This document covers the following topics:
Task 1: Generate Integration Server Connections and Listeners
Task 2: Generate Client Interface Objects and Build Client Application
This scenario uses the EntireX Workbench tools IDL Extractor for Integration Server and COBOL Wrapper of the Software AG Designer.
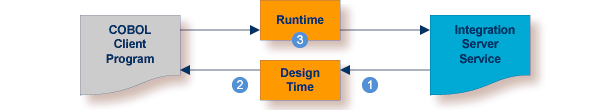
| Use IDL Extractor for Integration Server to generate Integration Server connections and listeners from the Integration Server service to be called. | |
| Generate client interface objects and build COBOL client application. | |
| Execute the call from the COBOL client to the Integration Server service. |
This scenario makes the following important assumptions:
For Task 1:
You have an Integration Server with the EntireX Adapter installed.
For Task 3:
You have an Integration Server with the EntireX Adapter installed.
You can call the Integration Server service at runtime using different methods:
This section describes your first steps to create a new Integration Server connection. This process creates the following:
a Software AG IDL file (metafile) in the EntireX Workbench; an IDL file contains definitions of the interfaces between client and server. See Software AG IDL File in the IDL Editor documentation and Software AG IDL to Integration Server Mapping in the Integration Server Wrapper documentation
a server connection
one of the following in Integration Server, depending on connection type specified in Step 4: Select the Connection Type below:
an RPC Listener
a Reliable RPC Listener
a Direct RPC Listener
The following steps are described in more detail under IDL Extractor for Integration Server.
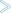 To start the IDL Extractor for Integration Server
To start the IDL Extractor for Integration Server
The IDL Extractor is a New Wizard in Eclipse. Choose New from the file menu, select IDL Extractor for webMethods IS in the following page and choose Next.
Note:
You can also choose New from the toolbar or
context menu of a view showing resources. Also Ctrl-N starts the
selection of the New Wizards.
If you are using the wizard for the first time without any predefined Integration Server connections, continue with Step 2: Connect EntireX Workbench with Integration Server below.
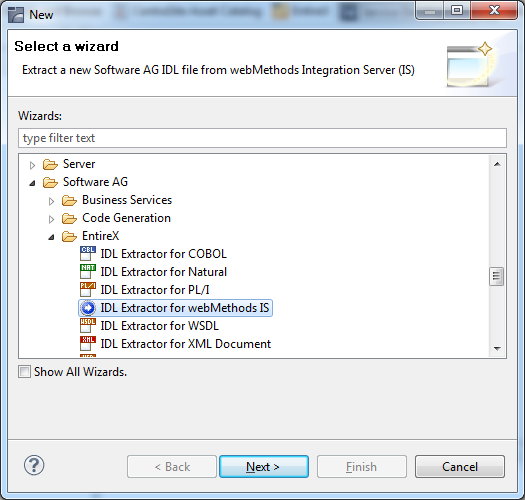
 To create a new Integration Server connection
To create a new Integration Server connection
Define the new Integration Server connection on the
following wizard page. The only required field is Server.
 More info
More info
Choose and continue with Step 3: Select the Integration Server Package to Extract.
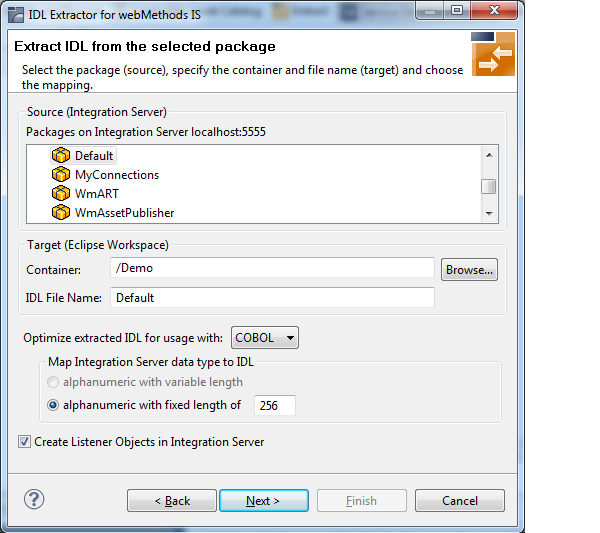
 To extract the IDL from the selected package
To extract the IDL from the selected package
Select the package to extract (from the list indicated by Source), for example the package "Default" in the screen above.
