This document describes the utility "ADAOPR".
The following topics are covered:
The DBA uses this utility to operate the Adabas nucleus.
This utility is a multi-function utility.
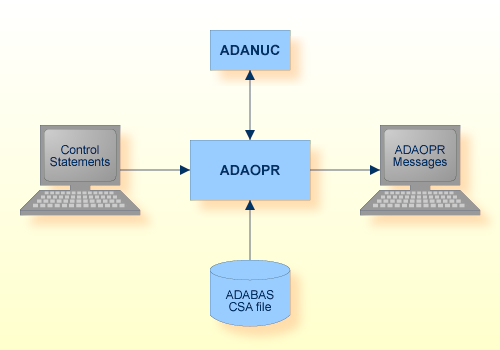
| Data Set | Environment Variable/ Logical Name |
Storage Medium | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control statements | stdin/ SYS$INPUT |
Utilities Manual | |
| ADAOPR messages | stdout/ SYS$OUTPUT |
Messages and Codes |
The following table shows the nucleus requirements for each function and the checkpoint written:
| Function | Nucleus must be active | Nucleus must NOT be active | Nucleus is NOT required | Checkpoint written |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FEOF=PLOG | SYNC |
The following control parameters are available:
ABORT
BFIO_PARALLEL_LIMIT = number
CANCEL
CLEAR_FILE_STATS = (number [- number] [, number [- number] ] ... )
CSA = string
DBID = number
DISPLAY = (keyword [,keyword]...)
ES_ID = number
D [NO]ET_SYNC
EXT_BACKUP = [PREPARE | CONTINUE | ABORT]
FEOF = (keyword [,keyword])
FILE = number
FREE_CLQ
ID = number
D [NO]IO_TIME
ISN = ( number [- number] [,number [- number] ] ... )
[UN]LOCK = (number [,number]...)
LOGGING = (keyword [,keyword]...)
LOGIN_ID = string
NISNHQ = number
NODE_ID = string
OPTIONS = (keyword [,keyword]...)
READ_PARALLEL_LIMITS = (records,blocks,total)
RESET = keyword
D [NO]RESPONSE_ABORT
RESPONSE_CHECK = (number[-number][,number[-number]]...)
SET_FILE_STATS = (number[-number][,number[-number]]...)
SHUTDOWN
STATUS = (keyword [,keyword]...)
STOP = (number[-number][,number[-number]]...)
TNAA = number
TNAE = number
TNAX = number
TT = number
USER_ID = string
WRITE_LIMIT = [number]
XA_RESPONSE_CHECK = (keyword [,keyword]...)
ABORT
This function terminates the Adabas session immediately. All command processing is immediately stopped. The session is terminated abnormally with a pending AUTORESTART.
ABORT causes the following files to be written to the databases's default directory:
The CSA dump file, which contains status information from the adabas nucleus. The name of the file is ADABAS.xxx.hh:mm:ss (UNIX), ADABAS.xxx.hh-mm-ss (Windows) or ADABAS-xxx-hh-mm-ss (OpenVMS),where xxx is the database ID and hh:mm:ss (or hh-mm-ss) is the time at which the file was created. ADAOPR can also display the same information that you can get for a running nucleus for a CSA dump file if you specify the CSA parameter.
The SMP dump file, which contains some diagnostic information. The name of the file is SAGSMP.xxx.hh:mm:ss (UNIX), SAGSMP.xxx.hh-mm-ss (Windows) or SAGSMP-xxx-hh-mm-ss where xxx is the database ID and hh:mm:ss (or hh-mm-ss) is the time at which the file was created.
BFIO_PARALLEL_LIMIT = number
This function sets the number of parallel I/O requests by a buffer flush, allowing earlier processing of concurrent I/Os from other threads. A large buffer flush, for example, can cause the I/O queue to be very busy, and other I/Os (such as buffer pool read I/Os and WORK I/Os) can be enqueued for a long time, slowing down command throughput and possibly causing applications to stall if a buffer flush is active.
If BFIO_PARALLEL_LIMIT is specified, the buffer flush sets up the specified number of I/Os and waits until these have been processed before issuing the next packet. The maximum value for ´number´ is defined by the Adabas system, If a value of 0 is specified, the number of buffer flush I/Os is unlimited.
CANCEL
This function terminates the Adabas session immediately. A BT command is issued for each active ET user and the session is terminated.
The communication link to the database is cut but the shared memory is still held. In this case, display functions are still possible with ADAOPR but parameter modification commands are no longer permitted.
CLEAR_FILE_STATS = (number [- number] [, number [- number] ] ... )
This function disables the collection of I/O statistics enabled by SET_FILE_STATS for the specified file(s).
CSA = string
`string' is a file specification of a file containing status information from an Adabas nucleus, a so-called CSA dump file. This file may be created by an ADAOPR ABORT function, by an abnormal termination of Adabas, or by response check trapping (refer to the RESPONSE_CHECK function for further information).
The following naming conventions are used for the file:
ADABAS.xxx.hh:mm:ss ADABAS.xxx.RSPyyy.hh:mm:ss
ADABAS.xxx.hh-mm-ss ADABAS.xxx.RSPyyy.hh-mm-ss
ADABAS-xxx-hh-mm-ss ADABAS-xxx-RSPyyy.hh-mm-ss
(with the NORESPONSE_ABORT option set), where
`xxx' is the three digit database ID;
`yyy' is the trapped three digit response code;
`hh:mm:ss' is the time the file was created (UNIX),
`hh-mm-ss' is the time the file was created (Windows and OpenVMS)
For example, if the database ID is 5, and the file creation was initiated by a trapped response code 113, the file name will start with ADABAS.005.RSP113, and then the time of creating will be appended, e.g. ADABAS.005.RSP113.12:16:50 (UNIX) or ADABAS.005.RSP113.12-16-50 (Windows) or ADABAS-005-RSP113.12-16-50 (OpenVMS).
The file will be created in the directory that is pointed to by the environment variable/logical name ADA_CSA_DUMP. The default is the directory from which the nucleus was started. If a file with the same name already exists in this directory, it will be overwritten.
The DBID and CSA parameters are mutually exclusive.
DBID = number
This parameter selects the database to which all subsequent ADAOPR commands apply. Multiple DBIDs are supported within one session.
The DBID and CSA parameters are mutually exclusive.
adaopr: dbid=1 adaopr: shutdown adaopr: dbid=2 adaopr: shutdown adaopr: dbid=3 adaopr: shutdown adaopr: quit
DISPLAY = (keyword [,keyword]...)
This parameter displays various information during an Adabas session.
The following keywords can be used:
| Keyword | Meaning |
|---|---|
| ACTIVITY | Database activities display. |
| BF_STATISTICS | Buffer flush statistics display. |
| BP_STATISTICS | Buffer pool statistics display. |
| COMMANDS | Command table display. |
| CQ | Command queue display. |
| DYNAMIC_PARAMETERS | Dynamic nucleus parameters display. |
| FILE_IO | File I/O display. |
| FP_STATISTICS | Format pool statistics display. |
| HIGH_WATER | High water marks display. |
| HQ | Hold queue display. |
| ICQ | Internal command queue display. |
| IO_TIMES | Container I/O times display. |
| PLOG_STATISTICS | Protection log statistics. |
| REPLICATIONS | Adabas - Adabas replications. |
| STATIC_PARAMETERS | Static nucleus parameters display. |
| TT | Thread table display. |
| UCB | Utility communication block. |
| UQ | User queue display. |
| UQ_FILES | User file list display. |
| UQ_FULL | Full information about user queue element. |
| UQ_TIME_LIMITS | User time limits display. |
The following examples show the information produced by the various keywords, together with explanations of the information that is displayed.
