This document describes the utility "ADAINV".
The following topics are covered:
The inverted list utility ADAINV creates, removes and verifies inverted lists for loaded files in a database. It does not require the Adabas nucleus to be active. The nucleus may, however, be active or shut down while ADAINV is running. The following functions are available:
The INVERT function establishes new descriptors;
The REINVERT function performs an implicit RELEASE and INVERT;
The RELEASE function removes existing descriptors;
The RESET_UQ function removes the unique status from descriptors;
The SET_UQ function establishes a unique status for existing descriptors;
The SUMMARY function displays the descriptor space summary for the specified descriptors and the required sizes to process these descriptors;
The VERIFY function checks the integrity of inverted lists.
A LOB file can only be specified for the functions REINVERT, SUMMARY and VERIFY.
These functions are mutually exclusive and only one of them may be executed each time this utility is run.
If the utility writes records to the error file, it will exit with a non-zero status.
This utility is a single-function utility.
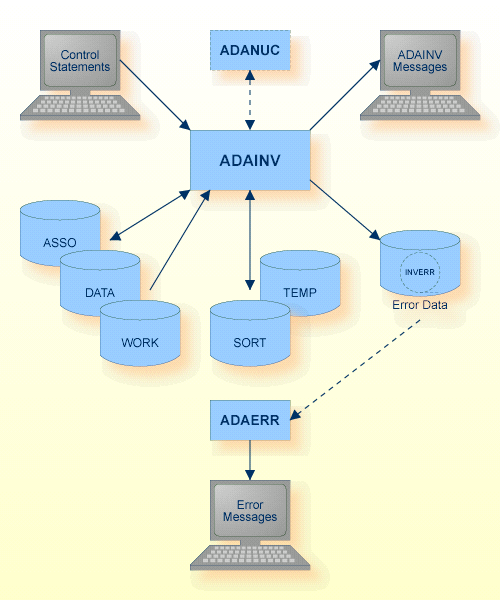
The sequential file INVERR can have multiple extents. For detailed information about sequential files with multiple extents, see Administration, Using Utilities.
| Data Set | Environment Variable/ Logical Name |
Storage Medium |
Additional Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| Associator | ASSOx | Disk | |
| Data storage | DATAx | Disk | |
| Rejected data | INVERR | Disk, Tape (* see note) | output of ADAINV |
| Sort storage | SORTx TEMPLOCx |
Disk | Administration Manual, temporary working space |
| Control statements | stdin/ SYS$INPUT |
Utilities Manual | |
| ADAINV messages | stdout/ SYS$OUTPUT |
Messages and Codes | |
| Temporary storage | TEMPx | Disk | |
| Work storage | WORK1 | Disk |
Note:
(*) A named pipe can be used for this sequential file
(not on OpenVMS, see Administration, Using
Utilities for details).
In cases without an active nucleus and no pending AUTORESTART, the WORK may be used as TEMP by setting the environment variable/logical name TEMP1 to the path name or raw disk section of a WORK container.
The following table shows the nucleus requirements for each function and the checkpoints written:
| Function | Nucleus must be active | Nucleus must NOT be active | Nucleus is NOT required | Checkpoint written | Nucleus operations allowed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INVERT | X | SYNP | R | ||
| REINVERT | X(* see note) | X | SYNP | ||
| RELEASE | X | SYNP | R | ||
| RESET_UQ | X | SYNP | R | ||
| SET_UQ | X | SYNP | R | ||
| SUMMARY | X | W | |||
| VERIFY | X(* see note) | X | SYNX | R |
Note:
(*) When processing an Adabas system file.
R: read operations allowed for the processed file.
W: read
und write operations allowed for the processed file.
The following control parameters are available:
M DBID = number
INVERT = number,
FIELDS {field_name [,UQ] [,TR] | derived_descriptor_definition | FDT},
... [END_OF_FIELDS]
[,FDT]
D [,LWP = number[K]]
D [,UQ_CONFLICT = keyword]
D [NO]LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES
REINVERT = number,
{ALL_FIELDS | FIELDS {descriptor_name | FDT}, ... [END_OF_FIELDS]}
[,FDT]
D [,[NO]FORMAT]
D [,LWP = number[K]]
D [,UQ_CONFLICT = keyword]
RELEASE = number,
{ALL_FIELDS | FIELDS {descriptor_name | FDT}, ... [END_OF_FIELDS]}
[,FDT]
D [,[NO]FORMAT]
RESET_UQ = number,
{ALL_FIELDS | FIELDS {descriptor_name | FDT}, ... [END_OF_FIELDS]}
[,FDT]
SET_UQ = number,
{ALL_FIELDS | FIELDS {descriptor_name | FDT}, ... [END_OF_FIELDS]}
[,FDT]
D [,UQ_CONFLICT = keyword]
SUMMARY = number,
{ALL_FIELDS | FIELDS
{descriptor_name | derived_descriptor_definition | FDT},
... [END_OF_FIELDS]}
[,FDT]
D [,FULL]
VERIFY = number,
{ALL_FIELDS | FIELDS {descriptor_name | FDT}, ... [END_OF_FIELDS]}
D [,ERRORS = number]
[,FDT]
D [,LWP = number[K]]
DBID = number
This parameter selects the database to be used.
