This document describes the utility "ADADBM".
The following topics are covered:
The ADADBM utility consists of the following functions which may be used to make modifications to the database:
The ADD_CONTAINER function adds a new container file to the Associator or Data Storage data set;
The ADD_FIELDS function adds new fields to the end of a file's FDT;
The ALLOCATE NI, UI, AC or DS function increases the Normal Index, Upper Index, Address Converter or Data Storage space assigned to a file;
The CHANGE function changes the standard length of a field in the Field Definition Table (FDT);
The CHANGE_FIELDS function modifies one or more field specifications in a file;
The DEALLOCATE functions are the inverse functions of ALLOCATE. The NI, UI, AC or DS function returns the Normal Index, Upper Index, Address Converter or Data Storage space which is no longer required by a file to the free space table (FST);
The DELCP function deletes old checkpoint records from the checkpoint file in the specified range of dates;
The DELETE function deletes a single Adabas file or a range of Adabas files from the database;
The DELETE_DATABASE function deletes a database. Depending on the keyword specified, either just the containers are deleted, or the database directory and its content are deleted.
The DISPLAY function displays the utility communication block (UCB);
The DROP_FIELDS function marks the specified fields as not existing, which means that they can no longer be accessed ;
The DROP_LOBFILE function is the inverse function of ADAFDU ADD_LOBFILE;
The DROP_REFINT function drops an existing referential constraint;
The EXTEND_CONTAINER function extends the last container file defined for the database;
The NEW_DBID function changes the identifier of the database in use;
The NEWWORK function allocates and formats a new Adabas WORK data set;
The PGM_REFRESH function enables or disables refreshing an Adabas file inside an application program with an E1 command;
The RBAC_FILE function creates the RBAC system file required for Adabas authorization mode.
The RECOVER function returns lost space to the free space table;
The REDUCE_CONTAINER function reduces the size of the last container file defined for the database;
The REFRESH function resets a single file or a range of files to the state of zero records loaded;
The REMOVE_CONTAINER function removes a container file from the Associator, or Data Storage data set;
The REMOVE_DROP function, used in conjunction with a subsequent REFRESH, removes dropped fields from the FDT;
The REMOVE_REPLICATION function stops all replication processing and deletes the replication system files;
The RENAME function changes the database name or names of loaded files;
The RENUMBER function renumbers a loaded file or exchanges the numbers of loaded files;
The REPLICATION_FILES function creates the system files required for Adabas - Adabas replication;
The RESET function removes entries from the UCB;
The RESET_REPLICATION_TARGET function resets the replication target flag of Adabas files;
The REUSE function controls the reusage of Data Storage space or ISNs by Adabas;
The SECURITY function sets the security mode of the database;
The SYFMAX function specifies the maximum number of values generated for a system generated multiple-value field in the file specified.
This utility is a multi-function utility.
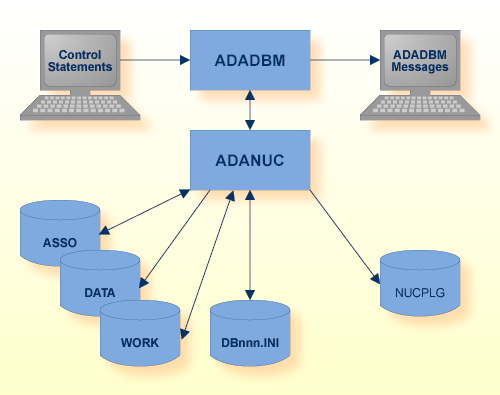
If the Adabas nucleus is active, ADADBM calls the nucleus to modify the database containers. For some tasks, no checkpoints are written, but the activity is logged in the database log, and in the case of a recovery, the activity is re-executed automatically.
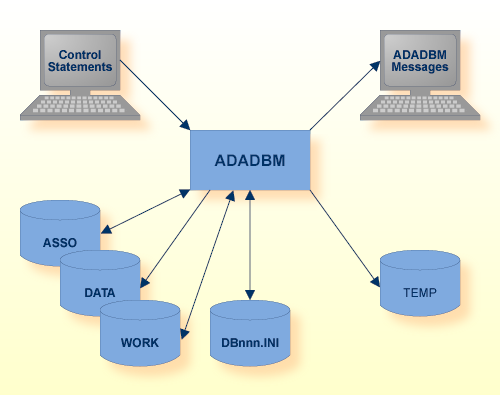
If the Adabas nucleus is not active, ADADBM itself modifies the database containers.
