This document covers the following topics:
To generate the Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB) source code, use the EntireX Workbench. This can be done interactively with the UI of the EntireX Workbench. The generation is controlled by the following properties:
| Description | Data Type | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| Broker ID | String | Localhost:1971 |
| Server class | String | RPC |
| Service class | String | SRV1 |
| Service name | String | CALLNAT |
| Package name | String | IDL file name without extension |
| Package name prefix | String | empty string |
During the generation process for each library with the name <libname>, the following interfaces and classes source files are created in the subdirectory EJB of the home directory of the <name>.idl file.
The interfaces are created in the subdirectory:
<Package Name Prefix><Package Name><file.separator>interfaces.
They will be a component of the package: <Package Name Prefix><Package Name>.interfaces
| Naming Conventions | Description |
|---|---|
| EJB<libname>.java | The remote interface. |
| EJB<libname>Home.java | The home interface. |
The EJB classes will be created in the subdirectory:
<Package Name Prefix><Package Name><file.separator>ejb
They will be a component of the package: <Package Name Prefix><Package Name>.ejb
| Naming Conventions | Description |
|---|---|
| EJB<libname>Bean.java | The enterprise bean class. |
| <libname><innerclassname>.java | Serializable classes for Software AG IDL groups/structs. |
| <libname><progname>Input.java | Serializable holder class for all IN and IN/OUT parameters of the program. |
| <libname><progname>Output.java | Serializable holder class for all OUT and IN/OUT parameters of the program. |
| <libname>Mapper.java | Mapper class. |
To build the JAR files for the different application servers, we generate an Ant script which uses the XDoclet tool. This file will be generated in the EJB subdirectory:
<Package Name Prefix><Package Name>.xml
If the package prefix/name contains dots, subdirectories will be created, for example: abc.def.library will become abc/def/library/...
![]() To use the Wrapper for EJB functions
To use the Wrapper for EJB functions
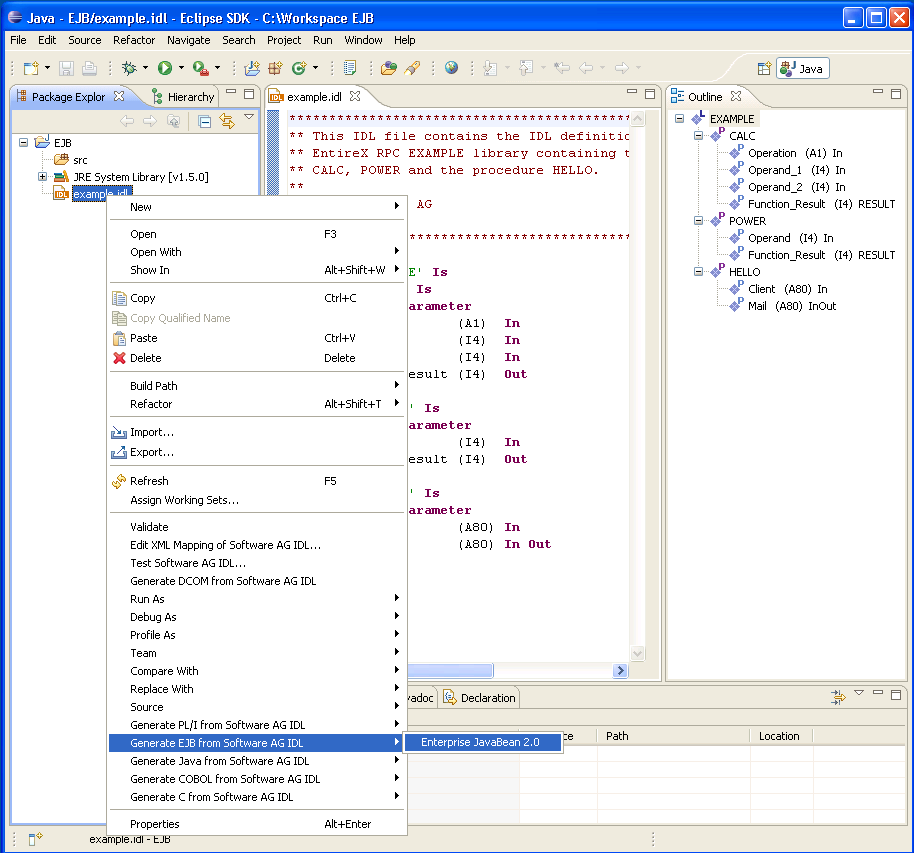
Open the EntireX Workbench.