Some of the following displays include percentages. The corresponding values are always truncated. An undefined value (divided by 0) is specified with " *%" and an overflow with "***%".
adaopr: display=activity
ADANUC Version <version number>
Database 76 Activity on 22-JAN-2014 13:19:30
I/O Activity Total Throwbacks Total
------------ ----- ---------- -----
Buffer Pool 5,440 Waiting for UQ context 87
WORK Read 728 Waiting for ISN 53
WORK Write 647 ET Sync 0
PLOG Write 194 DWP Overflow 0
NUCTMP 1,600
NUCSRT 531
Pool Hit Rate Total Interrupts Current Total
------------- ----- ---------- ------- -----
Buffer Pool 99.6% WP Space Wait 0 0
Format pool 98%
The information has the following meaning:
I/O ACTIVITY shows the total numbers of:
physical buffer pool I/Os (physical read I/Os + physical write I/Os);
read and write I/Os for WORK and PLOG.
I/Os for NUCTMP and NUCSRT
INTERRUPTS shows the current and total number of workpool space waits;
POOL HIT RATE shows:
the buffer pool hit rate. This is the relationship between the
logical read I/Os and the physical read I/Os. The buffer pool hit rate is
calculated using the following formula:
hit rate (in %) = ((logical read I/Os - physical read I/Os) * 100)
/ logical read I/Os
the format pool hit rate. This is the relationship between the
number of format buffer requests (required FBs) and the required format buffers
already translated in the format pool (translated FBs). The format pool hit
rate is calculated using the following formula:
hit rate (in %) = ((translated FBs * 100) / required FBs)
THROWBACKS shows:
the number of commands waiting for session context because internal commands were running;
the number of commands waiting because ISNs are held by another user;
the number of commands waiting for ET synchronization;
the number of commands thrown back because of dynamic work pool overflow.
adaopr: display=bf_statistics
ADANUC Version <version number>
Database 2 Buffer Flush Statistics on 05-JUN-2014 13:32:50
Buffer flush statistics:
------------------------
Write Number of Type Size Average IO Duration Rejected Seconds from
Limit Blocks (MB) time (msec) (sec) Locks last flush
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
10 4 DB 0.08 0.00 0.00 0
50 127967 Temp 511.82 0.00 1.24 10 33
10 10 DB 0.22 0.00 0.00 0 0
50 127883 Temp 511.50 0.01 1.59 7 2
Total number of flushes: 4
Explicit : 1
Write limit : 3
WORK limit : 0
Space : 0
Emergency : 0
Ignored blocks : 0
This display shows the statistics of the buffer flushes; if more than 100 buffer flushes have been performed in the current nucleus session, the last 100 buffer flushes are displayed. The following information is displayed for each buffer flush:
The current write limit. The write limit for database blocks can be modified via ADAOPR WRITE_LIMIT. The write limit for temporary blocks cannot be changed.
The number of blocks included in the buffer flush.
The type of buffer flush:
DB means flush of database blocks
Temp means flush of temporary blocks
The size in megabytes of the blocks included in the buffer flush.
The average I/O time of the I/Os performed by the buffer flush in milliseconds.
The duration of the buffer flush in seconds.
The number of rejected locks is the number of blocks that were not written immediately during the buffer flush, because the block was exclusively locked when the buffer flush tried to write the block. The rejected blocks are either written after having written the other blocks - then the buffer flush waits until the lock can be granted, or by a separate ignore-blocks buffer flush.
The number of seconds from last flush is the number of seconds between the end of the previous buffer flush and the start of the new buffer flush.
Note:
In the example, the third buffer flush is a write-limit buffer
flush that is performed immediately after the previous buffer flush, although
the write limit is not exceeded. This can happen if two threads determine at
the same time that the write limit is exceeded, and a buffer flush is not yet
running. Then both threads set a flag that a buffer flush is required. When the
first thread has set the flag, the buffer flush thread starts a buffer flush
and resets the flag. Then the second thread sets the flag again. When the
buffer flush is finished, a new buffer flush is started immediately. Because
such unnecessary buffer flushes do not cause errors, the flag is set without
synchronization.
After the table the total number of buffer flushes is displayed, and a breakdown of the reasons for the buffer flushes.
adaopr: display=bp_statistics
ADANUC Version <version number>
Database 34 Buffer Pool Statistics on 5-JUN-2014 13:11:28
Buffer Pool Size : 419,430,400
Pool Allocation RABNs present
--------------- -------------
Current ( 7%) : 32,835,584 ASSO : 33
Highwater ( 10%) : 42,676,224 DATA : 5
Internal ( 7%) : 30,770,176 WORK : 0
Workpool ( 0%) : 1,408,000 NUCTMP : 0
NUCSRT : 0
I/O Statistics Buffer Flushes
-------------- --------------
Logical Reads : 340 Total : 3
Physical Reads : 17 To Free Space : 0
Pool Hit Rate : 95.0% Temporary Blocks : 0
Write Limit ( 2%): 8,388,600
Physical Writes : 41 Modified ( 0%): 108,544
Limit Temp.B.( 50%): 209,715,000
Modified T.B.( 0%): 0
The information is interpreted as follows:
POOL ALLOCATION shows:
the size in bytes and percentage of the buffer pool that is currently in use;
the size in bytes and percentage of the buffer pool high water mark (see also the display for DISPLAY=HIGH_WATER).
RABNs PRESENT shows:
the number of ASSO, DATA and WORK RABNs currently in the buffer pool.
I/O STATISTICS shows:
the total number of logical and physical buffer pool read I/Os (both numbers are required in order to calculate the buffer pool hit rate);
the buffer pool hit rate (please refer to the example for DISPLAY=ACTIVITY for the buffer pool hit-rate formula);
the total number of physical buffer pool write I/Os.
BUFFER FLUSHES shows:
the total number of buffer flushes;
the total number of buffer flushes that were made in order to get free space;
the total number of buffer flushes for temporary blocks;
the size and percentage of the buffer pool WRITE LIMIT for database blocks;
the size in bytes and percentage of modified database blocks;
the size and percentage of the buffer pool WRITE LIMIT for temporary blocks;
the size in bytes and percentage of modified temporary blocks.
adaopr: display=commands
ADANUC Version <version number>
Database 76 Commands on 19-JAN-2014 14:58:10
ADABAS Commands: 9,884
A1 892 L2 553 OP 25
BT 736 L3 1,124 RC 89
C1 40 L4 569 RE 0
C3 0 L5 420 RI 0
C5 10 L6 436 S1 1,511
CL 32 L9 456 S2 81
E1 1,006 LF 20 S4 12
ET 72 MC 0 S8 230
HI 0 N1 877 S9 50
L1 643 N2 0
This command displays the total numbers of Adabas commands issued in the current session. For MC commands, the value displayed is the number of MC calls plus the number of single Adabas commands contained in the MC calls.
