A user definition consists of an authorization table in which you can authorize access to functions for classes of Natural ISPF objects, as well as of default settings on user profiles (PF key assignments, short names for libraries, magic characters, Editor profile, user defaults). All characteristics of the user profile are modifiable by the user. Authorization tables are modifiable only by authorized users.
This document provides information on the following topics:
Natural ISPF allows for three different types of user definition:
Single users:
You can create a separate definition for a specific user ID;
User groups:
You can create a definition for a group of users. You can choose one of the following
methods for associating user IDs with certain groups:
Prefix Method
Derivation from Natural Security
These are explained in the subsection User Group Definitions.
Default definition (user'*'):
It is highly recommended to create a definition for the asterisk (*). This can be
seen as a definition for a null prefix: users are assigned this definition if they log
on with a user ID that is not specifically defined and for which there is neither a
prefix definition nor a Natural Security group definition.
Note
Without a default definition (*), an undefined user ID to which no prefix definition
applies is granted full authorization for the system.
In the case of the prefix method, a user is assigned the definition which most closely matches that user's ID. The following table illustrates how some example user IDs are assigned definitions:
| Definition | Assigned to user ID: |
|---|---|
* |
U1 |
S* |
S1 |
SY* |
SY1 |
You can modify the default user definition, and add and modify single user and group (prefix) definitions at any time.
You can enter the user definition facility in any of two ways:
Select the USER option on the Administrator Menu to display the User
Entry Panel. You can specify a function command in the command line and parameters in
the input fields (see the following subsection);
You can access user definitions from any Natural ISPF screen using function command syntax. See the subsection Maintaining User Definitions with Function Commands.
You can create a definition for a group of users. By setting APPLYMOD 101 to
an appropriate value you can select one of the following methods for associating user IDs
with certain groups.
In this case, a definition for a prefix applies for all user IDs matching that prefix,
except for those users for which the corresponding profile item has been defined
specifically. For example, the definition for the ID SAG* applies to all
user IDs that start with SAG and have no unique definition.
The following flow diagram illustrates the internal handling for the prefix method when a user logs on:
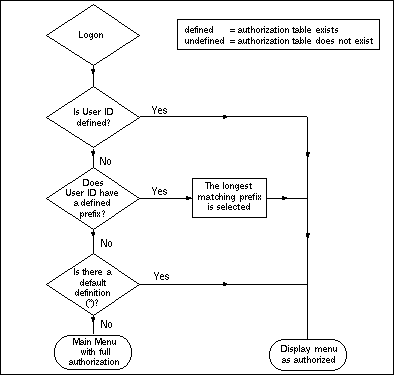
Note
Without a default definition (*), an undefined user ID to which no prefix definition
applies is granted full authorization for the system. When installing Natural ISPF and
setting up the system, you must therefore define at least a default definition (*) to
control access to the system (see the subsection Maintaining User
Definitions).
In this case, a definition made for an ID that has been defined as a user group in Natural Security will be used as a default definition that applies for all members of that group, except for those users for which the corresponding profile item has been explicitly defined.
If a user is a member of several groups, Natural ISPF will first search privileged groups in the specified order and then non-privileged groups in alphabetical order.
The following flow diagram illustrates the internal handling for the Natural Security (NSC) method when a user logs on:
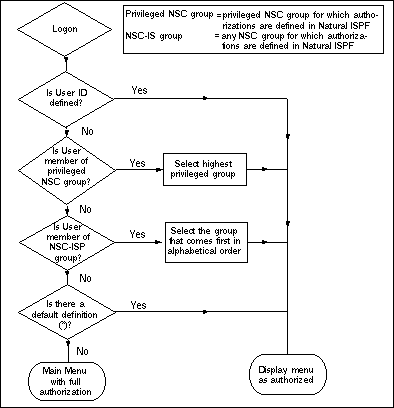
Note
If a user is a member of more than 20 groups, only the first 20 will be evaluated in
the above context.