| Data Set | Environment Variable/ Logical Name |
Storage Medium |
Additional Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| Associator | ASSOx | Disk | |
| Data storage | DATAx | Disk | |
| DBnnn.INI | Disk | Adabas Extended Operations Manual | |
| Control statements | stdin | Utilities Manual | |
| ADADBM messages | stdout | Messages and Codes | |
| Protection Log (online mode only) |
NUCPLG | Disk | Utilities Manual: ADANUC, ADAPLP |
| Temporary storage (offline mode only) |
TEMP1 | Disk | New WORK data set for the NEWWORK function. After this function is performed, the Work environment variable/logical name must be changed to point to the new Work data set. |
| Work | WORK1 | Disk |
The following table shows the nucleus requirements for each function and the checkpoints written:
| Function | Nucleus must be active | Nucleus must NOT be active | Nucleus is NOT required | Checkpoint written |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADD_CONTAINER | X | SYNP | ||
| ADD_FIELDS | X |
SYNP (offline) SYNX (online) |
||
| ALLOCATE | X | SYNP | ||
| CHANGE | X | - | ||
| CHANGE_FIELDS | X |
SYNP (offline) SYNX (online) |
||
| DEALLOCATE | X | SYNP | ||
| DELCP | X | SYNP | ||
| DELETE | X |
SYNP (offline) SYNX (online) |
||
| DELETE_DATABASE | X | - | ||
| DISPLAY | X | - | ||
| DROP_FIELDS | X |
SYNP (offline) SYNX (online) |
||
| DROP_LOBFILE | X | SYNP | ||
| EXTEND_CONTAINER | for WORK | for ASSO or DATA | SYNP | |
| NEW_DBID | X (see note 1) | SYNP | ||
| NEWWORK | X (see note 1) | SYNP | ||
| PGM_REFRESH | X | SYNP | ||
| RECOVER | X | SYNP | ||
| REDUCE_CONTAINER | for ASSO or DATA | SYNP | ||
| REFRESH | X | SYNP | ||
| REMOVE_CONTAINER | X | SYNP | ||
| REMOVE_REPLICATION | X |
SYNP (offline) |
||
| RENAME | X | SYNP | ||
| RENUMBER | X | SYNP | ||
| REPLICATION_FILES | X |
SYNP (offline) SYNX (online) (see note 2) |
||
| RESET | X | SYNX | ||
| RESET_REPLICATION_TARGET | ||||
| REUSE | X | SYNP | ||
| SECURITY | X | SYNP (offline) | ||
| SYFMAX | X |
SYNP (offline) SYNX (online) |
Notes:
The following control parameters are available:
ADD_CONTAINER = keyword
D [,BLOCKSIZE=number[K] ]
,SIZE = number [B|M]
ADD_FIELDS = number {field_specification|FDT} ... [END_OF_FIELDS]
ALLOCATE = keyword, FILE = number [,RABN = number],
SIZE = number [B|M]
CHANGE = number, FIELD = string, LENGTH = number
CHANGE_FIELDS = number {field_specification|FDT} ... [END_OF_FIELDS]
M DBID = number
DEALLOCATE = keyword, FILE = number [,RABN = number],
SIZE = numberB
DEFINE_REFINT = number constraint_specification
DELCP = { * | ([absolute-date] [,[absolute-date]]) }
DELETE = (number [-number][,number[-number]]...)
DELETE_DATABASE = keyword
DISPLAY = UCB
DROP_FIELDS = number {field_name|FDT} ... [END_OF_FIELDS]
DROP_LOBFILE = number
DROP_REFINT = number, NAME {=|:}constraint_name
EXTEND_CONTAINER = keyword, SIZE = number [B|M]
D [NO]LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES
NEW_DBID = number
NEWWORK [,BLOCKSIZE=number[K] ], SIZE = number [B|M]
PGM_REFRESH = keyword, FILE = number
RBAC_FILE = number
RECOVER
REDUCE_CONTAINER = keyword, SIZE = number B
REFRESH = (number [-number][,number[-number]]...)
REMOVE_CONTAINER = keyword
[NO]REMOVE_DROP
REMOVE_REPLICATION
RENAME = number, NAME {=|:} string
RENUMBER = (number, number)
REPLICATION_FILES = (file1, file2, file3, file4)
RESET = UCB, IDENT = { (number [,number]...) | * }
RESET_REPLICATION_TARGET = number
REUSE = (keyword [,keyword]), FILE = number
SECURITY = keyword
SYFMAX = number, FILE = number
ADD_CONTAINER = keyword
[,BLOCKSIZE=number[K] ]
,SIZE = number [B|M]
The ADD_CONTAINER function adds a new container file to an existing Associator or Data Storage dataset in accordance with the keyword used. The keyword can take the values ASSO or DATA .
The new container file may be allocated on the same device as the current container files or it may be allocated on a different device type.
The placement of the new container file depends on the environment variable/logical name ASSOx or DATAx. This has to be set to a legal file name with its whole path name. If ASSOx or DATAx is not set, the container files are created in the current directory.