A read command that is issued while the multifetch option is set is counted as a single command.
Updates made by utilities are not included in the display.
Note:
The command counts can be reset by ADAOPR RESET=COMMANDS.
adaopr: display=cq
ADANUC Version <version number>
Database 2 Command Queue on 14-NOV-2014 13:41:53
No Node Id Login Id ES Id APU Cmd File Status
-- ------- -------- ----- --- --- ---- -----
1 PC0001 miller 3316 1 RC 13 Ready to run
2 PC0001 jones 1360 2 S8 13 Running
3 PC0001 smith 6148 1 RC 13 Ready to run
4 PC0001 miller 4208 1 S8 13 Running
5 PC0001 jones 5224 2 S9 13 Ready to run
6 PC0001 dba 7024 2 U1 0 Running
7 PC0001 brown 3140 2 S1 13 Running
8 PC0001 meyer 6180 2 S8 13 Running
9 PC0001 smith 4756 1 S1 13 Running
10 PC0001 king 1240 2 ET 0 Ready to run
11 PC0001 meyer 836 2 RC 13 Ready to run
12 PC0001 brown 6272 1 L6 13 Ready to run
Selected: 12, Used: 12, Queue Size: 13
This display shows the current command-queue entries:
NODE ID shows the node identification string.
LOGIN ID shows the login user identification string;
ES ID shows the environment-specific identification (for example, the process ID);
APU shows the assigned Adabas Processing Unit of the command queue entry if the nucleus parameter APU is set. If APU has not been specified, the column APU is not displayed;
CMD shows the command string;
FILE shows the file number;
STATUS shows the status of the command-queue entry.
The final line of the display shows how many command queue entries were selected according to the currently active selection criteria, and how many entries are used in total in the command queue.
The possible status values are shown in the following table:
| Status | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Completed | Command processing completion; |
| Marked For Deletion | Command is marked for delete, user is no longer active; |
| New | Command is ready to be inserted in the scheduling queue; |
| Ready To Run | Placed in queue and ready for scheduling; |
| Running | Running in a thread (see DISPLAY=TT); |
| Waiting For Complex | Complex command is waiting to run; |
| Waiting For Et Sync | Waiting for ET synchronization; |
| Waiting For Group Commit | Waiting for group ET. No entry in thread table; |
| Waiting For Isn <isn> | Waiting for ISN in file shown in column "File" in the display. No entry in thread table; |
| Waiting For Space | Waiting for working space. No entry in thread table. |
| Waiting For Uqe | Waiting for user queue entry. The required entry is locked by an active internal command; |
Note:
The display may show command codes such as "U0", which are only
used internally by Adabas (for example, during a utility run).
The
"RUNNING" and "COMPLETED" values may differ even if the user has not specified
an explicit selection criterion.
adaopr: display=dynamic_parameters
ADANUC Version <version number>
Database 76 Dynamic Parameters on 19-JAN-2014 14:58:10
Resources: NISNHQ : 100 WRITE_LIMIT: -
Time Slices: TNAA : 900 TNAX : 900
TNAE : 900 TT : 300
Logging: CLOG : OFF
Read limits: 200, 10, 30
Response check with ABORT : 84,160,164-182,243,251-252
This display shows the current values of the dynamic nucleus parameters.
adaopr: display=file_io
ADANUC Version <version number>
Database 76 File I/O on 19-JAN-2014 14:58:10
Reads Hit
File Logical Physical Rate Writes
---- ------- -------- ---- ------
11 145,341 180 99% 2,869
12 99,070 148 99% 2,149
This display shows the logical and physical reads, their hit rate and the writes the buffer pool manager has made for every file since the file I/O statistiscs for the file in question were enabled (ADAOPR SET_FILE_STATS) - files for which the I/O statistics have not been enabled or for which no I/Os were performed are not displayed.
Notes:
adaopr: display=fp_statistics
ADANUC Version <version number>
Database 76 Format Pool Statistics on 19-JAN-2014 14:58:10
Maximum Local Pool Size: 251,656
Maximum Global Pool Size: 251,656
Pool Allocation Pool Contents
--------------- -------------
Local Current ( 22%) : 57,540 Local Format Buffers: 162
Local Highwater ( 27%) : 70,000 Global Format Buffers: 1
Global Current ( 0%) : 84
Global Highwater ( 0%) : 84
Pool Statistics Local Global
--------------- ----- ------
Scans 11,780 3
Hits 11,547 2
Hit Rate 98% 66%
Replacements 0 0
Overflows 0 0
This display shows the format pool statistics:
POOL ALLOCATION shows:
the size in bytes and percentage of the local and global format pools that are currently in use;
the size in bytes and percentage of the local and global format pool high water marks.
POOL STATISTICS shows:
the total number of scans and hits of valid format buffers in the format pool (both numbers are required in order to calculate the format pool hit rate);
the format pool hit rate (please refer to the example DISPLAY=ACTIVITY for the format pool hit-rate formula);
the total number of valid format buffers that are overwritten in the format pool (replacements).
Overflows. This is the number of times that a format buffer exceeded the format pool size, resulting each time in a response 42.
POOL CONTENTS shows:
the number of valid local format buffers in the format pool;
the number of valid global format buffers in the format pool.
adaopr: display=high_water
ADANUC Version <version number>
Database 2 High Water Marks on 21-NOV-2014 11:44:19
Area/Entry Size In Use High Water % Date/Time
---------- ---- ------ ---------- - ---------
User Queue 100 13 13 13 21-NOV-2014 11:44:00
Command Queue - 12 13 - 21-NOV-2014 11:44:19
APU 01 - 2 12 - 21-NOV-2014 11:44:02
APU 02 - 13 15 - 21-NOV-2014 11:44:00
Hold Queue - 2 2 - 21-NOV-2014 11:44:00
Client Queue 100 13 13 13 21-NOV-2014 11:44:00
HQ User Limit - - 1 - 21-NOV-2014 11:44:00
Threads 6 4 6 100 21-NOV-2014 11:44:00
Workpool 524,288,000 0 131,072,016 25 21-NOV-2014 11:42:16
ISN Sort 65,536,000 - 380,000 0 21-NOV-2014 11:44:04
Complex Search 65,536,000 - 0 0
Attached Buffer 1,048,576 219,136 219,136 20 21-NOV-2014 11:44:02
ATBX (MB) 20 0 0 0
Buffer Pool(KB) 2,048,000 957,962 1,009,978 49 21-NOV-2014 11:42:16
Protection Area 127,990
Active Area 38,397 - 4 0 21-NOV-2014 11:44:04
Group Commit 50 1 1 2 21-NOV-2014 11:42:17
Transaction Time 3,000 - 0 0
This display shows the high water marks for the current session:
SIZE shows the size in bytes of pools and buffers. For queues, threads and hold queue user limit, it shows the number of entries.
IN USE shows the size in bytes or number of entries currently in use.
HIGH WATER shows the maximum quantity required simultaneously for the given area/entry.
% shows the relationship between the high water mark and the size. If the high water mark exceeds the size, the value in this column can be larger than 100 %. For example, this can occur if the value is decreased by ADAOPR, or if the original area has been dynamically increased. This is normal Adabas behaviour, and no changes of Adabas parameters are required.