Create a new Java Project (e.g.: "EJB"), using .
Add the EntireX classes to the build path of the project (entirex.jar).
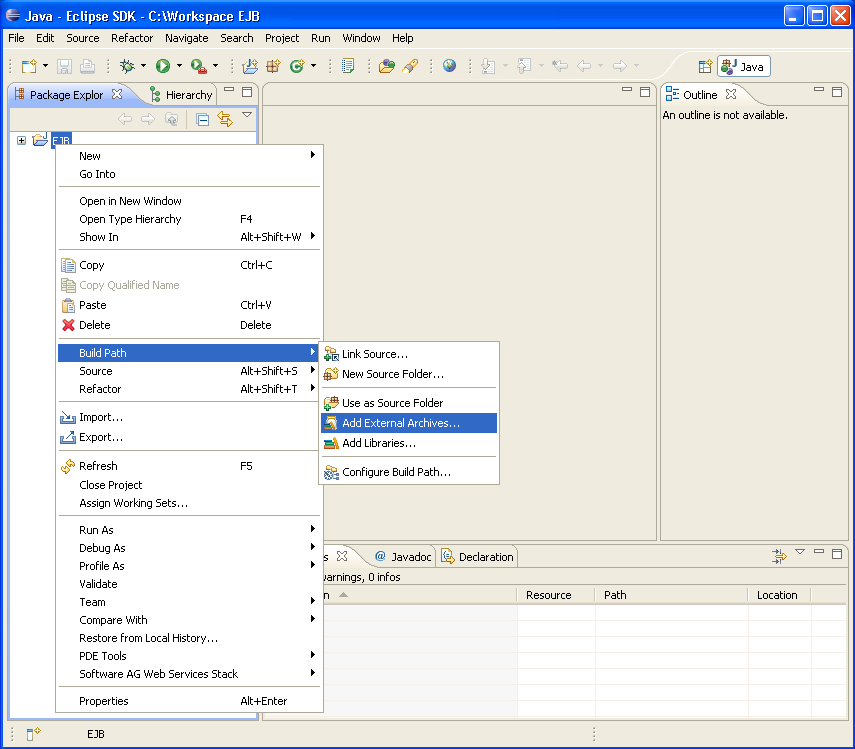
Add the Enterprise JavaBeans classes to the build path of the project (e.g.: j2ee.jar).