Notes:
This parameter specifies the block size in bytes (or in kilobytes, if "K" is specified after the number) of the new container file.
Adabas rounds up the value you specify to the next multiple of 1K. The minimum block size is 1K and maximum block size is 32K.
The default value for BLOCKSIZE is the block size of the last container file of the dataset in question that is currently present in the database.
This parameter specifies the number of blocks (B) or megabytes (M) to be allocated for the new container file. By default, the size is given in megabytes.
adadbm: add_container=data, size=10 %ADADBM-I-CREATED, dataset DATA2 , file /FS/fs0395/Adabas/adadb/db076/DATA2 created %ADADBM-I-FUNC, function ADD_CONTAINER executed
A new container file of 10 megabytes is added to the Data Storage. The block size is the same as the block size of DATA1.
ADD_FIELDS = number {field_specification|FDT}... [END_OF_FIELDS]
The ADD_FIELDS function adds one or more new fields to the end of the file defined by `number'. Specifying a LOB file is not permitted. The function is completed by entering END_OF_FIELDS.
If the field definitions are terminated with the END_OF_FIELDS parameter, this parameter must be specified in upper case when the LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES parameter is used. In addition, the FDT parameter must also be specified in upper case when the LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES parameter is used.
Note:
It is not possible to add derived descriptors using ADADBM -
you should use the utility ADAINV to do this instead.
The field specification list is entered in the same way as the FDT input in ADAFDU:
level-number, name [,length] [,format] [(,option)...]
The first field to be added must be a level-one field.
The NN option is not permitted. DE is only permitted when the Adabas nucleus is active and together with the NU or NC option. Otherwise use the ADAINV utility to give the new fields descriptor status. UQ is only permitted together with the DE option.
Note:
When you add system-generated fields (fields with the field
option SY) to a file, these fields have null values in the records that are
already in the database - this is the same behaviour as for fields without the
SY option.
This parameter displays the FDT of the file to which the fields are to be added.
adadbm: add_fields=12
adadbm: fdt
Field Definition Table:
Level I Name I Length I Format I Options I Flags
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 I AA I 15 I A I DE,UQ,NU I
1 I AB I 4 I F I FI I
1 I AC I 8 I A I DE I
1 I CD I I I I
2 I AD I 20 I A I DE,NU I SP
2 I AE I 20 I A I NU I
2 I AF I 10 I A I DE,NU I
1 I AG I 2 I U I NU I SP
1 I AH I 1 I A I DE,FI I
1 I AI I 1 I A I FI I
1 I AJ I 6 I U I NU I SP
1 I AK I I I I
2 I AL I 3 I A I NU I
2 I AM I 4 I P I NU,MU I
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Type I Name I Length I Format I Options I Parent field(s) Fmt
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SUPER I AN I 4 I B I NU I AJ ( 5 - 6 ) U
I I I I I AJ ( 3 - 4 ) U
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SUPER I AO I 22 I A I NU I AG ( 1 - 2 ) U
I I I I I AD ( 1 - 20 ) A
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
adadbm: 01,dd,1,a
adadbm: 01,gr
adadbm: 02,g1,20,a,fi
adadbm: fdt
Field Definition Table:
Level I Name I Length I Format I Options I Flags
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 I AA I 15 I A I DE,UQ,NU I
1 I AB I 4 I F I FI I
1 I AC I 8 I A I DE I
1 I CD I I I I
2 I AD I 20 I A I DE,NU I SP
2 I AE I 20 I A I NU I
2 I AF I 10 I A I DE,NU I
1 I AG I 2 I U I NU I SP
1 I AH I 1 I A I DE,FI I
1 I AI I 1 I A I FI I
1 I AJ I 6 I U I NU I SP
1 I AK I I I I
2 I AL I 3 I A I NU I
2 I AM I 4 I P I NU,MU I
1 I DD I 1 I A I I
1 I GR I I I I
2 I G1 I 20 I A I FI I
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Type I Name I Length I Format I Options I Parent field(s) Fmt
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SUPER I AN I 4 I B I NU I AJ ( 5 - 6 ) U
I I I I I AJ ( 3 - 4 ) U
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SUPER I AO I 22 I A I NU I AG ( 1 - 2 ) U
I I I I I AD ( 1 - 20 ) A
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
adadbm: end_of_fields
%ADADBM-I-FUNC, function ADD_FIELDS executed
ALLOCATE = keyword, FILE = number [,RABN = number], SIZE = number [B|M]
Depending on the keyword specified (AC, DS, NI or UI), the ALLOCATE function increases the Normal Index (NI), Upper Index (UI), Address Converter (AC) or Data Storage (DS) by a given size. Each extent for the required type is checked to see whether it can be extended or not. A new extent is created if none of the current extents can be extended.