DATE/TIME shows the date/time at which the high water mark occurred for the first time. There is no output in this column if the high water mark is 0.
The entries in the column AREA/ENTRY correspond to the ADANUC parameters NU (user queue), NCL (client queue), NISNHQ (hold queue user limit), NT (threads), APU (Adabas Processing Units, only displayed if the nucleus parameter APU is set), LWP (workpool), LBP (buffer pool), LAB (attached buffer), TT (transaction time). The hold queue and the command queue have no predefined size and are increased dynamically if required.
The entry "ACTIVE AREA" is the largest part of WORK part 1 that can be used by a single transaction. If a transaction's protection information spans more space than allowed by "Active Area", it receives a response 9 (LP), the nucleus displays a PLOVFL message and a value of more than 100 in the "%" column of the highwater display.
Users who have set user-specific timeout values in their OP call are not included in the values for Transaction Time.
Note:
1. Values for Attached Buffer and Command Queue are
not displayed correctly if the nucleus cannot be contacted by ADAOPR (for
example, if the ADAOPR parameter CSA is used.
2. Threads are used in
a round-robin manner. Therefore, the high water mark for threads will be the
same as the value shown in the Size column in most cases.
adaopr: file=11, display=hq
ADANUC Version <version number>
Database 76 Hold Queue on 19-JAN-2014 14:58:10
Id Node Id Login Id ES Id User Id File ISN Locks Flg
-- ------- -------- ----- ------- ---- --- ----- ---
15 sunxxx01 miller 6974 *adatst 11 2,222 X M
19 sunxxx01 smith 7056 *adatst 11 2 X
Selected: 2, Used: 8, Queue Size: 160
This display shows the current hold-queue entries:
ID shows the internal user identification of the user holding the ISN;
NODE ID shows the node identification string. The local node is represented by an empty string;
LOGIN ID shows the login user identification string;
ES ID shows the environment-specific identification (for example, process ID);
USER ID shows the user identification. Adabas utilities use the utility name preceded by an asterisk as the USER ID;
FILE shows the number of the Adabas file in which the ISN is located;
ISN shows the number of the ISN in hold;
LOCKS shows the kind of lock for the ISN, where X = exclusive lock , S = shared lock.
Note:
S is displayed for shared locks starting with Adabas version 6.3
SP 1; in previous releases R is displayed.
An M for FLG indicates that the record has been modified.
The final line of the display shows how many hold queue entries were selected according to the currently active selection criteria, and how many entries are used in total.
Entries are displayed in unsorted sequence.
adaopr: display=icq
ADANUC Version <version number>
Database 76 Internal Command Queue on 19-JAN-2014 14:58:10
Id Node Id Login Id ES Id Command Status
-- ------- -------- ----- ------- ------
00000002 *system 00000000 SHUT Running
Selected: 1, Used: 1, Queue Size: 101
This display shows the internal command queue:
| Command | Meaning |
|---|---|
| AR | Autorestart |
| BT | Back out transaction |
| BTCL | Back out open transaction and close user |
| CANCEL | Cancel nucleus |
| DELUQE | Release file list and delete user queue element |
| ETSYNC | Start an ET-SYNC status check after a global transaction has received a timeout |
| SHUT | Shut down nucleus |
| STOP | STOP from ADAOPR |
| TIMEOUT | Non-activity timeout |
The status of internal commands can be READY TO RUN, RUNNING, WAITING FOR ET SYNC or WAITING FOR UQE.
The final line of the display shows how many internal command queue entries were selected according to the currently active selection criteria, and how many entries are used in total.
adaopr: display=io_times
ADANUC Version <version number>
Database 76 IO Statistics on 19-NOV-2014 12:16:48
Number of IOs Maximum IO time Average IO time
------------- --------------- ---------------
ASSO Read : 735574 14397 1
ASSO Write : 12136 2 1
DATA Read : 2023257 13910 1
DATA Write : 444 1 1
WORK Read : 4 1 1
WORK Write : 660 2 1
NUCSRT Read : 4060 940 1
NUCSRT Write : 4060 1 0
NUCTMP Read : 30 1 1
NUCTMP Write : 896 1 1
The number of IOs shows the number of physical read and write I/O accesses to ASSO, DATA, WORK, NUCSRT and NUCTMP.
The maximum IO time shows the maximum duration of a single I/O read and write access to ASSO, DATA, WORK, NUCSRT and NUCTMP in microseconds.
The average IO time shows the average time of a single I/O access to ASSO, DATA, WORK, NUCSRT and NUCTMP in microseconds.
Logging of I/O times is only available if ADAOPR IO_TIME is enabled..
adaopr: display=plog_statistics
ADANUC Version <version number>
Database 76 PLOG Statistics on 19-JAN-2014 14:59:41
PLOG Environment
----------------
NUCPLG (active) : /FS/fsxxxx/sag/ada6180102/ada/db076/NUCPLG
Active PLOG
-----------
Session Number : 37
Extent : 2
Active Since : 19-JAN-2014 14:59:41
Duration : 00:00:01
Allocated Space : 24,683 KB
Used Space ( 0%) : 32 KB
Average Growth Rate : 115,200 KB/h
adaopr: display=replications
ADANUC Version <version number>
Database 34 Replications on 19-JAN-2014 09:47:48
ID From FNR To DB To FNR Status Remark
-- -------- ----- ------ ------ ------
1 111 37 111 Inactive
86 86 37 86 Active
2 transactions pending:
---------------------------
To DB Transactions
----- ------------
37 2
5 commands pending:
-------------------------
From FNR Commands
-------- --------
86 5
111 0
This display shows the Adabas - Adabas replications currently defined. This is only relevant for customers who are using the Adabas Event Replicator with Adabas - Adabas replication.
Note:
Replications to other replication targets, for example SQL
databases, are not displayed. Such replications can only be displayed with the
administration tools of the event replication.
The display shows the following information:
“ID” is the ID of the replication that is also used in the replication administration.
"From FNR” is the file number of the file to be replicated to another Adabas file.
“To DB” and “To FNR” are the database ID and file number of the target file for the replication.
"Status" can have the following values and meanings:
| Status | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Inactive | Currently no data are replicated to the target file, and at the moment no activities have been made to initiate the replication. |
| Prepare | This status indicates that it is planned to perform the initial state processing for the replication. This status is the prerequisite for creating a backup of files to be replicated via ADABCK with parameter REPLICATION. |
| Initialization | This status indicates that ADABCK with parameter REPLICATION is running and creates a backup containing the initial state of files to be replicated. |
| Recording | Adabas is currently recording the update transactions within the replication command file and the replication transaction file, but currently does not replicate the update operations to the target database. |
| Active | The replication is active; all modifications of the source file are replicated to the target file. |
| Error | An unexpected error occurred during replication. In order to continue replication, a new initial state processing is required. |
“Pending Transactions” is the number of transactions that have not yet been replicated to the target file.
Notes:
“Pending Commands” is the number of commands that have not yet replicated to the target file.
