The EntireX WebSphere MQ RPC Server allows standard RPC clients to send and receive asynchronous and synchronous messages to a WebSphere MQ queue manager. The EntireX WebSphere MQ Listener receives asynchronous and synchronous messages from a WebSphere MQ queue and calls a standard RPC server.
The WebSphere MQ Listener uses the WebSphere MQ base Java classes from IBM.
The WebSphere MQ Listener can connect to a WebSphere MQ either as a WebSphere MQ client using TCP/IP (client mode) or in so-called bindings mode where it is connected directly to WebSphere MQ running on the same machine. Note that on z/OS, only bindings mode is supported; and on IBM System z, only client mode is supported. If the WebSphere MQ Listener wants to connect in client mode via TCP/IP to an MQ server on z/OS, the client attachment feature needs to be installed on the target queue manager.
The WebSphere MQ RPC Server runs as an RPC server and processes RPC
client calls. An RPC client can send an asynchronous message (MQ PUT call) if
it uses a program with IN parameters. An RPC client can receive an asynchronous
message if it uses a program with OUT parameters (MQ GET call). The receiver
must use the same parameters in a program as the sender, but with the direction
OUT instead of IN. Processing of synchronous messages (request/reply scenario)
is possible if the program uses a mixture of IN and OUT parameters. The images
below illustrate message transport when sending and receiving messages. If the
RPC client application uses conversational RPC, the MQ calls are issued
transactionally (using the SYNCPOINT option), a Backout Conversation will send
a backout to the queue manager, and a Commit Conversation will send a commit to
the queue manager.
The WebSphere MQ RPC Server registers to one RPC service. On the MQ side it uses one input queue and one output queue.
The WebSphere MQ Listener runs as a listener on an MQ queue and
processes MQ messages. An RPC client can send an asynchronous message (MQ PUT
call) if it uses a program with IN parameters. An RPC client can receive an
asynchronous message if it uses a program with OUT parameters (MQ GET call).
The receiver must use the same parameters in a program as the sender, but with
the direction OUT instead of IN. Processing of synchronous messages
(request/reply scenario) is possible if the program uses a mixture of IN and
OUT parameters. The images below illustrate message transport when sending and
receiving messages.
The WebSphere MQ Listener sends messages to one RPC service. On the MQ side it uses one listen queue.
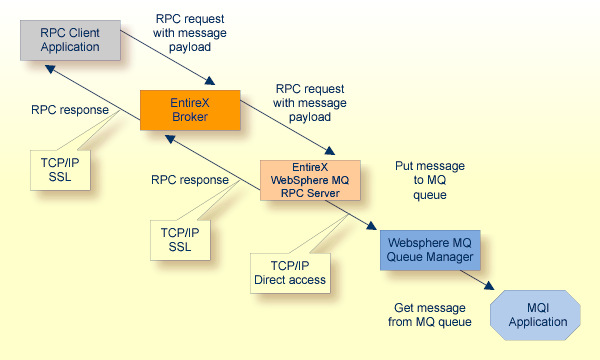
Note:
All messages sent to a WebSphere MQ RPC Server instance via a specific RPC service
are put on the same MQ output queue.
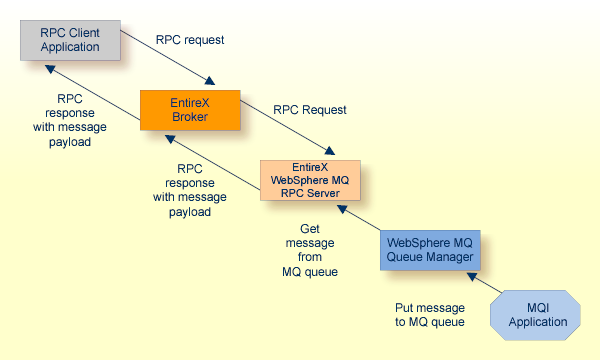
Note:
All messages retrieved by the WebSphere MQ RPC Server from the MQ input queue are
passed to the same RPC service. Messages are retrieved in the order they appear
on the queue.
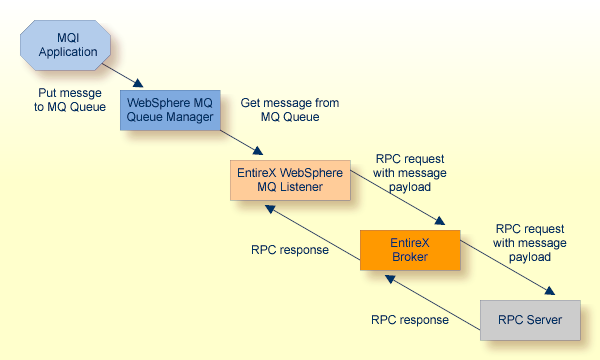
Note:
All messages retrieved by the WebSphere MQ Listener from the
MQ listen queue are passed to the same RPC service. Messages are retrieved in
the order they appear on the queue.