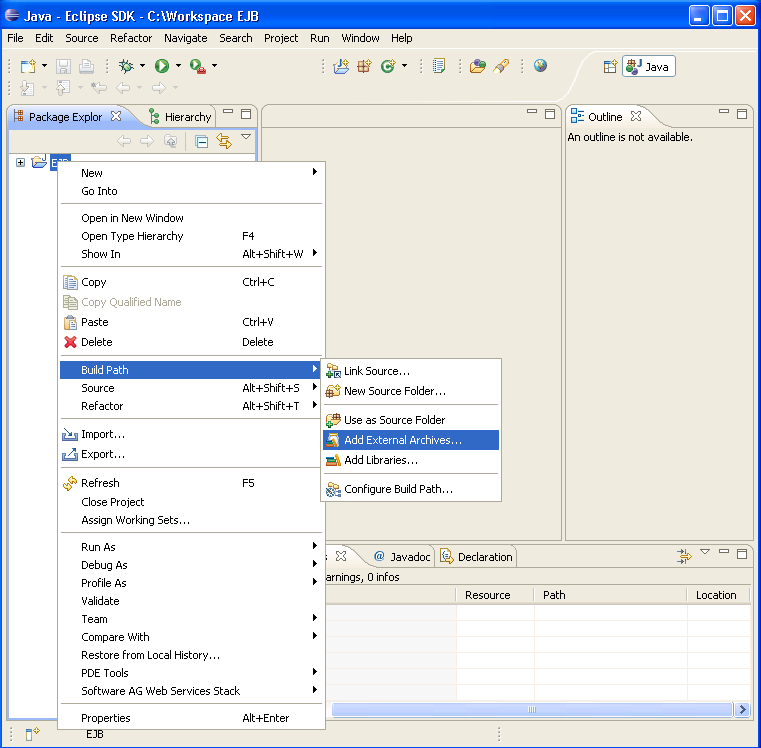
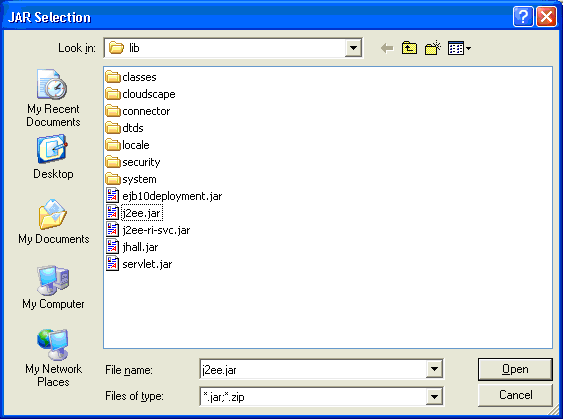
Import the IDL file into the project.
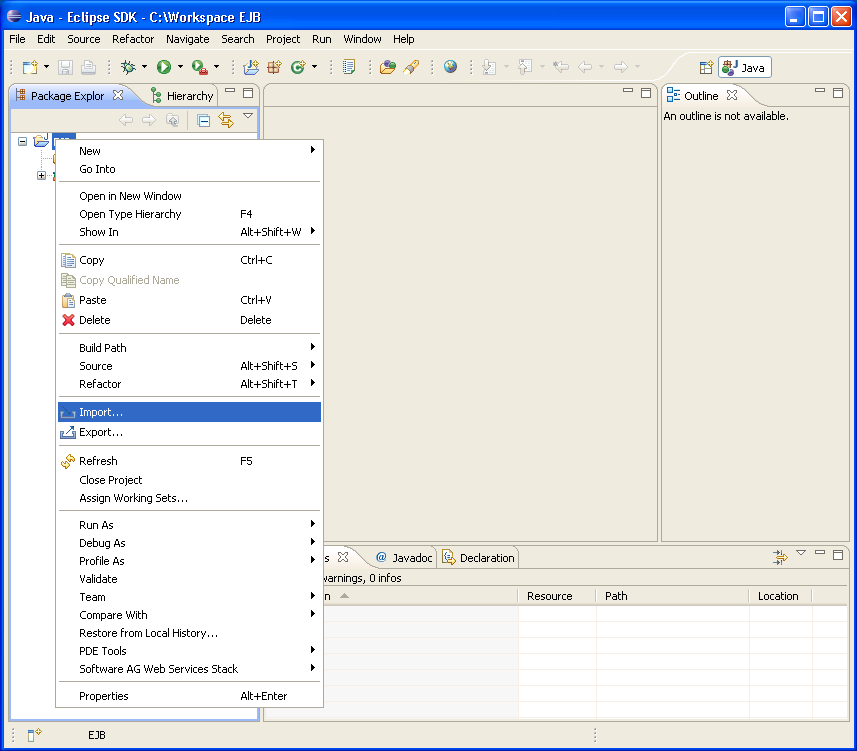