Notes:
If ADAOPR DISPLAY=REPLICATIONS is executed in non-interactive mode, ADAOPR returns one of the following exit status values:
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 0 | At least one replication has been defined, and no replication is in status Error. |
| 12 | There is a replication in status Error. |
| 15 | Replication has not been activated, or no replication has been defined. |
adaopr: display=static_parameters
ADANUC Version <version number>
Database 22 Static Parameters on 21-NOV-2014 11:13:25
Resources: LAB : 1,048,576 NT : 6
LBP : 104,857,600 NU : 50
LWP : 1,000,000 NCL : 50
LABX : 20,971,520
APU : ( 2, 3, 2)
Logging: PLOG, BI
Options: AUTO_EXPAND
This display shows the static nucleus parameters.
Note:
The nucleus parameter APU is only displayed if it has been
specified.
adaopr: display=tt
ADANUC Version <version number>
Database 2 Thread Table on 21-NOV-2014 11:49:38
No APU Cmd Count File Cmd Status
-- --- --------- ---- --- ------
1 2 120,715 13 S9 Complex, waiting for DATA / 2785
2 1 120,146 13 S8 Complex, waiting for TEMP / 35794
3 2 124,364 0 Free
4 1 122,300 13 S8 Complex, waiting for TEMP / 168654
5 2 120,325 13 S8 Complex, active
6 1 123,210 13 S1 Simple , active
This display shows the entries in the thread table. The number of displayed entries is simultaneously the high water mark for threads.
APU shows the assigned Adabas Processing Unit of the thread if the nucleus parameter APU is set. If APU has not been specified, the column APU is not displayed.
CMD COUNT shows the total number of Adabas commands processed from the corresponding thread context. The sum of these counts will normally differ from the sum shown by DISPLAY=COMMANDS, because internal commands are also counted.
FILE shows the file number of the Adabas command that is currently being processed from the corresponding thread context. The file number is 0 if the corresponding thread context is not active, or if the command is a global one which is not linked to a particular file.
CMD shows the command string of the Adabas command that is currently being processed from the corresponding thread context. There is no output in this column if the corresponding thread context is not active.
STATUS shows the command type and the status of the corresponding thread context.
Possible command types are:
Update
Simple
Complex
Possible entries for the thread status are shown in the following table:
| Status | Meaning |
|---|---|
| free | available for allocation |
| ready | ready to run |
| active | running |
| waiting for io <rabn>/<block type> |
waiting for I/o completion of block <rabn> |
| waiting for <rabn>/<block type> |
waiting for access/update synchronization
of block <rabn> |
| waiting for space <size> bytes |
waiting for <size> bytes of work pool space |
The block type can be ASSO, DATA, WORK, FILE or PLOG.
adaopr: display=ucb
ADANUC Version <version number>
Database 76 UCB on 19-JAN-2014 14:59:45
Date/Time Entry Id Utility Mode Files
--------- -------- ------- ---- -----
19-JAN-2014 14:59:41 42 adaopr UTO 13
This display shows the utility communication block.
DATE/TIME shows the date and time on which the given files were locked.
ENTRY ID shows the allocated identification of the entry.
UTILITY shows the name of the utility.
MODE shows the mode in which the files are being accessed. The possibilities are:
ACC open for access
UPD open for update
EXU open for exclusive update (parallel access allowed)
UTO open for utilities only
UTI open for exclusive access (no parallel access or update allowed)
Files shows the file numbers of the files that are locked.
adaopr: display=uq
ADANUC Version <version number>
Database 76 User Queue on 19-JAN-2014 14:58:10
Id Node Id Login Id ES Id User Id Type Status
-- ------- -------- ----- ------- ---- ------
26 sunxxx01 dba 4473 *adaopr UT
23 sunxxx01 smith 3075 ET E
20 sunxxx01 jones 3178 ET I
19 sunxxx01 jones 1946 ET IE
18 sunxxx01 smith 4689 ET
16 sunxxx01 smith 4661 ET
17 sunxxx01 jones 4638 ######## T
14 sunxxx01 miller 4379 ET R
13 sunxxx01 dba 3967 *adatst AC
12 sunxxx01 dba 3651 *adatst EX,ET E
11 sunxxx01 dba 4025 DBADMIN EX RU
Selected: 11, Used: 11, Queue Size: 100
This display shows the current user queue entries.
ID shows the internal user identification;
NODE ID shows the node identification string;
LOGIN ID shows the login identification string;
ES ID is the process ID of the client process;
Note:
ES ID means "Environment Specific ID". This term was used,
because in previous Adabas versions on Windows, instead of the process ID, a
random number was used as the ES ID in order to avoid double usage of the same
Adabas session ID - this was because on Windows, the process IDs could be
reused after a short time. After adding a timestamp to the Adabas session ID,
reusage of the same Adabas session ID can no longer happen, therefore the
process ID can also be used as the ES ID on Windows. The timestamp is displayed
only with ADAOPR DISPLAY=UQ_FULL.
USER ID shows the user identification specified in Additions 1 in the Open command for the current Adabas session;
Note:
If you don't use the nucleus option OPEN_REQUIRED, the USER ID
information is deleted following a non-activity timeout. When this happens, the
USER ID is displayed as "########". If the nucleus option OPEN_REQUIRED is
used, not only the user information, but also the complete user queue element
is deleted; this means that DISPLAY=UQ no longer displays such user queue
elements.
TYPE shows the user type:
AC access only user
ET ET user
EX exclusive update user
EX,ET exclusive update user with ET logic
UT utility user.
STATUS shows the status of the user:
E user at ET status
G global timeout (XA)
I user session started with an implicit OPEN
P pending ET (XA)
R restricted file list
T user has received a time-out
U user specific timeout interval value
Note:
The description for the components of the Adabas session ID (Node
ID, Login ID, ES ID and the timestamp not displayed by ADAOPR DISPLAY=UQ) is
only correct if the function lnk_set_adabas_id is not used (see Command
Reference). This function lets you define your own Adabas session IDs.
The final line of the display shows how many user queue entries were selected according to the currently active selection criteria, and how many entries are used in total.
adaopr: display=uq_files
ADANUC Version <version number>
Database 76 User Files on 19-JAN-2014 14:58:10
Id Type Mode Files
-- ---- ---- -----
26 UT
23 ET UPD 11-12
20 ET UPD 11-12
19 ET UPD 11-12
18 ET UPD 11-12
16 ET UPD 11-12
14 ET UPD 11-12
13 AC
12 EX,ET EXU 14
11 EX ACC 11
EXU 13
Selected: 10, Used: 11, Queue Size: 100
This display shows the file lists for active users.
ID shows the internal user identification;
TYPE shows the user type (please refer to the DISPLAY=UQ example for more information).
MODE shows the mode in which the files are being accessed:
ACC open for access
EXF open for exclusive access (no parallel access or update allowed)
EXU open for exclusive update (parallel access allowed)
UPD open for update
UTI open for exclusive access (no parallel access or update allowed)
UTO open for utilities only
FILES shows the Adabas file list of the user entry. If the list is too large to be displayed in one line, several lines will be used: file numbers are not omitted.