INVERT = number,
FIELDS {field_name [,UQ] [,TR] | derived_descriptor_definition | FDT},
... [END_OF_FIELDS]
[,FDT]
[,LWP = number[K]]
[,UQ_CONFLICT = keyword]
This function establishes new elementary, sub-, super-, hyper-, phonetic and collation descriptors at any time after a file has been initially loaded. `number' specifies the file containing the fields to be inverted. You are not allowed to specify the number of a LOB file.
This parameter displays the FDT of the selected file. This option may be specified before or within the field specification list.
This parameter specifies fields to be inverted. It can contain one or more
field name,
phonetic descriptor or
sub-, super-, hyper- or collation descriptor
specifications, each starting on a separate line. See Administration, FDT Record Structure for valid specifications of field names, phonetic, sub-, super-, hyper- or collation descriptors.
The options UQ and TR are used to specify whether the field in question is a unique descriptor or whether index truncation will be performed. See Administration, Definition Options for further information about the UQ and TR options.
Note:
Only fields for which the values are stored in the base file can be
used as descriptors or parent fields of derived descriptors. For this reason,
an invert function will be aborted if a field to be inverted or a parent field
of a derived descriptor to be created has the LA or LB option and values are
stored in the LOB file. LA and LB fields can be used as descriptors or parent
fields of derived descriptors, but then all values are limited to 16 KB – 3,
and the base record including these LA or LB field values must fit into one
data block.
If the field definitions are terminated with the END_OF_FIELDS parameter, this parameter must be specified in upper case when the LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES parameter is used. In addition, the FDT parameter must also be specified in upper case when the LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES parameter is used.
This parameter specifies the size of the Work Pool in bytes or in kilobytes (K) to be used for the sort while creating the inverted lists.
You can use the SUMMARY function to determine the required value for this parameter.
The minimum size is 0 bytes and the default size is 0 bytes.
This parameter determines which action is to be taken when duplicate values are found for a unique descriptor. `keyword' may take the values ABORT or RESET. If ABORT is specified, ADAINV terminates execution and returns an error status if duplicate UQ descriptor values are found. If RESET is specified, the UQ status of the descriptors in question is removed and processing continues.
The default is UQ_CONFLICT = ABORT.
[NO]LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES
If LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES is specified, Adabas field names are not converted to upper case. If NOLOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES is specified, Adabas field names are converted to upper case. The default is NOLOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES.
This parameter must be specified before the FIELDS parameter.
REINVERT = number,
{ALL_FIELDS | FIELDS {descriptor_name | FDT}, ... [END_OF_FIELDS]}
[,FDT]
[,[NO]FORMAT]
[,LWP = number[K]]
[,UQ_CONFLICT = keyword]
This function performs an implicit RELEASE and INVERT. This reduces the probability of a typing error, especially for sub- and superdescriptors.
Note:
The purpose of ADAINV REINVERT is to recreate a descriptor if the
index tree becomes unbalanced as a result of a large number of updates, or if
an index error occurred. Descriptors are always recreated with the same
definition as before; if you want to change the definition of a descriptor, for
example a superdescriptor, you must perform ADAINV RELEASE followed by ADAINV
INVERT with the new descriptor definition.
This parameter specifies that all descriptors of the selected file are to be released/inverted.
This parameter displays the FDT of the selected file. This option may be specified before or within the fields specification list.
This parameter specifies the descriptors to be released/reinverted. It can be followed by one or more field names, each starting on a separate line. See Administration, FDT Record Structure for a description of valid field name specifications.
If the field definitions are terminated with the END_OF_FIELDS parameter, this parameter must be specified in upper case when the LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES parameter is used. In addition, the FDT parameter must also be specified in upper case when the LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES parameter is used.