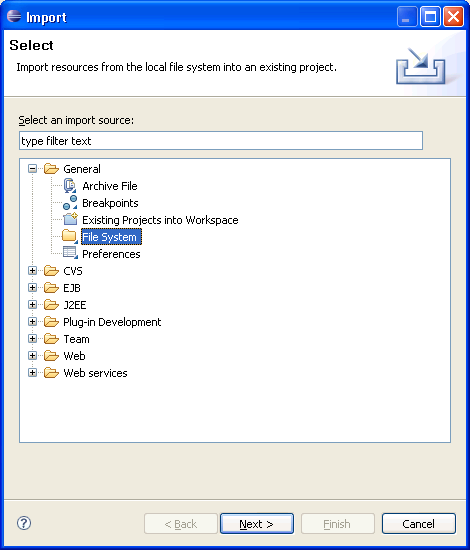
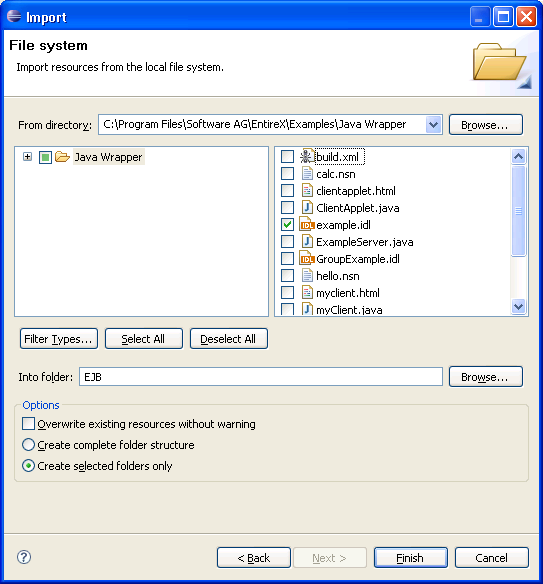
Activate the example.idl file.
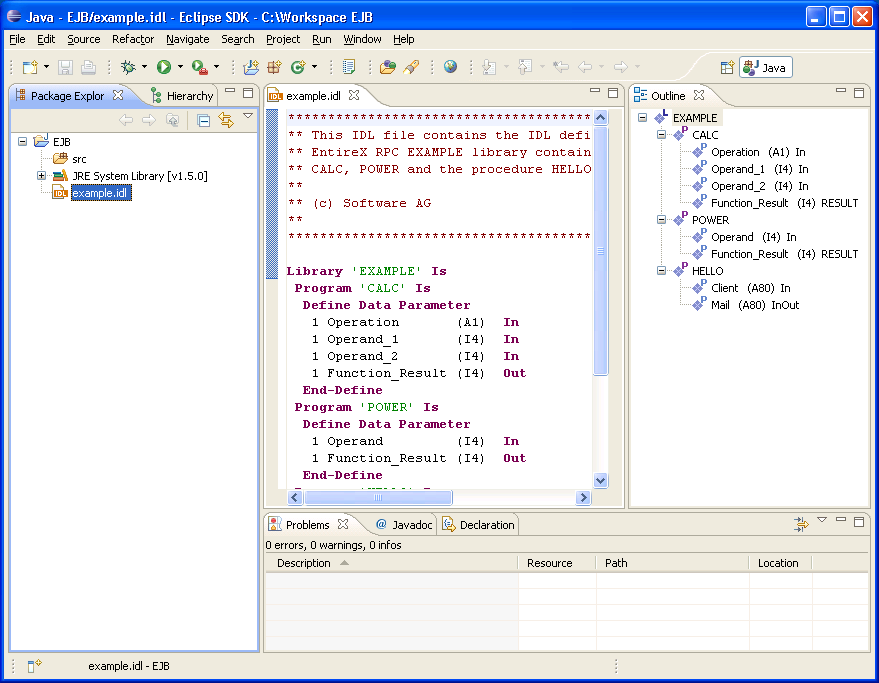
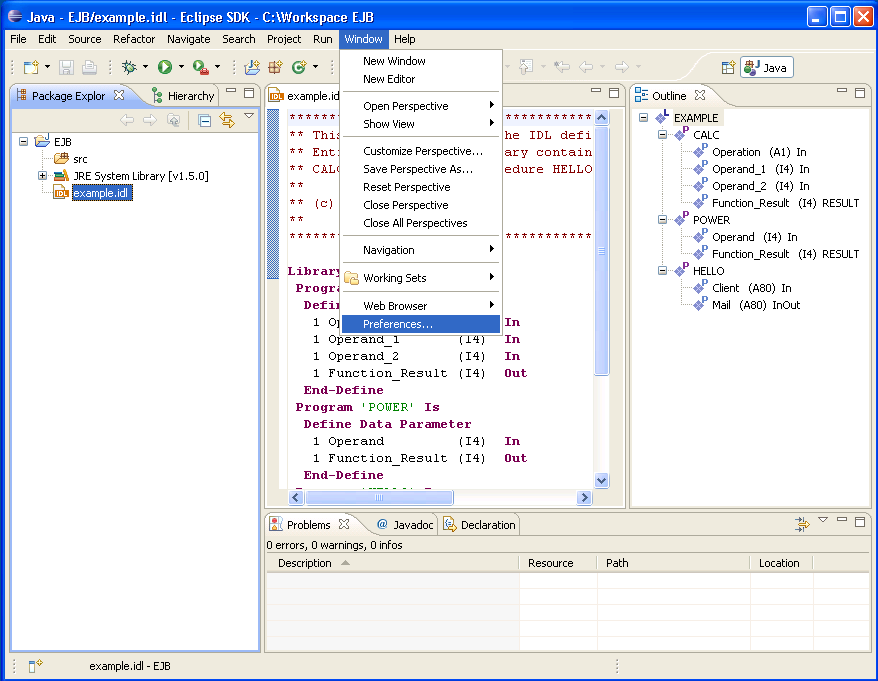