The final line of the display shows how many user queue entries were selected according to the currently active selection criteria, and how many entries are used in total.
adaopr: disp=uq_full
ADANUC Version <version number>
Database 36 Full User Queue Entry on 3-SEP-2014 17:12:24
User Entry: Id : 8 ES Id : 17937
Node Id : sunada05 Login Id : smith
User Id : *adaopr
Timestamp Id : 3-SEP-2014 17:12:18:182,671
User Type : UT User Status :
Time Stamps: Session Start : 3-SEP-2014 17:12:17
Trans. Start :
Last Activity :
Time Limits: TT : 0 TNA : 0
Resources: ISN Lists : 0 ISNs Held : 0
Open Files : 0
Activity: ADABAS Calls : 1 Transactions : 0
Settings: User Encoding : UTF-8
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
User Entry: Id : 6 ES Id : 15808
Node Id : sunada05 Login Id : jones
User Id : JONES001
Timestamp Id : 3-SEP-2014 17:11:32:113,750
User Type : ET User Status :
Time Stamps: Session Start : 3-SEP-2014 17:11:31
Trans. Start : 3-SEP-2014 17:11:56
Last Activity : 3-SEP-2014 17:11:56
Time Limits: TT : 300 TNA : 300
Resources: ISN Lists : 0 ISNs Held : 1
Open Files : 1
Activity: ADABAS Calls : 3 Transactions : 1
Settings: User Encoding : UTF-8
This display shows detailed information about user queue elements.
Additionally to the information shown by ADAOPR DISPLAY=UQ, the following information is shown:
TIMESTAMP ID shows the timestamp added to the Adabas session ID to guarantee the uniquenes of the Adabas session ID;
The timestamps show when the current Adabas user session was started, when the last transaction of the session was started, and when the last activity for the session was performed.;
The time limits show the transaction time limit and the non-activity time limit defined for the Adabas user session;
Note:
Normally the time limits are the default values defined via
ADANUC parameters, but it is possible to override these default values in the
Open command of the Adabas user session.
Resources shows the number of ISN lists currently active for the Adabas user session, the number of ISNs in the hold queue for the session, and the number of Adabas files in use in the session;
Activity displays the number of Adabas calls and the number of transactions performed in the Adabas user session.
Settings displays the default user encoding for W fields used in the current Adabas sessions as specified in the Open command of the session. If nothing was specified, the default UTF8 is used.
adaopr: display=uq_time_limits
ADANUC Version <version number>
Database 76 User Time Limits on 19-JAN-2010 14:58:10
TNAA Interval : 00:15:00 TNAX Interval : 00:15:00
TNAE Interval : 00:15:00 TT Interval : 00:05:00
Id St Limit Timeout Interval Remaining Time Start Date/Time
-- -- ----- ---------------- -------------- ---------------
23 TNAE 00:15:00 00:15:00 19-JAN-2014 14:58:10
TT 00:05:00
22 TNAE 00:15:00 00:15:00 19-JAN-2014 14:58:10
TT 00:05:00
21 TNAE 00:15:00 00:15:00 19-JAN-2014 14:58:10
TT 00:05:00 00:05:00 19-JAN-2014 14:58:10
20 TNAE 00:15:00 00:15:00 19-JAN-2014 14:58:10
TT 00:05:00 00:05:00 19-JAN-2014 14:58:10
19 TNAE 00:15:00 00:15:00 19-JAN-2014 14:58:10
TT 00:05:00
18 TNAE 00:15:00 00:15:00 19-JAN-2014 14:58:10
TT 00:05:00 00:04:50 19-JAN-2014 14:58:00
17 TNAA 00:15:00 00:15:00 19-JAN-2014 14:58:10
16 TNAE 00:15:00 00:15:00 19-JAN-2014 14:58:10
TT 00:05:00 00:05:00 19-JAN-2014 14:58:10
14 TNAE 00:15:00 00:15:00 19-JAN-2014 14:58:10
TT 00:05:00 00:05:00 19-JAN-2014 14:58:10
13 TNAA 00:15:00 00:10:01 19-JAN-2014 14:53:11
12 TNAE 00:15:00 00:10:01 19-JAN-2014 14:53:11
TT 00:05:00
11 U TNAX 00:40:00 00:34:57 19-JAN-2014 14:53:07
Selected: 12, Used: 14, Queue Size: 100
This display shows the current timeout limits for the user queue entries.
ID shows the internal user identification;
ST shows the status of the entry. Possible values are:
U user specific timeout value
T a timeout is pending, response 9 has not been collected yet by the client.
LIMIT describes the timeout type;
TIMEOUT INTERVAL shows the current active timeout intervals.
REMAINING TIME shows the amount of time remaining until the next timeout mark.
START DATE/TIME shows the starting date and time of the entry.
The final line of the display shows how many user queue entries were selected according to the currently active selection criteria, and how many entries are used in total.
ES_ID = number
This function influences the output of the DISPLAY options CQ, HQ, ICQ, UQ, UQ_FILES, UQ_FULL, UQ_TIME_LIMITS. Only entries with the specified environment-specific ID are displayed.
[NO]ET_SYNC
This option controls the behaviour of the FEOF=PLOG function. It must be specified before specifying FEOF=PLOG. Refer to the FEOF=PLOG function for more information.
The default is NOET_SYNC.
EXT_BACKUP = [PREPARE | CONTINUE | ABORT]
This function is used to backup a database using an external backup system, which can be considerably faster with very large databases than using ADABCK.
The keyword PREPARE prepares the database for backup. During this phase, the following restrictions apply:
new transactions will be stalled
no updating utility functions (e.g. ADADBM) can be started
the functions SHUTDOWN, CANCEL, LOCK, STOPUSER, UNLOCK and FEOF=PLOG are not permitted once the EXT_BACKUP = PREPARE call has finished processing
all non-activity timeout checks are disabled
The keyword CONTINUE is used to resume normal database operations following completion of the external backup. The following actions are performed:
open a new PLOG with a new session number
re-enable non-activity timeout checks
re-enable update utilities
wake up all waiting users (start of new transactions)
The keyword ABORT is used to abort an external backup for which a PREPARE has already been issued. In this case, the PLOG isn't switched and no checkpoint is written.
The following scenario shows a backup and restore using a third-party backup tool (tar is not a real alternative, and is used for demonstration purposes only):
Dumping the database
% adaopr dbid=37 ext_backup=prepare %ADAOPR-I-STARTED, 14-NOV-2012 16:18:30, T-Version 6.3.99.00 (Solaris 64Bit) Database 37, startup at 14-NOV-2012 16:18:10 ADANUC T-Version 6.3.99.00, PID 15245 %ADAOPR-I-EXTBPREP, preparing for external backup, 14-NOV-2012 16:18:30 %ADAOPR-I-TERMINATED, 14-NOV-2012 16:18:30, elapsed time: 00:00:00 % tar cvf $BACKUPDIR/backup.tar ASSO* DATA* # external dump <external backup output> % adaopr dbid=1 ext_backup=continue %ADAOPR-I-STARTED, 14-NOV-2012 16:18:45, T-Version 6.3.99.00 (Solaris 64Bit) Database 37, startup at 14-NOV-2012 16:18:10 ADANUC T-Version 6.3.99.00, PID 15245 During ET Sync (phase 2), for external backup %ADAOPR-I-EXTBCONT, continue from external backup, 14-NOV-2012 16:18:45 %ADAOPR-I-TERMINATED, 14-NOV-2012 16:18:45, elapsed time: 00:00:00
Restoring and recovering the database
% tar xvf $BACKUPDIR/backup.tar # external restore % adastart 37 % setenv RECPLG plog.0017 # Set RECPLG for ADAREC (C shell) % adarec dbid=37 regenerate=* plog=17
The external backup is logged in the ADANUC log file
%ADANUC-I-DBSTART, Database 37, session 16 started, 14-NOV-2012 16:17:10 %ADANUC-I-EXTBPREP, preparing for external backup, 14-NOV-2012 16:18:30 %ADANUC-I-DBSTART, Database 37, session 17 started, 14-NOV-2012 16:18:45 %ADANUC-I-PLOGCRE, plog NUCPLG, file 'plogs/plog.0017' created %ADANUC-I-EXTBCONT, continue from external backup, 14-NOV-2012 16:18:45
FEOF = (keyword [,keyword])
In accordance with the keywords specified, the log file(s) are closed and a new log file is created.