Specify the target. By default, the wizard tries to find a valid container based on your position in the Navigator or Package Explorer View.
Or:
Choose to select a container from
your workspace.
Notes:
Optimize the extracted IDL. Use the combo-box and select the target programming language:
COBOL
For usage with the COBOL Wrapper. Enter the default length for IDL type A(default-length) fields which map then to COBOL alphanumeric data items PIC X(default-length).
For this scenario, make sure Create Listener Objects in Integration Server is checked.
Choose to store the IDL file in the selected container in the Eclipse workspace. When you go to the next page, the button is disabled, because the IDL file has already been created and this step cannot be reverted.
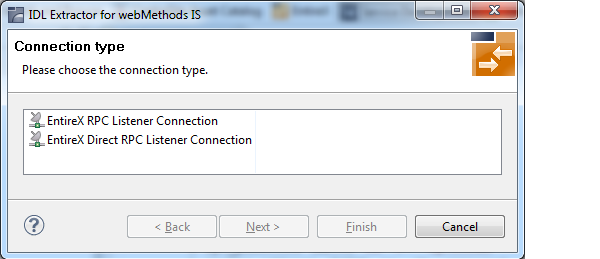
 To select the connection type
To select the connection type
As a prerequisite, the IDL file has been stored in the workspace and the button is now disabled.
Select a Connection type and click .
Notes:
IN parameters.
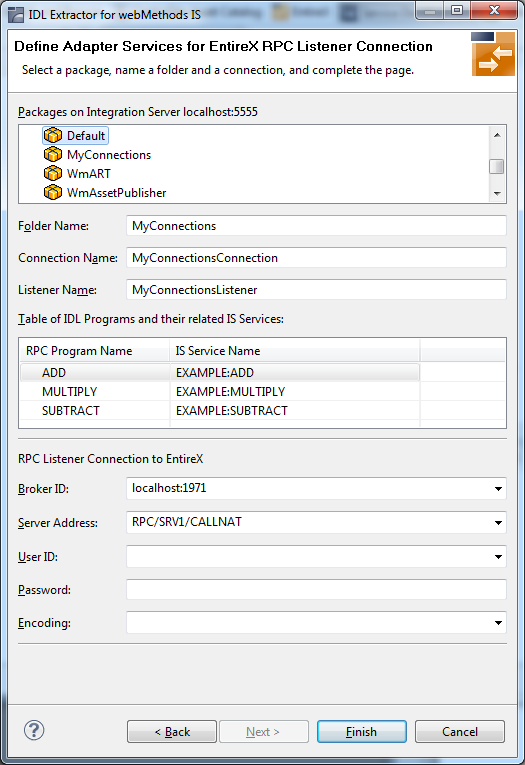
 To define a listener
To define a listener
Select an Integration Server package where the listener will be stored.
Specify the names for Folder Name (default:
library name), Connection
Name (default: library
nameConnection) and Listener Name
(default: library nameListener).
Advanced users: You can alter the Integration Server services in the table headed by the RPC Program Name and IS Service Name. Note that a selected service must exist in some package of the Integration Server! This step is not recommended. Only perform it if required.
If necessary, edit the Broker settings for the Listener (Broker ID, Server Address, User ID, Password, and Encoding).
The check box Overwrite existing Objects in Integration Server can be used to re-generate the objects after you have changed the IDL file.
Notes:
WmEntireX) with the version currently used.
Choose .