This function lets the DBA override the automatic extension method and can be used to preallocate smaller or larger extents. This can be useful when adding a large number of records. Exclusive control of the file is NOT required for this function.
This parameter specifies the file to be extended.
This parameter specifies the allocation start RABN. For NI or UI allocation for a LOB file, the block size of the RABN specified must be less than 16 KB. For DS allocation for a LOB file, the block size of the RABN specified must be 32 KB.
This parameter specifies the size of the expansion area. If a 'B' is appended to size, the size is in blocks, otherwise it is in megabytes.
adadbm: allocate=ni, file=11, size=100b %ADADBM-I-ALLOC, 100 NI blocks allocated (611 - 710) adadbm: allocate=ds, file=11, size=10 %ADADBM-I-DEALLOC, 2560 DS blocks allocated (245 - 2804)
CHANGE = number, FIELD = string, LENGTH = number
This function changes the standard length of a field in the file specified by number. Specifying a LOB file is not permitted. The length of fixed storage fields (option FI) and floating point fields (format G) cannot be changed.
Changing the length of a field does not lead to any modifications within the Data Storage, but may affect programs that use the standard length.
Fields defined with the option SY=OPUSER cannot be changed.
This parameter specifies the field whose standard length is to be changed. The field must be defined in the Field Definition Table for this file.
This parameter defines the new standard length of the field.
adadbm: change=12, field=ac, len=11 %ADADBM-I-FUNC, function CHANGE executed
CHANGE_FIELDS = number {field_specification|FDT}... [END_OF_FIELDS]
The CHANGE_FIELDS function modifies one or more field specifications of the file defined by `number'. The function is completed by entering END_OF_FIELDS.
If the field definitions are terminated with the END_OF_FIELDS parameter, this parameter must be specified in upper case when the LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES parameter is used. In addition, the FDT parameter must also be specified in upper case when the LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES parameter is used.
The changes that are allowed depend on the existence of records in the file. The following restrictions apply to all files:
The field level number must not change;
A group must either remain a group or may be converted to a periodic group if it is defined on level 1;
A periodic group must either remain a periodic group or may be converted to a non-periodic group;
A field that is not a group or periodic group must not be converted to a group or a periodic group.
The following additional restrictions apply to non-empty files:
Field length: the new length must be compatible with the new field format and field options. Such a change changes the behaviour of adabas commands in which the field length is not specified in the format buffer;
Field format: A may be changed to W and vice versa. It is the responsibility of the user to ensure that the field contains UTF-8 values if the format is changed from A to W. After changing the format from W to A, the field will contain UTF-8 values. Please note that the format specified in the format buffer of Adabas commands must be identical to the format in the field definition for A and W fields - therefore it may be necessary to adapt existing programs accordingly. Other changes of the field format except for the change between A and W are not allowed.
Field options: it is not allowed to add or remove the options DE, FI, HF, MU and UQ.
The following field option changes are allowed:
| Old Field Options | New Field Options | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| DT not set | DT set, TZ not set or set | No check is made to see whether the
values in the database are compliant with the date/time edit mask specified. TZ
may not be set for edit mask names DATE, TIME and NATDATE.
Caution: |
| DT set | DT not set | Specifying a date/time edit mask for the field in the format buffer is no longer allowed. |
| HF set | HF not set | The behaviour of cross-platform calls changes. The file must be empty to apply this change. |
| HF not set | HF set | |
| LA and LB not set | LA or LB set | The behaviour of calls accessing the field with variable length changes. |
| LA set | LA not set, LB set | |
| LB set | LB not set, LA set | Only allowed if there is no LOB file defined for the file or if the field is a descriptor of the parent of a derived descriptor. The behaviour of calls accessing the field with variable length changes. |
| NB not set | NB set | |
| NC and NN set | FI, NC, NU and NN not set | After this change, the field is no longer mandatory in the format buffer for N1/N2 commands; if not specified, the field gets the Adabas null value. |
| NC and NN set | NC set, NN not set | After this change, the field is no longer mandatory in the format buffer for N1/N2 commands; if not specified, the field gets the SQL null value. |
| NU set | NC set | Empty values are converted to NULL values. Note that NC set -> NU not set because NU and NC are mutually exclusive. |
| NV set | NV not set | The behaviour of cross-platform calls changes. |
| NV not set | NV set | |
| SY not set | SY set | The behaviour of A1, N1 and N2 commands changes. The field format must be compatible with the SY option. Note that no check is made to ensure that the existing values are reasonable. |
| SY set | SY not set | The behaviour of A1, N1 and N2 commands changes. |
| TR not set | TR set | |
| TZ not set DT set | TZ set, DT unchanged | Values in the database will be converted from UTC to local time when you specify a date/time edit mask. |
| TZ set | TZ not set | Values in the database are no longer converted from UTC to local time when you specify a date/time edit mask. |
The field specification list is entered in the same way as the FDT input in ADAFDU:
level-number, name [,length] [,format] [(,option)...]