| Keyword | Meaning |
|---|---|
| CLOG |
closes command log file. |
| PLOG |
closes protection log file. This depends on the [NO]ET_SYNC option: If NOET_SYNC is specified: |
The FEOF command will be rejected if the keyword PLOG is used while running ADAREC REGENERATE = * (see ADAREC for more detailed information).
FILE = number
This influences the output of the DISPLAY options HQ, ICQ, UQ, UQ_FILES, UQ_FULL and UQ_TIME_LIMITS. Only entries related to the specified file number are displayed.
FREE_CLQ
Normally, obsolete entries in the client queue are released automatically when the client queue is full. With ADAOPR FREE_CLQ, you can enforce the client queue cleanup before the client queue becomes full.
ID = number
This function influences the output of the DISPLAY options CQ, HQ, ICQ, UQ, UQ_FILES, UQ_FULL and UQ_TIME_LIMITS. Only entries related to the specified internal ID are displayed.
[NO]IO_TIME
The parameter IO_TIME enables logging of the I/O times for the ASSO, DATA, WORK, NUCSRT and NUCTMP containers. The times are given in microseconds.
If logging of I/O times is already enabled, enabling it again resets all I/O time and I/O counter statistics.
The default is NOIO_TIME.
ISN = ( number [- number] [,number [- number] ] ... )
This function influences the output of the DISPLAY option HQ. Only entries related to the specified ISNs are displayed.
[UN]LOCK = (number [,number]...)
The file(s) specified by the file number(s) are locked or unlocked. The specified files are locked for all non-utility use; Adabas utilities can use the file(s) normally. Specifying 0 means lock/unlock the complete database.
For users who have one or more files to be locked in their open file list, a STOP <user-ID> command is issued internally. Refer to the description of the ADAOPR STOP parameter for more details.
Notes:
LOGGING = (keyword [,keyword]...)
This parameter starts command logging for the buffers specified in the list of keywords.
The following keywords can be used:
| Keyword | Meaning |
|---|---|
| CB | Enables logging of control block |
| FB | Enables logging of format buffers |
| RB | Enables logging of record buffers |
| SB | Enables logging of search buffer |
| VB | Enables logging of value buffer |
| IB | Enables logging of ISN buffer |
| ABD | Enables logging of Adabas buffer descriptions |
| IO | Enables I/O list logging |
| OFF | Stops logging of all buffers, but keeps the command log file open |
If the nucleus was started with LOGGING=OFF and buffer logging is requested, then the CLOG file will be created.
LOGIN_ID = string
This function influences the output of the DISPLAY options CQ, HQ, ICQ, UQ, UQ_FILES, UQ_FULL and UQ_TIME_LIMITS. Only entries with a login ID that begin with the specified string will be selected. Please note that the string specification must be case sensitive. If you want to select explicitly a login ID shorter than 8 characters, but not other login IDs beginning with this login ID, you must add "^ " (Windows platforms) or "\ " (non-Windows platforms) to the login ID.
NISNHQ = number
This parameter specifies the maximum number of records that can be placed into hold at any time by a single user.
If the specified value is less than the corresponding high-water value, a warning is issued.
The minimum value is 0, where 0 means unlimited.
NODE_ID = string
This function influences the output of the DISPLAY options CQ, HQ, ICQ, UQ, UQ_FILES, UQ_FULL and UQ_TIME_LIMITS. Only entries with a node ID that begin with the specified string will be selected. Please note that the string specification must be case sensitive. If you want to select explicitly a node ID shorter than 8 characters, but not other node IDs beginning with this node ID, you must add "^ " (Windows platforms) or "\ " (non-Windows platforms) to the node ID.
OPTIONS = (keyword[,keyword])
The available keywords are:
| Keyword | Meaning |
|---|---|
| [NO]LOCAL_UTILITIES |
If LOCAL_UTILITIES is specified, the nucleus rejects all remote utility calls, i.e. the Adabas utilities cannot be run from a remote node across a network. |
| [NO]UTILITIES_ONLY |
If UTILITIES_ONLY is selected, all calls other than for utilities will be rejected. Note, however, that this restriction only applies to new users; users who were already active when OPTIONS=UTILITIES_ONLY was specified can continue processing normally. If you want exclusive utility control over files or the entire database, use the LOCK function of ADAOPR instead. |
These options can be disabled using the prefix `NO', e.g. OPTIONS=NOUTILITIES_ONLY.
READ_PARALLEL_LIMITS = (records,blocks,total)
This parameter is used to modify the nucleus parameter READ_PARALLEL_LIMITS. Please refer to the description in ADANUC for further information.
RESET = keyword
RESET=HIGH_WATER resets the high water mark values to the value currently in use.
RESET=COMMANDS resets the command counts displayed by ADAOPR DISPLAY=COMMANDS.
[NO]RESPONSE_ABORT
If response checking is enabled with the RESPONSE_CHECK parameter of ADAOPR, the RESPONSE_ABORT option determines whether the nucleus aborts when one of the specified responses occurs (RESPONSE_ABORT), or whether the nucleus resumes operation and a database section file is written to disk (NORESPONSE_ABORT).
The setting of the [NO]RESPONSE_ABORT option can only be changed before the RESPONSE_CHECK parameter. The same applies for XA_RESPONSE_CHECK (not on OpenVMS).
The default is NORESPONSE_ABORT.
Refer to the RESPONSE_CHECK parameter for further information.
RESPONSE_CHECK = [(number[-number][,number[-number]]...)]
This function enables the DBA to gather information if one of a list of Adabas response codes occurs. The information written may be used to analyze possible problems in the database's operation. If a response check for an Adabas response code is enabled, the database section file is written to disk if this response code occurs.
Depending on the setting of the RESPONSE_ABORT option, the nucleus either aborts or continues operation:
if the RESPONSE_ABORT option is set, the database section file (Adabas.xxx.hh:mm:ss [UNIX], or Adabas.xxx.hh-mm-ss [Windows] or Adabas-xxx-hh-mm-ss [OpenVMS]) is written to the database's default directory. The database section file is also called the CSA dump file. See ADANUC and the environment variable ADA_CSA_DUMP for more information.