If a descriptor is released or reinverted, the new index created is generally smaller than the old index and requires less disk space. The FORMAT option can be used to format the blocks that are no longer used by the index but which are still allocated to the file.
The default is NOFORMAT.
This parameter specifies the size of the Work Pool to be used for the sort. This is an internal sort to recover lost index blocks when rebuilding the upper index.
You can use the SUMMARY function to determine the required value for this parameter.
The minimum size is 0 bytes and the default size is 0 bytes.
This parameter determines which action is to be taken when duplicate values are found for a unique descriptor. `keyword' may take the values ABORT or RESET. If ABORT is specified, ADAINV terminates execution and returns an error status if duplicate UQ descriptor values are found. If RESET is specified, the UQ status of the descriptors in question is removed and processing continues.
The default is UQ_CONFLICT = ABORT.
RELEASE = number,
{ALL_FIELDS | FIELDS {descriptor_name | FDT}, ... [END_OF_FIELDS]}
[,FDT]
[,[NO]FORMAT]
This function removes elementary, sub-, super-, hyper-, phonetic and collation descriptors from the file specified by `number'. You are not allowed to specify the number of a LOB file.
This parameter specifies that all descriptors of the selected file are to be released.
This parameter displays the FDT of the selected file. This option may be specified before or within the fields specification list.
This parameter specifies the descriptors to be released. It can be followed by one or more field names, each starting on a separate line. See Administration, FDT Record Structure for a description of valid field name specifications.
If the field definitions are terminated with the END_OF_FIELDS parameter, this parameter must be specified in upper case when the LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES parameter is used. In addition, the FDT parameter must also be specified in upper case when the LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES parameter is used.
If a descriptor is released or reinverted, the new index created is generally smaller than the old index and requires less disk space. The FORMAT option can be used to format the blocks that are no longer used by the index but which are still allocated to the file.
The default is NOFORMAT.
RESET_UQ = number,
{ALL_FIELDS | FIELDS {descriptor_name | FDT}, ... [END_OF_FIELDS]}
[,FDT]
This function removes the unique status from elementary, sub-, hyper-, super- and collation descriptors defined in the file specified by `number'. You are not allowed to specify the number of a LOB file.
This parameter specifies that the unique status is to be removed from all unique descriptors in the specified file.
This parameter displays the Field Definition Table (FDT) of the selected file. This option may be specified before or within the fields specification list.
This parameter specifies the descriptors that are to have unique status removed. It can be followed by one or more field names, each starting on a separate line. See Administration, FDT Record Structure for a description of valid field name specifications.
If the field definitions are terminated with the END_OF_FIELDS parameter, this parameter must be specified in upper case when the LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES parameter is used. In addition, the FDT parameter must also be specified in upper case when the LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES parameter is used.
SET_UQ = number,
{ALL_FIELDS | FIELDS {descriptor_name | FDT}, ... [END_OF_FIELDS]}
[,FDT]
[,UQ_CONFLICT = keyword]
This function establishes the unique status for elementary, sub-, hyper-, super- and collation descriptors defined in the file specified by `number'. You are not allowed to specify the number of a LOB file.
This parameter specifies that the unique status is to be established for all elementary, sub-, hyper-, super- and collation descriptors defined in the specified file.
This parameter displays the FDT of the selected file. This option may be specified before or within the fields specification list.
This parameter specifies the descriptors for which the unique status is to be established. It can be followed by one or more field names, each starting on a separate line. See Administration, FDT Record Structure for a description of valid field name specifications.
If the field definitions are terminated with the END_OF_FIELDS parameter, this parameter must be specified in upper case when the LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES parameter is used. In addition, the FDT parameter must also be specified in upper case when the LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES parameter is used.
This parameter determines which action is to be taken when duplicate values are found for a unique descriptor. `keyword' may take the values ABORT or RESET. If ABORT is specified, ADAINV terminates execution and returns an error status if duplicate descriptor values are found. If RESET is specified, the UQ status of the descriptors in question is not established and processing continues.
The default is UQ_CONFLICT = ABORT
SUMMARY = number,
{ALL_FIELDS | FIELDS
{descriptor_name | derived_descriptor_definition | FDT},
... [END_OF_FIELDS]}
[,FDT]
[,FULL]
This function displays the descriptor space summary (DSS) for the specified descriptors and the required sizes to process the descriptors.