If you select the USER option from the Administrator Menu, the User Entry
Panel appears:
---------------------------- USER - ENTRY PANEL -------------------------------
COMMAND ===>
User ===> *
Profile type ===> ( A,K,L,C,E,D,B,Y,N,O)
Enter-PF1---PF2---PF3---PF4---PF5---PF6---PF7---PF8---PF9---PF10--PF11--PF12---
Help Split End Suspe Rfind Rchan Up Down Swap Left Right Curso
|
Meaning of the input fields:
| Field | Meaning | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
User |
User ID of user definition to be maintained. You can also
enter the asterisk wildcard (*) to list all user definitions, or ABC*
to list all definitions beginning with ABC.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Profile type |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Note
The Profile type field is not used as selection criterion for the
LIST command. It is used to select sections of the user
profile for EDIT, DELETE or
COPY operations. The whole profile can be selected for
COPY and DELETE operations by
entering the asterisk wildcard (*) in this field.
The user authorization table (characteristic A) can only be modified by
users authorized to access configuration functions. All other characteristics are
modifiable by the user and are described in detail in the section Profile Maintenance in the
Natural ISPF User's Guide. You can access them here to maintain the
default settings.
Once you have entered the specified user definition, you can scroll the profile sections
using the UP and DOWN commands
(usually assigned to PF7 and PF8 respectively).
To access the user authorization table for a user profile, specify the profile name (user
ID, group ID, prefix followed by the wildcard *, or wildcard * only) in the
User field and A in the Profile type field. The
authorization table for the specified definition appears, for example:
--------------------- EDIT USER BRY , Byrone, Rinaldi ------------------------
COMMAND ==>
Authorization Class Level Main Menu ===>
Natural programming ==> 9
PDS Maintenance ==> 9
Data Sets Maintenance ==> 9 + --- COMMANDS LEVEL REMINDER ---- +
SYSOUTS ==> 9 ! Lvl Command Abbreviation !
System info ==> 9 ! --- -------------------- !
Active jobs ==> 9 ! 1 - L,B,ZP,XT,I,ET,DI,DF,RU,XE !
Operator commands ==> 9 ! EX,OT,FR,DW,CR,BPSTAT !
NSPF Administrator ==> 9 ! 2 - E,R,SB,PL,PR,CP,A,CT,U,FL !
PANVALET ==> 9 ! ST,CC,RL,HL,DS,UP !
LIBRARIAN ==> 9 ! 3 - D,PG,CH,NSPR,GENN !
USER defined ==> 9 ! 4 - CM,OPER !
! !
! !
! !
+----------------------------------+
Enter-PF1---PF2---PF3---PF4---PF5---PF6---PF7---PF8---PF9---PF10--PF11--PF12---
Help Split End Suspe Rfind Rchan Up Down Swap Left Right Curso
|
The above authorization table could be in place for user definitions in a z/OS environment that includes CA Panvalet.
Header
The header line contains the function (EDIT USER) and the
user ID invoked.
Main Menu
The field labelled Main Menu contains the name of the menu displayed
when the user logs on to Natural ISPF. The default menu is the Main Menu,
MAIN (see the section Menu
Maintenance).
Authorization class
The column headed Authorization Class contains a list of items that
correspond to Natural ISPF objects and certain administration functions. The classes
displayed correspond to the subsystem(s) installed at your site. For a list of
possible classes, see Authorization
Classes at the end of this documentation.
The extent to which the user is authorized for each class of objects is determined by the authorization level.
Authorization level
The column headed Level contains the numerical identifier of the level
to which the user is authorized for the corresponding class of objects. An
authorization level is a command or group of commands defined in the window headed
Commands Level Reminder. Typing a level number against a class of
objects authorizes the user to issue these commands for the class of objects. The
lowest possible level is blank or 0 (zero) and means that the corresponding object
option does not appear on the user's Main Menu. The highest possible level is 9 and
includes all commands on Levels 1-9.