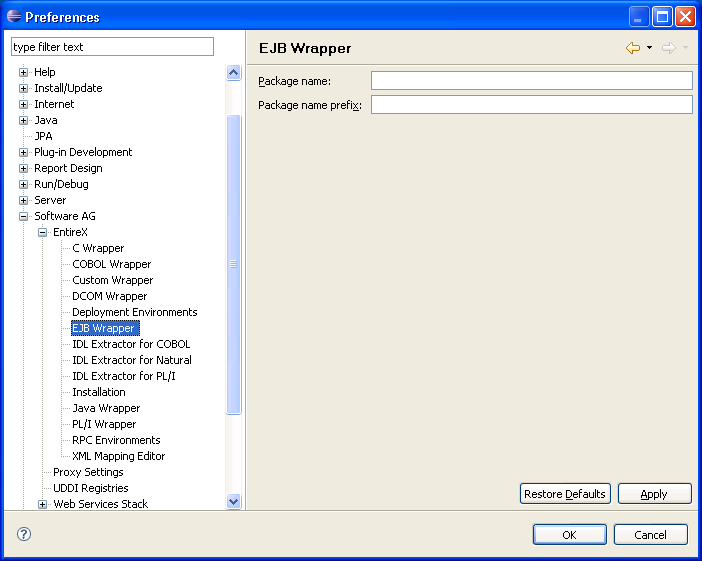
![]() To set/modify the preferences
To set/modify the preferences
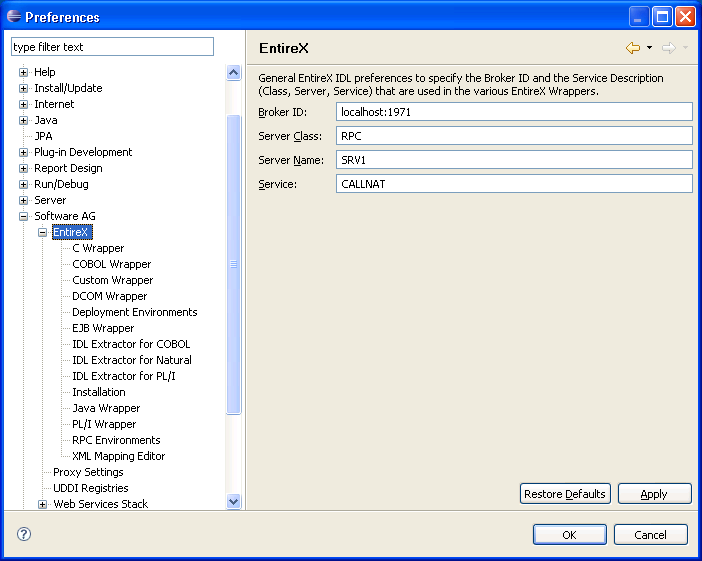
Display the Preferences window.