The first field to be added must be a level-one field.
This parameter displays the FDT of the file to which the fields are to be added.
DBID = number
This parameter selects the database to be used.
Note:
Utility functions which require or allow the nucleus to be shut
down need logical assignments for the data sets.
adadbm: dbid=76 %ADADBM-I-DBOFF, database 76 accessed offline adadbm: dbid=76 %ADADBM-I-DBON, database 76 accessed online
DEALLOCATE = keyword, FILE = number [,RABN = number],
SIZE = numberB
Depending on the keyword specified (AC, DS, NI or UI), this function releases a given amount of space from the Address Converter (AC), Data Storage (DS), Normal Index (NI) or Upper Index (UI).
If too much space is allocated to an extent, either automatically or manually, the DBA can release this space and return it to the Free Space Table (FST).
Deallocation is done for only one extent at a time. To release space from multiple extents, DEALLOCATE has to be called several times.
This parameter specifies the file.
This parameter specifies the first RABN to be deallocated. If this parameter is omitted, deallocation starts at the end of the last extent.
This parameter specifies the size of the area to be deallocated, in blocks.
adadbm: deallocate=ni, file=11, size=110b
SIZE=110B
^
%ADADBM-E-VALUP, value has to be less-equal 100
%ADADBM-I-ABORTED, 14-NOV-2002 14:44:01, elapsed time: 00:00:00
adadbm: deallocate=ni, file=11, size=100b %ADADBM-I-DEALLOC, 100 NI blocks deallocated (611 - 710) adadbm: deallocate=ni, file=11, size=10b %ADADBM-I-DEALLOC, 10 NI blocks deallocated (323 - 332)
DEFINE_REFINT = number constraint_specification
This function adds a referential constraint to the file 'number', which contains a foreign key. The syntax for the constraint is the same as that used in the FDT file for ADAFDU and is described in Administration, FDT Record Structure, Referential Constraints. The constraint is also included in the FDT of the primary file, therefore, the constraint name must not already be defined in the primary file.
Adding a referential constraint is not allowed if the file specified as the primary file is defined with PGM_REFRESH=YES.
If there are violations of the referential integrity, adding of the constraint will fail - no updates are performed on the data of the file in order to establish referential integrity.
DELCP = { * | ([absolute-date] [,[absolute-date]]) }
This function deletes checkpoint records from the checkpoint file.
If an asterisk '*' is entered, all checkpoint records are deleted.
adadbm: delcp=13-NOV-2006:15:09:48 %ADADBM-I-DELCP, 1 record deleted from CHECKPOINT file adadbm: delcp=(13-NOV-2006:15:09:48,) %ADADBM-I-DELCP, 81 records deleted from CHECKPOINT file adadbm: delcp=(,14-NOV-2006:14:37:24) %ADADBM-I-DELCP, 41 records deleted from CHECKPOINT file adadbm: delcp=(14-NOV-2006:14:37:25,14-NOV-1996:14:38:15) %ADADBM-I-DELCP, 42 records deleted from CHECKPOINT file adadbm: delcp=* %ADADBM-I-DELCP, 20 records deleted from CHECKPOINT file
DELETE = (number [-number][,number[-number]]...)
The DELETE function deletes one or more files or ranges of files from the database and returns all space which was allocated for this file to the Free Space Table (FST). LOB files specified are ignored, but the LOB files assigned to all base files specified are deleted too. There must not be a referential constraint between a file that is to be deleted and another file, which is not specified. Deletion of system files is not allowed.
Note:
If you want to stop using Adabas-to-Adabas replication, and
therefore want to delete the replication system files, you must use ADADBM
REMOVE_REPLICATION, not the DELETE FUNCTION.
ADADBM does not request confirmation of the files to be deleted, i.e. care should be taken when entering the file numbers.
adadbm: delete=(4-11,14) %ADADBM-I-DELETED, file 11 deleted %ADADBM-I-DELETED, file 14 deleted
DELETE_DATABASE = keyword
The DELETE_DATABASE function deletes a database. Depending on the keyword specified (CONTAINER or FULL), either just the containers are deleted, or the database directory and its contents are deleted.
If you specify the keyword CONTAINER, the container files and the DBID entry in the [DB_LIST] section of the ADABAS.INI file will be deleted. If you specify the keyword FULL, the database directory and all of its contents will be deleted.
adadbm: dbid=12 delete_database=container
The containers of the database with the DBID 12 will be deleted.