Command Level Reminder
This window tells you which commands belong to which level. The abbreviations
correspond to the valid abbreviations of the respective commands as follows:
| Level 1 Abbreviation | Function |
|---|---|
L |
LIST |
B |
BROWSE |
ZP |
ZAPS |
XT |
EXTERNS |
I |
INFORMATION |
ET |
EXTENTS |
DI |
DIFFERENCE |
DF |
DEFINITION |
RU |
RUN |
XE |
EXECUTE |
EX |
EXPORT |
OT |
OUTPUT |
FR |
FORMAT |
DW |
DOWNLOAD |
CR |
COMPARE |
BPSTAT |
BPSTAT |
| Level 2 Abbreviation | Function |
|---|---|
E |
EDIT |
R |
RENAME |
SB |
SUBMIT |
PL |
PLAY |
PR |
PRINT |
CP |
COPY |
A |
ALLOCATE |
CT |
CATALOG |
U |
UNCATALOG |
FL |
FOLLOW |
ST |
STATUS
|
CC |
Condition codes |
RL |
RELEASE |
HL |
HOLD |
DS |
DESCRIPTION |
UP |
UPLOAD |
| Level 3 Abbreviation | Function |
|---|---|
D |
DELETE |
PG |
PURGE |
CH |
CHANGE |
NSPR |
Natural ISPF parameters |
GENN |
Generate command processor |
| Level 4 Abbreviation | Function |
|---|---|
CM |
COMPRESS |
OPER |
Issue operator commands |
You can update an authorization by modifying the Main Menu name and/or modifying the authorization level for one or more classes.
For example, if you type 0 in the authorization level field for the Natural
class, the user cannot access Natural objects; this option will not appear on his Main
Menu when he logs on, and he cannot use direct commands for Natural objects.
If you type 1 in the authorization level field for the SYSOUT class, the
user can perform browse functions on job SYSOUTs, but he cannot perform any other
operations. Whether the JOBS option appears on that user's Main Menu depends
on the system authorization level for the option (see the section Menu Maintenance).
If an option does not appear on the user's Main Menu but the user is authorized for some functions on the object type, he or she can use appropriate direct commands.
To save user authorizations, issue the END command (usually
assigned to PF3 ) after having modified any value on the screen.
Below is an example of a default authorization table (*):
-------------------------------- EDIT USER * ----------------------------------
COMMAND ==>
Authorization Class Level Main Menu ===> NULL
Natural programming ==>
PDS Maintenance ==>
Data Sets Maintenance ==> + --- COMMANDS LEVEL REMINDER ---- +
SYSOUTS ==> ! Lvl Command Abbreviation !
System info ==> ! --- -------------------- !
Active jobs ==> ! 1 - L,B,ZP,XT,I,ET,DI,DF,RU,XE !
Operator commands ==> ! EX,OT,FR,DW,CR,BPSTAT !
NSPF Administrator ==> ! 2 - E,R,SB,PL,PR,CP,A,CT,U,FL !
PANVALET ==> ! ST,CC,RL,HL,DS,UP !
LIBRARIAN ==> ! 3 - D,PG,CH,NSPR,GENN !
USER defined ==> ! 4 - CM,OPER !
! !
! !
! !
+----------------------------------+
Enter-PF1---PF2---PF3---PF4---PF5---PF6---PF7---PF8---PF9---PF10--PF11--PF12---
Help Split End Suspe Rfind Rchan Up Down Swap Left Right Curso
|
Explanation: Since all authorization levels are blank (zeroes), undefined users who do
not belong to a prefix group cannot execute any secured function, and they will be
presented with menu NULL when they log on to Natural ISPF (see the section
Menu Maintenance for an
example of menu NULL).
Notes:
END command
or by pressing PF3 without having modified any of the values on the screen,
the authorization table of the individual user specified will not be updated. From this
scenario, you cannot even be sure if the authorization table displayed has been defined
for the user explicitly or if it has been inherited from a prefix definition or from a
(Natural Security-based) user group definition. To be certain that a user has an
individual authorization table, look at the list of Natural ISPF users: all users with
an individual authorization table will be listed with Auth next to user ID
and last access date.