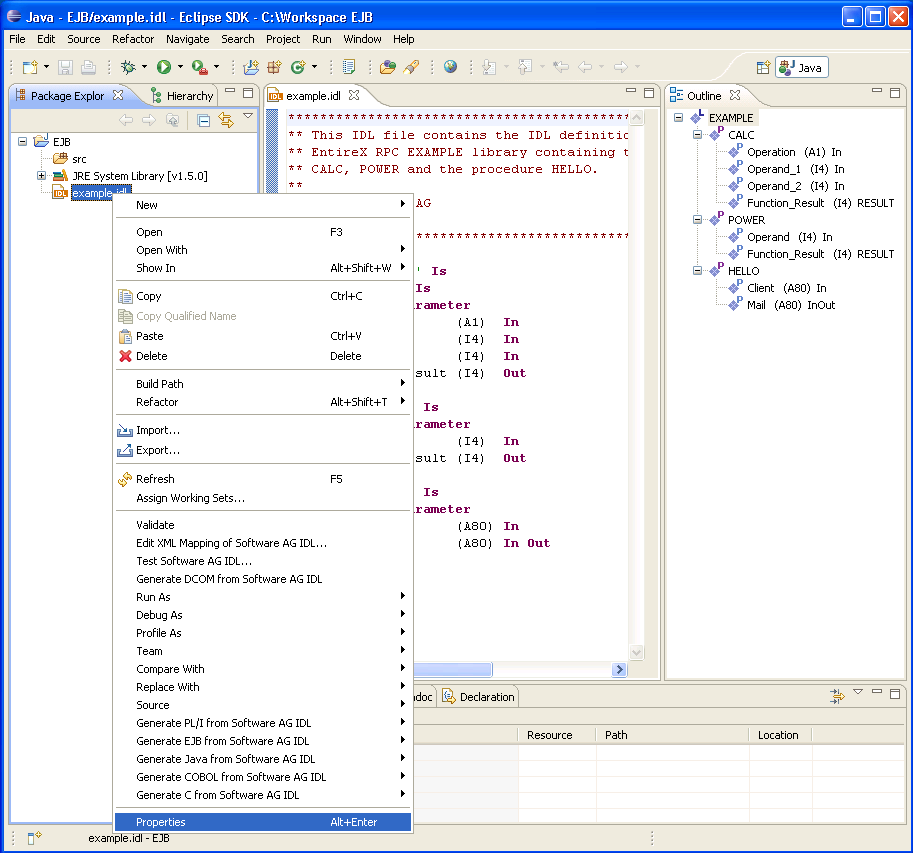
![]() To set/modify the properties
To set/modify the properties
Display the Properties window; use either the pop-up menu or, from the menu, choose .
