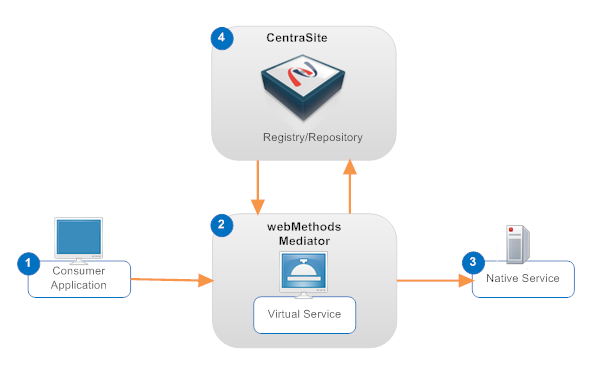

# | Description |
1 | Consumer applications submit requests for operations that are provided by Web services that reside on various systems in the network. As shown in the figure above, a consumer application submits its request to a virtual service on the webMethods Mediator and not directly to the Web service itself. |
2 | webMethods Mediator hosts virtual services, which are proxy services that receive requests from consumer applications on behalf of a particular Web service. A virtual service enforces standard policies that you define for your environment (such as security enforcement and audit-trail logging) and handles mediation measures between consumer and provider such as protocol bridging, message transformation and message routing. Besides serving as an intermediary between consumer applications and native services, the Mediator also collects performance statistics and event information about the traffic flowing between consumer applications and the native services and reports this data to CentraSite. |
3 | Native services are Web services that process requests submitted by consumer applications. If a native service produces a response, it returns the response to the virtual service and the virtual service returns it to the consumer application. |
4 | CentraSite serves several key roles in the run-time environment. Besides serving as the system of record for virtual services, run-time policies and related artifacts in the SOA environment, CentraSite provides the tools you use to define virtual services and deploy them to webMethods Mediator. Additionally, CentraSite receives and logs the performance metrics and event data collected by webMethods Mediator and provides tools for viewing this data. |