Natural ISPF users are separate objects within Natural ISPF with object type
USR. This means that you (and other authorized users) can maintain user
definitions with function command syntax entered from any system screen.
The available function commands are:
| Command | Object Parameter Syntax |
|---|---|
LIST |
user-id |
EDIT |
user-id
TYPE=t |
DELETE |
user-id
TYPE=t |
COPY |
user-id
TYPE=t,target-user-id,REP |
| Parameter | Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
user-id |
Can be a specific user ID, a prefix notation or the default definition (*). | ||||||||||||||||||||||
t |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
target-user-id |
New user definition to be created or replaced. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
REP |
Specify to replace target definition, if it already exists. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Notes:
USR after the command
keyword.
The following examples are provided below:
The command:
EDIT USR SAG* TYPE=K
displays the PF key table assigned to all users with prefix SAG. You can
modify this table. The update is performed every time you press the ENTER
key, provided the screen contains valid update data. You can leave the screen with the
command END (usually assigned to PF3).
The command:
DELETE USR *
deletes the default definition (*). Note that without a default definition, any undefined user for whom there is no prefix definition receives full authorization at logon.
The command:
COPY USR MBE TYPE=Y
can be used to copy the layout definition of object lists from one user to another. The following window opens:
+---------------------------------------------------+ ! ! ! Copy User MBE Section: LAYOUT ! ! to User ! ! Replace NO ! ! Enter to perform , PF3 to exit ! +---------------------------------------------------+ |
Enter the user ID of the recipient user in the to User input field to copy the layout
definitions from user MBE. All list layouts defined by user
MBE are copied. For details on list layout, see the section LAYOUT Command for
Lists in the section Useful Features of the
Natural ISPF User's Guide.
The command:
LIST USR *
lists all Natural ISPF users, for example:
LIST-USR:* -------------------------------------- Row 0 of 15 - Columns 010 076
COMMAND===> SCROLL===> CSR
USER DATE DEFINED CHARACTERISTICS
** ******************************** top of list *******************************
* *Edited Auth,Edit,Default,Char,
BRY 94/12/13 Auth,Edit,Key,Natural,
GW 94/12/08
HHH Edit,
JWO 94/12/13 Auth,Edit,Default,Char,Key,Color,Natural,Lib,
JWOAB Default,
MAK 94/11/12 Default,Key,
MSE 94/12/09
MZC 94/12/13 Auth,Edit,Default,Char,Key,Layout,Natural,Lib,
MZCC 94/10/27 Auth,Edit,Default,Char,Key,Lib,
SML 94/12/09
UHE 94/10/11 Auth,
WHE 94/10/17
WKK 94/12/01
WOS 94/11/23
** ****************************** bottom of list ******************************
Enter-PF1---PF2---PF3---PF4---PF5---PF6---PF7---PF8---PF9---PF10--PF11--PF12---
Help Split End Suspe Rfind Rchan Up Down Swap Left Right Curso
|
The list contains all users who have logged on Natural ISPF, as well as all defined user definitions (authorization tables and profile sections).
Meaning of the column headings:
| Column | Meaning | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
USER |
User ID, user prefix or *. Each user appears in the list after first logon | ||||||||||||||||||||||
DATE |
Date the user logged on to Natural ISPF last. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
DEFINED CHARACTERISTICS |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
A user characteristic attains defined status when you create or modify it for the user ID, or when a user modifies any characteristic in his or her user profile while working with Natural ISPF.
You can select any user or definition from the list with the
E (EDIT),
CP (COPY) or
D (DELETE) line command entered
in the input field preceding the user ID. The EDIT option
allows you to modify the user's command authorization table as described above, and any
profile setting as described in the section Profile Maintenance in the Natural ISPF
User's Guide.