As a result, the following objects will be created:
one connection of type EntireX RPC Listener, EntireX Reliable RPC Listener or EntireX Direct RPC Listener
one listener object
For a connection of type EntireX Reliable RPC Listener the following objects will be created in addition for each IDL program:
one notification object
one trigger object
one document type object
This section covers the following topics:
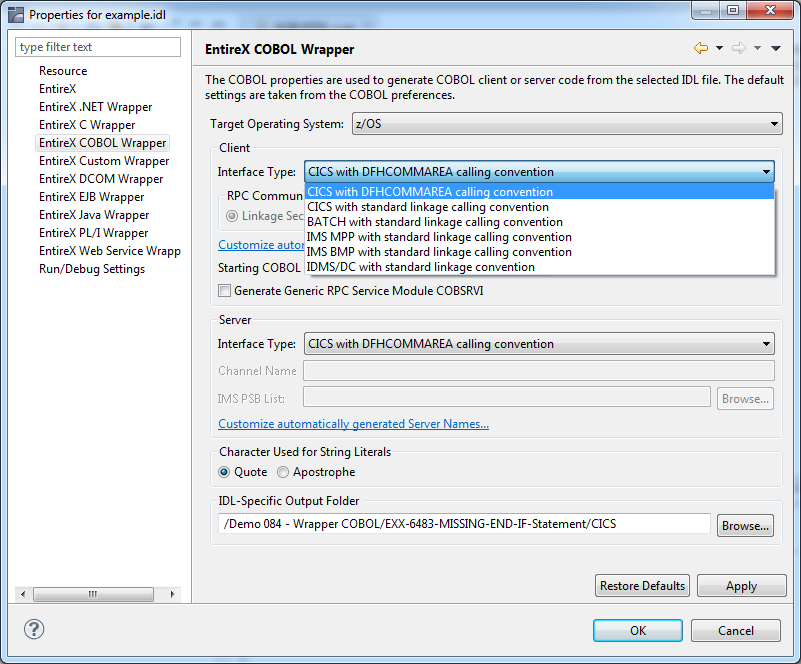
From the context menu on the IDL file extracted as described under Task 1: Generate Integration Server Connections and Listeners above, choose Properties > EntireX COBOL Wrapper and set the following properties:
Set the Target Operating System to "z/OS".
Set the Client Interface Type to "IDMS/DC with standard linkage calling convention"
The COBOL Wrapper can be used with a call interface in IDMS/DC. This means you can build an application where the COBOL client program, every generated client interface object, the generic RPC services module and the broker stub are linked together, similar to the batch scenario. See Using the COBOL Wrapper for Batch (z/OS, BS2000, z/VSE and IBM i).
For more information see Target Operating System and Client Interface Types under Generating COBOL Source Files from Software AG IDL Files in the COBOL Wrapper documentation.
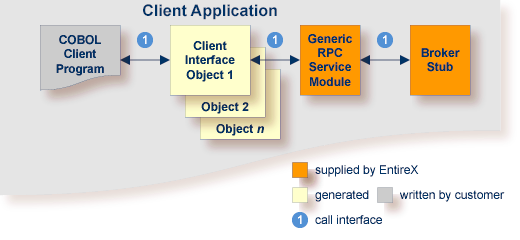
The following steps are described in more detail under Using the COBOL Wrapper for IDMS/DC with Call Interfaces (z/OS):
 To use the COBOL Wrapper for IDMS/DC
To use the COBOL Wrapper for IDMS/DC
Generate the client interface object(s) for the target operating
system "z/OS", and use the interface type
"IDMS/DC with standard calling convention".
See Generating COBOL Source Files from Software AG IDL Files.
Check the option Generate the generic RPC service module COBSRVI.
 More info
More info
If necessary, use FTP to transfer the client interface object(s)to the target platform where you write your client application.
You may need to adapt the broker stub that supports the required transport (TCP, NET). See Adapting the Used Broker Stub.
Write your COBOL client program. See Writing Applications with the COBOL Wrapper, in particular the section Using the RPC Communication Area with a Standard Call Interface, and take into consideration the information given in Software AG IDL to COBOL Mapping.
Using the IDMS/DC translator for COBOL provided with your IDMS/DC installation and a COBOL compiler supported by the COBOL Wrapper, translate and compile:
the generated client interface object(s)
your COBOL client program
Take care the generated copybooks (see Using the Generated Copybooks) are accessed correctly by the compiler and not confused with the client interface objects, because the copybooks and client interface objects have identical file names. See your compiler documentation.
Using the standard linker (binder) of the target platform, link (bind) all translated and compiled modules, and, if required, the broker stub, together to a IDMS/DC program, using the standard linker (binder) of the target platform.
Install the IDMS/DC program within IDMS/DC.
Make sure the correct broker stub is used and can be called dynamically by the generic RPC service module COBSRVI.
See the broker installation documentation and use a broker stub for IDMS/DC (for example IDMSETB) from the common load library EXX912.LOAD. See also Administering Broker Stubs.
After building your client application in Task 2 above, you can test your scenario.