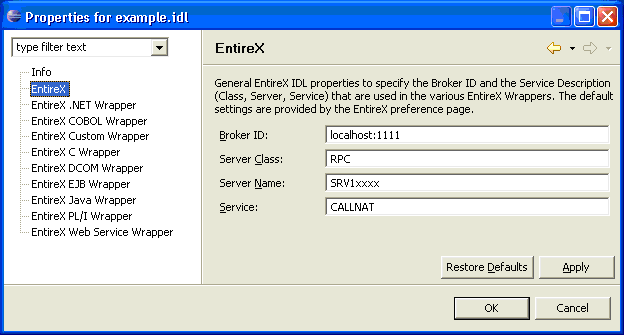
In the Properties window, choose the EntireX tab.
Here it is possible to modify the common default properties for the IDL file.
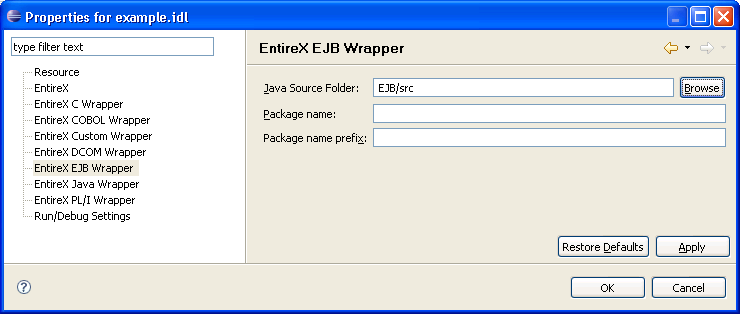
Choose the EntireX Wrapper for Enterprise JavaBeans tab.
Here it is possible to modify the defaults (see table Default Properties for the IDL File, below).
Confirm the entries with .
From the context menu, choose .
All generated EJB sources are in the subdirectory EJB of the home directory of the IDL file.
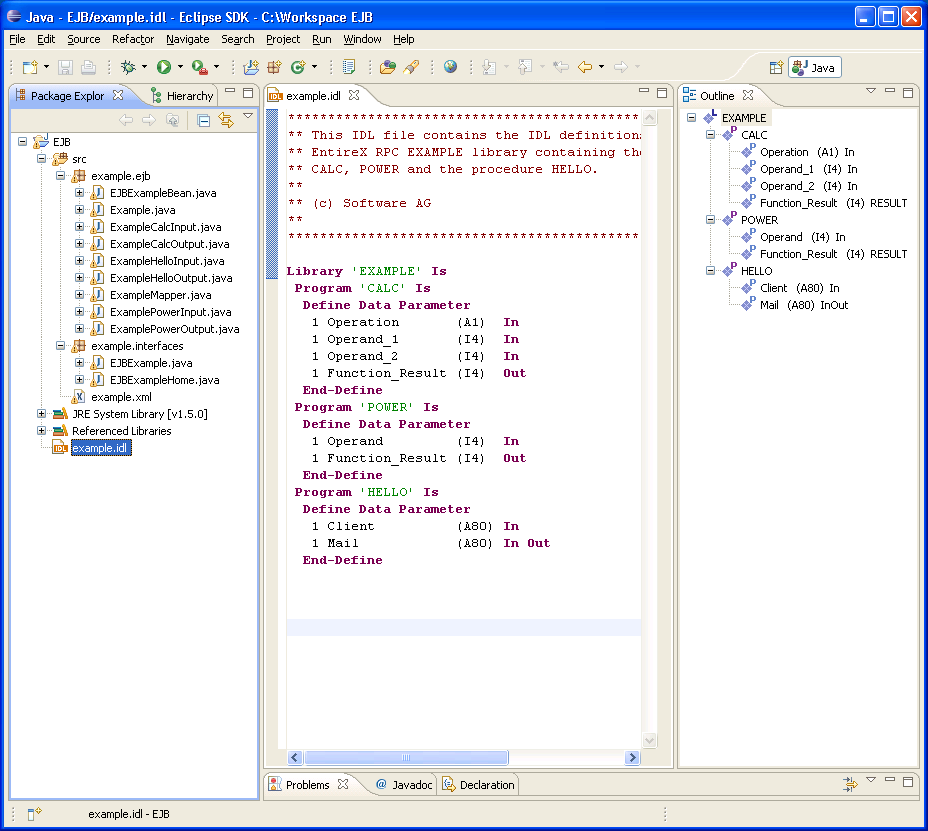
The workbench generates the following interfaces and classes from the Software AG IDL file sources.