DISPLAY = UCB
The DISPLAY function displays the utility communication block. This function can also be executed during a pending AUTORESTART.
adadbm: display=ucb
Date/Time Entry Id Utility Mode Files
--------- -------- ------- ---- -----
14-NOV-2006 14:38:40 233 adaopr UTO 11
14-NOV-2006 14:38:42 234 adabck ACC *
The display shows the following items:
DATE/TIME shows the date and time on which the given files were locked.
ENTRY ID shows the allocated identification of the entry.
UTILITY shows the name of the utility.
MODE shows the mode in which the files are being accessed.
FILES shows the file numbers of the files that are locked.
DROP_FIELDS = number {field_name|FDT}... [END_OF_FIELDS]
The DROP_FIELDS function drops one or more fields from the file defined by `number' - the specified fields are marked as no longer existing and they cannot be accessed. Specifying a LOB file is not permitted. The function is completed by entering END_OF_FIELDS.
If the field definitions are terminated with the END_OF_FIELDS parameter, this parameter must be specified in upper case when the LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES parameter is used. In addition, the FDT parameter must also be specified in upper case when the LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES parameter is used.
If you specify a group or a periodic group, all of the fields that belong to the group or periodic group are dropped. You must not specify a field that is a descriptor or from which a descriptor is derived - if you want to drop such a field, you must first release all corresponding descriptors with ADAINV.
Once the DROP_FIELDS function has been executed, you can redefine the names of the dropped fields, for example using ADADBM's ADD_FIELDS function.
Notes:
This parameter displays the FDT of the file from which the fields are to be dropped.
DROP_LOBFILE = number
The number must specify the file number of a base file with an empty assigned LOB file to be deleted.
DROP_LOBFILE is not allowed if the assigned LOB file is not empty.
DROP_REFINT = number, NAME {=|:} constraint_name
The function removes a referential constraint from the file specified by 'number', which contains the foreign key. The constraint is also removed from the FDT of the primary file.
EXTEND_CONTAINER = keyword, SIZE = number [B|M]
The EXTEND_CONTAINER function extends the last Associator, Data Storage or WORK container file defined for the database in accordance with the keyword used. The keyword can take the values ASSO, DATA or WORK.
Note:
The WORK container can only be extended in the offline
mode.
This parameter specifies the size of the expansion area in blocks (B) or megabytes (M). By default, the size is in megabytes.
[NO]LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES
If LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES is specified, Adabas field names are not converted to upper case. If NOLOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES is specified, Adabas field names are converted to upper case. The default is NOLOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES.
This parameter must be specified before the ADD_FIELDS, CHANGE_FIELDS or DEFINE_REFINT parameters.
NEW_DBID = number
This function is used to change the identifier of the database in use. The new identifier may not already be in use by another active database.
adadbm: new_dbid=77 %ADADBM-I-FUNC, function NEW_DBID executed
NEWWORK [,BLOCKSIZE = number[K] ], SIZE = number [B|M]
This function removes the existing WORK1 container file and replaces it with a new WORK1 container file. The new WORK1 container file is allocated and then formatted, if required.
Before a new WORK can be created, the nucleus and all utilities using the database must have been successfully terminated. Since this function requires the current WORK, it must not be deleted before NEWWORK has been executed. TEMP1 must point to the new work file when this function is used.
Note:
The new WORK can be directed to a
disk section or to a file system. If TEMP1 points to the same disk section as
WORK1, then ADADBM tries to extend/reduce the existing WORK file. In each case
the name of the new WORK container file is WORK1. If the function completes
successfully, the old WORK1 gets deleted.
This parameter specifies the block size in bytes (or in kilobytes, if "K" follows the number) of the new container file.
Adabas rounds up the value you specify to the next multiple of 1024.
The minimum block size allowed is 3072 and the maximum block size allowed is 32768.
In addition to these minimum and maximum values, the following size restrictions apply in general to the block sizes for ASSO and WORK:
MAX (ASSOBLS) < WORKBLS
where MAX(ASSOBLS) represents the largest ASSO block size and WORKBLS represents the WORK block size.
The default value for BLOCKSIZE is the block size of the old WORK file.
This parameter specifies the number of blocks or megabytes to be allocated for the new WORK file. By default, the size is in megabytes. The minimum value is 200 blocks or the equivalent value in megabytes.
PGM_REFRESH = keyword, FILE = number
This function is used to disable or enable refreshing an Adabas file inside an application program with an E1 command (ISN = 0, CID = BLANK). Specifying a LOB file is not permitted. The keyword can take the values YES or NO. It is not allowed to set PGM_REFRESH=YES for files that are primary files of referential constraints.