When the CSA dump file is written, the SMP dump file is also written (UNIX platforms only); the name of the SMP dump file is SMPPOS.APP:hh:mm:ss.
if the NORESPONSE_ABORT option is set (default setting), the nucleus continues running and the database section file (Adabas.xxx.RSPyyy.hh:mm:ss [UNIX], or Adabas.xxx.RSPyyy.hh-mm-ss [Windows] or Adabas-xxx-RSPyyy-hh-mm-ss [OpenVMS]) is written to the database's default directory. See ADANUC and the environment variable ADA_CSA_DUMP for more information. Only one dump is generated for one response code; if a response code occurs, the RESPONSE_CHECK option is deactivated for that response code, but if it has been activated for other response codes, it remains active for the other response codes.
Refer to the RESPONSE_ABORT action for further information.
By default, no response is trapped and the nucleus continues operation.
To disable response trapping, use "RESPONSE_CHECK =" without arguments.
Note:
Some response codes can be generated outside
the nucleus (e.g. by ADALNK and ENTIRE NET-WORK). If this happens, they cannot
be trapped by Adabas. The response codes in question for ADALNK are: 9, 17, 22,
40, 146-154, 241, 252, 255.
SET_FILE_STATS = [(number[-number][,number[-number]]...)]
This function enables the file level I/O statistics for the specified files. Only these files will be displayed by DISPLAY = FILE_IO.
SHUTDOWN
This function terminates the Adabas session normally. No new users are accepted. ET-user updating is continued until the end of the current transaction for each user. When all update activity has ended as described above, the Adabas session is terminated.
The communication link to the database is cut but the shared memory is still held. In this case, display functions are still possible with ADAOPR but parameter modification commands are no longer permitted.
STATUS = (keyword [,keyword] ,... )
This function influences the output of the DISPLAY parameter options HQ, ICQ, UQ, UQ_FILES, UQ_TIME_LIMITS, UQ_FULL. Only entries in the specified state will be displayed.
The valid keywords are:
| Keyword | Meaning |
|---|---|
| [NO]TIMEOUT | User without or with "T" status. |
| [NO]ET_STATUS | Users at "ET" status with open transactions. |
| [NO]PENDING_ET | Users without or with "P" status. |
STOP = (number[-number][,number[-number]]...)
This parameter terminates the user with the specified ID (internal identification). The ID can be retrieved with DISPLAY = UQ.
The message "Stop handling started for n users" is displayed, where "n" is the number of users who will be stopped.
Note:
Utilities cannot always be stopped in this way.
The actions that Adabas takes when a user is stopped depend on the user type, and also whether the nucleus requires an explicit OP (open) command at the start of a user session, as shown in the following table.
The abbreviation SUQE used in the table means "Stop user queue element", and consists of the following actions: release all Command IDs, scratch the file list, scratch the user ID, scratch the user type, set response 9 for the next call.
| User Type | Adabas Actions without ADANUC OPTIONS=OPEN_REQUIRED | Adabas Actions with ADANUC OPTIONS=OPEN_REQUIRED |
|---|---|---|
| ACC |
For ID user: SUQE For non-ID user: session closed |
session closed |
| ET, ET Status |
For ID user: SUQE For non-ID user: session closed |
session closed |
| ET, no ET Status | Backout transaction, SUQE | Backout transaction, session closed |
| EX | SUQE, CLSE checkpoint | session closed |
| EX, ET with ET status | SUQE, CLSE checkpoint | session closed |
| EX, ET, no ET status | Backout transaction, SUQE, CLSE checkpoint | Backout transaction, session closed |
| UT | session closed | session closed |
If a STOP command is issued for a user while running
ADAREC REGENERATE = *
it will be rejected (see ADAREC in this manual for more information).
TNAA = number
This parameter sets the non-activity time limit (in seconds) for access-only users who have not explicitly specified a TNAA value in the OP command (see Command Reference, OP command).
Note that the figure you specify for this parameter is only approximate. In any particular instance, the actual amount of time can vary from this value by up to 10 seconds.
The minimum value is 20, the maximum value is 2592000.
TNAE = number
This parameter sets the non-activity time limit (in seconds) for ET logic users who have not explicitly specified a TNAE value in the OP command (see Command Reference, OP command).
Note that the figure you specify for this parameter is only approximate. In any particular instance, the actual amount of time can vary from this value by up to 10 seconds.
The minimum value is 20, the maximum value is 2592000.
TNAX = number
This parameter sets the non-activity time limit (in seconds) for EXU and EXF users who have not explicitly specified a TNAX value in the OP command (see Command Reference, OP command).
Note that the figure you specify for this parameter is only approximate. In any particular instance, the actual amount of time can vary from this value by up to 10 seconds.
The minimum value is 20, the maximum value is 2592000.
TT = number
This parameter sets the transaction time limit for ET logic users who have not explicitly specified a TT value in the OP command (see Command Reference, OP command).
If the specified value is less than the corresponding high-water value, a warning is issued.
Note that the figure you specify for this parameter is only approximate. In any particular instance, the actual amount of time can vary from this value by up to 10 seconds.
The minimum value is 20, the maximum value is 2592000.
USER_ID = string
This function influences the output of the DISPLAY parameter options CQ, HQ, ICQ, UQ, UQ_FILES, UQ_TIME_LIMITS, UQ_FULL. Only entries with a user ID that begin with the specified string will be selected. Please note that the string specification must be case sensitive. If you want to select explicitly a user ID shorter than 8 characters, but not other user IDs beginning with this user ID, you must add "^ " (Windows platforms) or "\ " (non-Windows platforms) to the user ID.
WRITE_LIMIT = [number]
This parameter specifies the percentage of modified blocks permitted in the buffer pool before an implicit buffer flush is taken.
Note that "WRITE_LIMIT=" (keeping the equals sign but omitting the number) is equivalent to "WRITE_LIMIT=0".
The minimum value is 0 and the maximum value is 70; 0 means that Adabas will dynamically choose an appropriate value.
XA_RESPONSE_CHECK = (keyword [,keyword] ,... )
This function enables the DBA to gather information if one of a list of XA response codes occurs (not on OpenVMS). The information written may be used to analyze possible problems in the database's operation. If a response check for an XA response code is enabled, the database section file is written to disk if this response code occurs.
Depending on the setting of the RESPONSE_ABORT option, the nucleus either aborts or continues operation:
if the RESPONSE_ABORT option is set, the database section file (Adabas.xxx.hh:mm:ss) is written to the database's default directory;
if the NORESPONSE_ABORT option is set (default setting), the nucleus continues running and the database section file (Adabas.xxx.XAyyyy.hh:mm:ss) is written to disk (refer to the ADAOPR FILE parameter for further information).
By default, no response is trapped and the nucleus continues operation.
Refer to the RESPONSE_ABORT option for further information.
To disable response trapping, use "XA_RESPONSE_CHECK =" without arguments.
The following keywords are supported:
XA_RBROLLBACK
XA_RBCOMMFAIL
XA_RBDEADLOCK
XA_RBINTEGRITY
XA_RBOTHER
XA_RBPROTO
XA_RBTIMEOUT
XA_RBTRANSIENT
XA_NOMIGRATE
XA_HEURHAZ
XA_HEURCOM
XA_HEURRB
XA_HEURMIX
XA_RETRY
XAER_ASYNC
XAER_RMERR
XAER_NOTA
XAER_INVAL
XAER_PROTO
XAER_RMFAIL
XAER_DUPID
XAER_OUTSIDE
XA_RBROLLBACK
For more information, see Administration, XA Support.