The generated home interfaces EJB<libname>Home.java contain the create methods. These methods can be called by an EJB client.
EJB<libname> create()
Calling this method creates an EJB with the default settings.
EJB<libname> create(String user)
where: String user is the Broker user name
Calling this method creates an EJB with the default settings except for the user name.
EJB<libname> create(String user,String password)
where: String user is the Broker user name and String password the Broker user password
Calling this method creates an EJB with the default settings except for the user name and the password.
The generated remote interfaces EJB<libname>.java contain the customer methods. For each RPC program a customer method is generated with the following naming conventions.
<libname><program>Output <program> (<libname><program>Input input)
where: Output is the output object and Input is the input object
These methods can be called by an EJB client.
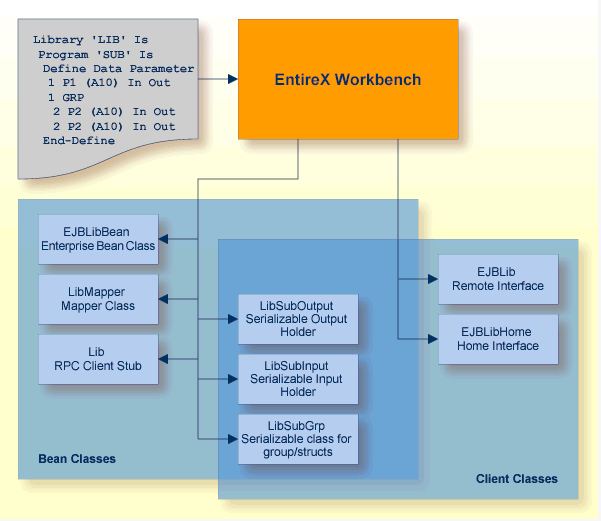
The generated EJB class EJB<libname>Bean.java extends <libname>Mapper.java class. Bean implements the EJB session bean and controls the EntireX RPC communication.
The generated <libname>Mapper.java class extends the Java RPC client stub <libname>.java. It implements a method for each RPC Program. Methodname is <program>. The method has one parameter, an instance of <libname><progname>Input.class.The return value of the method is an instance of <libname><progname>Output.class.
The group classes are serializable representations of the inner classes of the groups of the RPC library, filename is <libname><progname><innerclassname>.java. The class contains all parameters of the group.
The struct classes are serializable representations of the inner classes of the structs of RPC library, filename is <libname><innerclassname>.java. The class contains all parameters of the struct.
These classes are serializable representations of all in, out, in/out parameters of RPC program. The filename of the input classes is <libname><progname>Input.java, it holds all in and in/out parameters of the program.The filename of the output classes is <libname><progname>Output.java, it holds all out and in/out parameters of the program.
The generated Java RPC Stub <libname>.java extends com.softwareag.entirex.aci.RPCService class. It is the connecting link between the EJB and the EntireX server.
This section describes how to prepare the JBoss Application Server so it can access the EntireX Java Runtime and to deploy a packed Enterprise Java bean.
To load, install, and verify JBoss, see http://www.jboss.org. After installing and verifying the application server, copy file entirex.jar to <JBOSS HOME>/server/default/lib to access the EntireX Runtime.
After the bean archive has been created, copy it to <JBOSS HOME>/server/default/deploy.
An example is delivered in directory
<drive>:\SoftwareAG\EntireX\examples\EJBWrapper (Windows) or
/opt/softwareag/EntireX\examples\EJBWrapper (UNIX).
See the README.TXT.