This parameter specifies the file for which refreshing is to be enabled/disabled.
RBAC_FILE = number
This function creates the RBAC system file and loads the initial security definitions.
adadbm: rbac_file=200
RECOVER
This function returns lost space within the Associator and Data Storage to the Free Space Table (FST).
Space can be lost by a non-successful termination of an Adabas utility.
adadbm: recover %ADADBM-I-FUNC, function RECOVER executed
REDUCE_CONTAINER = keyword, SIZE = number B
The REDUCE_CONTAINER function deallocates free space at the end of the Associator or Data Storage container defined for the database in accordance with the keyword used. The keyword can take the values ASSO or DATA.
The requested number of blocks must not be in use at the end of the container specified. If the complete space of one or more container extents is to be released, the container extents are removed. Note that the message informing you that a container extent is removed is not displayed by ADADBM if ADADBM is executed online - instead, it is included in the nucleus log.
If less blocks than requested are free at the end of the container, all free space at the end of the container is deallocated, and the following warning is displayed:
%ADADBM-W-PREDCONT, not all requested blocks removed
This parameter specifies the size by which the container is to be reduced, in blocks.
REFRESH = (number [-number][,number[-number]]...)
This function resets the files specified by `number' to the state of zero records loaded. Only the first extents for Normal Index, Address Converter and Data Storage are kept. The remaining extents are returned to the Free Space Table (FST). The Upper Index is rebuilt and the unused Upper Index extents are then returned to the Free Space Table. LOB files specified are ignored, but the LOB files assigned to all base files specified are refreshed too. The primary file of a referential integrity constraint may be refreshed only if the foreign file of the referential constraint is also refreshed.
ADADBM does not request confirmation of the files to be refreshed, i.e. care should be taken when entering the file numbers.
This function is useful for clearing a test file in a test environment. This method is faster than deleting and reloading the file.
Files using the ADAM feature cannot be refreshed.
If the REMOVE_DROP function has been specified, dropped fields are removed from the FDT.
adadbm: refresh=13 %ADADBM-I-REFRESH, file 13 refreshed
REMOVE_CONTAINER = keyword
This function removes the last database container file from an existing Associator or Data Storage data set in accordance with the keyword used. The keyword can take the values ASSO or DATA.
The container file to be removed must not be in use when this function is executed, i.e. all of the blocks in the file must be free.
The container file will be deleted from the file system or from the raw disk section.
Before a container file can be removed, the nucleus and all of the utilities using the database must have terminated successfully.
Note:
If you remove a container, the corresponding entry for this
container file in the DBnnn.INI file is deleted.
adadbm: remove_container=data %ADADBM-I-DMCONREM, container DATA2 removed
[NO]REMOVE_DROP
If you specify REMOVE_DROP, subsequent REFRESH functions will remove dropped fields from the FDT.
If you specify NOREMOVE_DROP, subsequent REFRESH functions will not remove dropped fields from the FDT.
The default is NOREMOVE_DROP.
adadbm: remove_drop adadbm: refresh=2 %ADADBM-I-REFRESH, file 2 refreshed adadbm: refresh=3 %ADADBM-I-REFRESH, file 3 refreshed adadbm: noremove_drop adadbm: refresh=4 %ADADBM-I-REFRESH, file 4 refreshed
File 2 has been refreshed and dropped fields have been removed from the FDT. File 3 has been refreshed and dropped fields have been removed from the FDT. File 4 has been refreshed and dropped fields have not been removed from the FDT.
REMOVE_REPLICATION
This function stops all replication processing and deletes all replication system files.
Note:
This function is only relevant for customers who are using the
Adabas Event Replicator with Adabas - Adabas replication.
RENAME = number, NAME {=|:} string
This function changes the name of a file or a database. `number' is the number of the file whose name is to be changed. If `number' is 0, the name of the database is changed.
`string' is the new name of the specified file or database. If you specify an equals sign, the value given for 'string' will be converted to upper case; if you specify a colon, no upper-case conversion is performed.
adadbm: rename=11, name=employee-file %ADADBM-I-FUNC, function RENAME executed
RENUMBER = (number, number)
This function changes the file number of a loaded Adabas file. If, however, the file's new number already belongs to a loaded file, the numbers of these files are exchanged.
The first `number' is the file number currently assigned to the file. The second `number' is the new file number to be assigned to the file.
adadbm: renumber=(12,14) %ADADBM-I-RENUM, File 12 renumbered to 14 %ADADBM-I-RENUM, File 14 renumbered to 12
REPLICATION_FILES = (file1, file2, file3, file4)
This functions performs all of the necessary initialization steps for the Adabas - Adabas replication and creates the replication system files.