Note:
Processing the exact size would be too complicated. It may be that
sizes a little smaller than those displayed are sufficient. If the file is
updated during or after the SUMMARY function, the displayed values might also
be too small.
This parameter specifies that all descriptors of the selected files are to be checked.
This parameter displays the FDT of the selected file. This option may be specified before or within the fields specification list.
This parameter specifies the descriptors for which the unique status is to be established. It can be followed by one or more field names, phonetic descriptors, subdescriptors, superdescriptors, hyperdescriptors or collation descriptors, each starting on a separate line. You can specify fields that are descriptors or fields that are not descriptors. See Administration, FDT Record Structure for a description of valid field name specifications.
If the field definitions are terminated with the END_OF_FIELDS parameter, this parameter must be specified in upper case when the LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES parameter is used. In addition, the FDT parameter must also be specified in upper case when the LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES parameter is used.
If this is specified, each descriptor is displayed along with the sizes that are required for the descriptor. This can be helpful if not all of the specified fields are to be processed.
VERIFY = number,
{ALL_FIELDS | FIELDS {descriptor_name | FDT}, ... [END_OF_FIELDS]}
[,ERRORS = number]
[,FDT]
[,LWP = number[K]]
This function checks the integrity of inverted lists of the file specified by `number'.
This parameter specifies that all descriptors of the selected file are to be checked.
This parameter specifies the number of errors that have to be reported in order to terminate the verification of a descriptor.
The default is 20.
This parameter displays the FDT of the selected file. This option may be specified before or within the fields specification list.
This parameter specifies the descriptor fields to be verified. It can be followed by one or more field names, each starting on a separate line. See Administration, FDT Record Structure for a description of valid field name specifications.
If the field definitions are terminated with the END_OF_FIELDS parameter, this parameter must be specified in upper case when the LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES parameter is used. In addition, the FDT parameter must also be specified in upper case when the LOWER_CASE_FIELD_NAMES parameter is used.
This parameter specifies the size of the Work Pool to be used for the sort while verifying the inverted lists.
You can use the SUMMARY function to determine the required value for this parameter.
The minimum size is 0 bytes and the default size is 0 bytes.
ADAINV has no restart capability. However, it may or may not be possible to re-start an abnormally terminated ADAINV from the beginning.
If ADAINV terminates abnormally, it can usually be restarted from the beginning. However, if ADAINV has modified the index, the following points have to be considered:
The function REINVERT ... FIELDS is the same as the function RELEASE ... FIELDS followed by the function INVERT ... FIELDS. So if ADAINV has aborted in the INVERT phase, perform the function INVERT ... FIELDS to restart the operation.
If ADAINV is performed offline, there is a very small amount of time where a few records that together form a logical unit are written to disk. If ADAINV terminates after the first of these records has been written and before the last has been written, ADAINV cannot be restarted. In this case, the function REINVERT ... ALL_FIELDS is required. This cannot happen if ADAINV is performed online.
If ADAINV terminates abnormally, it can happen that some index blocks are lost. These index blocks can only be recovered by the function REINVERT ... ALL_FIELDS or by using the utility ADAORD or by using the utilities ADAULD and ADAMUP.
adainv: dbid=1 adainv: invert=10, fields adainv: HO
The elementary field HO in file 10 of database 1 is inverted.
adainv: dbid=1 adainv: invert=10 adainv: lwp=600k adainv: fields adainv: ph=phon(na) adainv: sp=na(1,3),yy(1,2),uq adainv: bb,uq
Three new descriptors are established for file 10 in database 1. PH is a phonetic descriptor based on the field NA. SP is a unique superdescriptor derived from bytes 1 to 3 of field NA and bytes 1 to 2 of field YY. The elementary field BB is changed to descriptor status and the unique flag is set. The size of the work pool to be used for the sort is increased to 600 K.
adainv: dbid=1 adainv: release=10 adainv: fields adainv: ho adainv: ph
The two descriptors HO and PH from the examples above are released.
adainv: dbid = 1, verify = 10 adainv: errors = 5 adainv: fields adainv: sp adainv: na adainv: end_of_fields
The descriptors SP and NA are verified. The descriptor value table entries generated for descriptor NA are checked against the decompressed values of this field. Verification is terminated if more than five errors are reported for each descriptor.
adainv: dbid = 1, reinvert = 10 adainv: fields adainv: na
The descriptor NA in file 10 of database 1 is to be reinverted (this may be necessary if errors are reported in example 4).
adainv: db=12 adainv: reinvert=9 adainv: all_fields
The complete index is recreated for file 9 in database 12.
