte order and encoding form, primarily of unmarked plain-text files. On Windows, a byte order mark is used by some editors (for example, Notepad) to mark UTF-8 files. The Natural for Windows editors will recognize an UTF-8 byte order mark when reading an object. If the object has no other encoding defined so far, Natural will interpret it as UTF-8 and when the object is saved, UTF-8 will be stored as the encoding for the object. The byte order mark is removed in this case.
The following topics are covered below:
The program, map and data area editors provided with Natural for
Mainframes are not Unicode-enabled. Instead the sources are stored with code
page information. According to the setting of the profile parameter
SRETAIN,
Natural sources with code page information may be converted automatically from
the current code page of the source into the default code page of the current
Natural session (value of the system variable
*CODEPAGE)
if the source is loaded into the editor. If there are any characters that
cannot be converted, a window displays a code point conversion error and asks
for substitute values for those code points that cannot be converted. The
display of this message is independent from the current setting of the
parameter CPCVERR. In this
case, the user can decide to open the editor with or without converting the
source into the default code page. Saving or stowing a converted source will
save the new code page information. Sources without code page information (for
example, sources that have been saved or stowed with previous Natural versions)
are loaded into the editors without any conversion. According to the setting of
the profile parameter SRETAIN, the current code page
information of the source will be retained.
Inserting sources with the .I command or the
split screen function will also convert sources, if necessary, according to the
setting of the profile parameter SRETAIN. If characters
cannot be converted, the defined substitution character will be inserted
instead.
The check and conversion of the source is performed when the editor is
started, not when the program is loaded into the source area. If a program is
executed via RUN
program-name, a conversion is not
performed. This causes different behavior, depending on whether
RUN program-name is
entered on the NEXT screen or on an editor screen. If
RUN program-name is
entered on the NEXT screen, no conversion follows; if it is
entered on an editor screen, the editor is started right after the execution of
the program and a conversion is performed.
See the table below for the code page that is assigned to an existing
Natural source that is saved or stowed, depending on the values of the profile
parameters SRETAIN and
CP.
| Original Source Code Page Information | Setting of
SRETAIN |
Source Code Page Information after
SAVE or STOW if
CP is Set to a Value other than OFF |
Source Code Page Information after
SAVE or STOW if
CP is set to OFF |
|---|---|---|---|
| Source without code page information |
SRETAIN=ON SRETAIN=(ON,EXCEPTNEW) |
No code page information | No code page information |
| Source without code page information |
SRETAIN=OFF |
Code page resulting from evaluation of
CP |
No code page information |
| Source is encoded in code page 1 |
SRETAIN=ON SRETAIN=(ON,EXCEPTNEW) |
Original code page (code page 1) | Original code page (code page 1) |
| Source is encoded in code page 1 |
SRETAIN=OFF |
Code page resulting from evaluation of
CP |
Original code page (code page 1) |
The table below shows the code page that is assigned to a new Natural
source that is saved or stowed, depending on the values of the profile
parameters SRETAIN and
CP.
Setting of
SRETAIN |
Source Code Page Information after
SAVE or STOW if
CP is Set to a Value other than OFF |
Source Code Page Information after
SAVE or STOW if
CP is set to OFF |
|---|---|---|
SRETAIN=ON |
Code page resulting from evaluation of
CP |
No code page information |
SRETAIN=OFF |
Code page resulting from evaluation of
CP |
No code page information |
SRETAIN=(ON,EXCEPTNEW) |
No code page information | No code page information |
By default, the system command LIST displays
sources as they are stored in the system file without any conversions.
The CONVERTED option
of the LIST command converts the source into the
default code page (value of the system variable
*CODEPAGE)
if the code page information of the source is provided. All non-convertible
characters are then replaced by the defined substitution character.
The system command
LIST
DIR shows the used code page information of a Natural
source in the directory window.
Similar to the editors, the system command
SCAN
converts the sources before executing the actual
SCAN command.
The Object Handler unloads and loads sources with different code page information and preserves the original code page information.
The transfer format option UTF-8 converts sources from any code page to UTF-8 format while unloading, and stores information about the original code page in the work file. The corresponding load function converts the source back to the original code page or to another code page, if specified. This option can also be used to provide code page information for sources which have been saved or stowed with previous Natural versions and which therefore do not contain any code page information.
Unload and load sources in internal format will keep the code page information, if available.
The SYSCP
utility can be used to obtain information on code pages and to check
or change the code page assignment of a source.