Notes:
RESET = UCB, IDENT = { (number [,number]...) | * }
This function removes one or more entries from the utility communication block (UCB). This option can also be used during a pending AUTORESTART.
The UCB is used to control access to certain resources (the whole database, one or more files, etc.) within a database. It saves information about the Adabas utilities processing the database and the resources attached to them.
An entry is made in the UCB each time a utility is granted access to a resource. This entry contains information about the utility and the resources it locks. The utility automatically removes the entry when the resource is no longer required. Please refer to the DISPLAY=UCB function of this utility for information about how to display the contents of the UCB.
However, certain special conditions (e.g. an aborted ADAMUP) can cause entries to remain in the UCB and keep allocated resources locked. The RESET function releases these resources by removing one or more entries from the UCB.
Resetting a UCB entry also removes the associated entry from the user queue and returns lost blocks to the free space table if the nucleus is active. Otherwise, the resource can be returned to the free space table by using the RECOVER function.
This parameter specifies the unique ID of the entry to be removed. '*' removes all entries.
If the RESET UCB function is used offline, only `*' may be specified.
adadbm: reset=ucb, ident=233 %ADADBM-I-RESUCB1, 1 entry deleted from UCB adadbm: reset=ucb, ident=(235,234) %ADADBM-I-RESUCB, 2 entries deleted from UCB adadbm: reset=ucb, ident=* %ADADBM-I-RESUCB1, 1 entry deleted from UCB
RESET_REPLICATION_TARGET = number
This function resets the replication target flag of Adabas files, after which they are handled as normal files again. If you specify 0, the replication target flag of all replication target files is reset; if you specify a file number, the replication target flag of the file with this file number is reset.
Notes:
REUSE = (keyword [,keyword]), FILE = number
The REUSE function controls the reuse of Data Storage space or ISNs by Adabas.
The File Control Block (FCB) for the specified file is modified to indicate the type of allocation technique to be used when adding new records or moving updated records.
The valid keywords are [NO]DS and [NO]ISN.
If the DS keyword is specified, Adabas scans the Data Storage Space Table (DSST) in order to locate a block with sufficient space. In this case, the first block found with sufficient space is used.
If the NODS keyword is specified, then all newly-added records, together with records that have to be moved to another block (as a result of record expansion caused by updating), are placed in the last used block in the Data Storage extent allocated to the file. If there is not sufficient space in this block, the next block is used.
DS and NODS are mutually exclusive. The default is REUSE = DS.
If the ISN keyword is specified, Adabas may reuse the ISN of a deleted record.
If the NOISN keyword is specified, Adabas does not reuse the ISN of a deleted record for a new record. Each new record will be assigned the next-highest unused ISN.
ISN and NOISN are mutually exclusive. The default is REUSE = NOISN.
This parameter specifies the file.
adadbm: reuse=nods, file=11 %ADADBM-I-FUNC, function REUSE executed adadbm: reuse=(ds,isn), file=12 %ADADBM-I-FUNC, function REUSE executed
SECURITY = keyword
The SECURITY function sets the security mode of the database. The keyword can either be ACTIVE or WARN.
The ACTIVE keyword enables the security functionality. ACTIVE implies that only authenticated users are allowed access to the database. Security violations, like authentication errors, are protocolled as “Error” in the Audit-Trail.
In case of a security violation, access to the database is rejected.
Important:
Database security cannot be disabled, after it has been
activated.
The WARN keyword enables the security functionality. WARN implies that all users are allowed access to the database. Security violations, like authentication errors, are protocolled as “Warning” in the Audit-Trail. In case of a security violation, access to the database is not rejected.
This mode is intended for transitioning applications to use a secure database. See also Nucleus user exit 21.
Important:
The security mode WARN can only be changed to mode
ACTIVE.
The WARN keyword enables the security functionality. WARN implies that all users are allowed access to the database. Security violations, like authentication errors, are protocolled as “Warning” in the Audit-Trail. In case of a security violation, access to the database is not rejected.
This mode is intended for transitioning applications to use a secure database. See also Nucleus user exit 21.
Important:
The security mode WARN can only be
changed to mode ACTIVE.
By default security is not enabled.
SYFMAX = number, FILE = number
This parameter specifies the maximum number of values generated for a system generated multiple-value field in the file specified. There is no explicit maximum value, but you should bear in mind, that you can get a record overflow if the value is defined too high; the compressed data record should also fit into one DATA block is SYFMAX values are defined for system generated multiple-value fields. If the SYFMAX value is decreased and a record contains more values for system generated fields than the new value of SYFMAX, the excess values are removed during the next update operation for this record.
This parameter specifies the file.
ADADBM has no restart capability. At the end of each function, however, the system reports whether execution was successfully completed or not. If it is not successfully completed, the function has to be re-started.