The following output is produced:
%ADAINV-I-FILE, file 9, EMPLOYEES %ADAINV-I-UIUPD, upper index being modified %ADAINV-I-SORTDESC, sorting descriptor KA %ADAINV-I-LOADDESC, loading descriptor KA %ADAINV-I-SORTDESC, sorting descriptor S3 %ADAINV-I-LOADDESC, loading descriptor S3 %ADAINV-I-SORTDESC, sorting descriptor S2 %ADAINV-I-LOADDESC, loading descriptor S2 %ADAINV-I-SORTDESC, sorting descriptor PA %ADAINV-I-LOADDESC, loading descriptor PA %ADAINV-I-SORTDESC, sorting descriptor FB %ADAINV-I-LOADDESC, loading descriptor FB %ADAINV-I-SORTDESC, sorting descriptor AA %ADAINV-I-LOADDESC, loading descriptor AA %ADAINV-I-SORTDESC, sorting descriptor BC %ADAINV-I-LOADDESC, loading descriptor BC %ADAINV-I-SORTDESC, sorting descriptor CN %ADAINV-I-LOADDESC, loading descriptor CN %ADAINV-I-SORTDESC, sorting descriptor JA %ADAINV-I-LOADDESC, loading descriptor JA %ADAINV-I-SORTDESC, sorting descriptor H1 %ADAINV-I-LOADDESC, loading descriptor H1 %ADAINV-I-SORTDESC, sorting descriptor EA %ADAINV-I-LOADDESC, loading descriptor EA %ADAINV-I-SORTDESC, sorting descriptor LC %ADAINV-I-LOADDESC, loading descriptor LC %ADAINV-I-SORTDESC, sorting descriptor S1 %ADAINV-I-LOADDESC, loading descriptor S1 %ADAINV-I-SORTDESC, sorting descriptor AC %ADAINV-I-LOADDESC, loading descriptor AC %ADAINV-I-NULLDESC, no values for descriptor IJ %ADAINV-I-LOADDESC, loading descriptor IJ %ADAINV-I-NULLDESC, no values for descriptor IB %ADAINV-I-LOADDESC, loading descriptor IB %ADAINV-I-NULLDESC, no values for descriptor FI %ADAINV-I-LOADDESC, loading descriptor FI %ADAINV-I-UIUPD, upper index being modified %ADAINV-I-DSPASSES, data storage passes : 17 %ADAINV-I-REMOVED, dataset SORT1, file C:\Program Files\Software AG\Adabas/db012 \SORT01_3664.012 removed %ADAINV-I-IOCNT, 1 IOs on dataset SORT %ADAINV-I-IOCNT, 85 IOs on dataset DATA %ADAINV-I-IOCNT, 49 IOs on dataset ASSO
Notes:
adainv: dbid = 1, set_uq=10 adainv: fields adainv: na adainv: end_of_fields adainv: uq_conflict=reset
The unique status is to be established for the descriptor NA in file 10 of database 1. If there is more than one ISN per descriptor value, the conflicting ISNs are written to the error log and the unique status is removed.
adainv: dbid = 1, reset_uq=10 adainv: fields adainv: sp
The unique status is to be removed from the descriptor SP in file 10 of database 1.
adainv: db=33 adainv: summary=112 adainv: fields adainv: ab adainv: ae adainv: s1=ap(1,1),aq(1,1),ar(1,1) adainv: s2=ac(1,3),ad(1,8),ae(1,9) adainv: s3=ao(2,3)
This produces the following output:
Descriptor summary:
===================
Descriptor AB : 1,194,469 bytes, 581,209 occ
Descriptor AE : 3,605,545 bytes, 538,769 occ
Descriptor S1 : 1,566,501 bytes, 581,209 occ
Descriptor S2 : 1,520,169 bytes, 72,389 occ
Descriptor S3 : 1,340,949 bytes, 446,983 occ
Required sizes to process these descriptors:
============================================
- SORTSIZE (LWP= 0 KB) = 8 MB
- LWP for incore sort = 13,230 KB
- TEMPSIZE (1 pass) = 24 MB
- TEMPSIZE (2 passes) = 13 MB
- TEMPSIZE (recommended minimum size) = 5 MB
%ADAINV-I-IOCNT, 1710 IOs on dataset DATA
%ADAINV-I-IOCNT, 3 IOs on dataset ASSO
%ADAINV-I-TERMINATED, 24-NOV-2006 14:15:06, elapsed time: 00:04:03