The Broker HTTP(S) Agent is a Java-based component that implements a Java servlet for servlet-enabled Web servers. It builds the bridge between a Web server and EntireX Broker in the intranet. This component was formerly referred to as "Tunnel Servlet".
This document covers the following topics:
When communicating with EntireX Broker over the internet, direct access to the EntireX Broker's TCP/IP port is necessary. This access is often restricted by proxy servers or firewalls. With EntireX, Java-based communication components can pass communication data via HTTP or HTTPS. This means a running EntireX Broker in the intranet is made accessible by a Web server without having the need to open additional TCP/IP ports on your firewall (HTTP tunneling). HTTP or HTTPS tunneling can also be used for Java RPC.
The EntireX Java ACI is able to send and receive data via an HTTP
protocol controlled by constructor
com.softwareag.entirex.aci.Broker. See How to Enable HTTP Support in a Java Component under Writing Advanced Applications - EntireX Java ACI.
The EntireX Java component
com.softwareag.entirex.aci.TunnelServlet.class implements a Java
servlet for servlet-enabled Web servers. It builds the bridge between Web
server and EntireX Broker in the intranet.
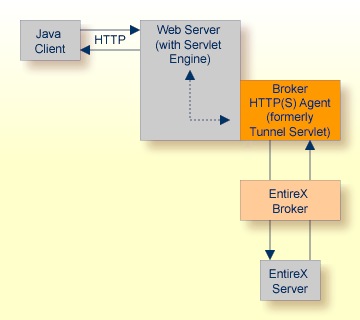
The figure above shows how the communication works. In this scenario, a Java client program communicates via HTTP and EntireX Broker with an EntireX server. By using a Broker ID starting with http:// (passing the URL of the installed HTTP(S) Agent) each Broker request is sent to a Web server, which immediately processes the HTTP(S) Agent, passes the contents to EntireX Broker, receives the response and sends it back via HTTP. For the two partners (client and server) it is transparent that they are communicating through the Web. Java server programs can also communicate via HTTP if necessary.
To use the HTTP(S) Agent you need a servlet-enabled Web server. See Prerequisites for EntireX RPC under UNIX | Windows.
| Parameter | Description | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| broker | The broker you want to address (syntax: as Broker ID in Java). | ||||
| log |
|
In the following, "tunnel" is used as the agent name.
![]() To adapt the HTTP(S) Agent
To adapt the HTTP(S) Agent
The following steps describe the deployment with the Web
archive entirex.jar in detail. You can test the
HTTP(S) Agent with
http://<host>:<port>/entirex/tunnel,
where entirex is the name of the Web application.
Create the new subfolders in the Web application directory of your Web server, e.g. tunnel, tunnel/WEB-INF, tunnel/WEB-INF/lib.
Copy the entirex.jar into tunnel/WEB-INF/lib.
Create a file named web.xml in the folder tunnel/WEB-INF with the following content:
<web-app>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>tunnel</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.softwareag.entirex.aci.TunnelServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>broker</param-name>
<param-value>yourbroker</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>log</param-name>
<param-value>yes</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>tunnel</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
Restart your Web server and test the installation by calling the HTTP(S) Agent in your Web browser. The URL is: http://<yourhost>/tunnel. If the agent is installed properly, an information page is displayed.
Run the Java ACI client/server example or the Java RPC example delivered with EntireX and use the agent's URL for client or server or both.
Internationalization is transparent for the HTTP(S) Agent. The client sending the EntireX ACI request with HTTP over the Web server through the HTTP(S) Agent fully controls Internationalization. No configuration is necessary for the HTTP(S) Agent.
![]() To switch on tracing for the HTTP(S) Agent
To switch on tracing for the HTTP(S) Agent
Set the system property entirex.trace to
one of the values 1, 2, or 3. See Tracing under Writing Advanced Applications - EntireX Java ACI.
![]() To switch on logging
To switch on logging
Set the configuration parameter log=yes.
This logs the parameters from the HTTP header, the HTTP messages and error messages to the logging facility of the Web server.