The EntireX RPC-ACI Bridge allows standard RPC clients to communicate with an ACI server. The RPC-ACI Bridge transforms RPC requests from clients into ACI messages. This document covers the following topics:
The RPC-ACI Bridge
acts on one side as an RPC server and on the other side as an ACI client. In
this documentation we distinguish between the Broker for RPC, which sends the
RPCs from the client to the server side of the RPC-ACI Bridge
and the Broker for ACI, which sends the messages to the ACI server. These two
brokers can be the same instance. Use distinct CLASS/SERVER/SERVICE broker attributes for the RPC requests and ACI messages.
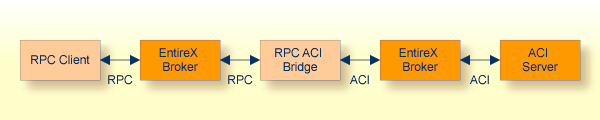
The RPC-ACI Bridge can connect to ACI servers written in programming languages where the ACI is supported, such as Natural | Assembler | C | COBOL | Java | PL/I. More detailed information is given on writing ACI servers for the RPC-ACI Bridge in COBOL and Natural.
For existing server programs, use an extractor to generate the Software AG IDL File for the RPC clients.
For COBOL, use the IDL Extractor for COBOL
For PL/I, use the IDL Extractor for PL/I
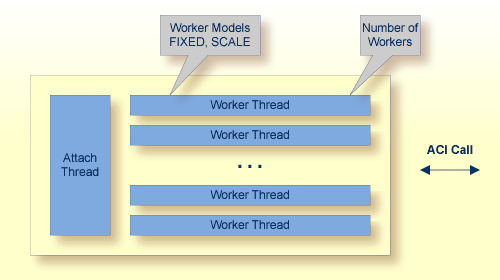
RPC requests are worked off inside the RPC server in worker threads.
Every RPC request occupies during its processing a worker thread.
If you are using RPC conversations, each RPC conversation requires its own thread during the lifetime of the conversation.
The RPC-ACI Bridge can adjust the number of worker threads to the number of parallel requests.
Use the properties entirex.server.fixedservers,
entirex.server.maxservers and
entirex.server.minservers
to configure this scalability. The RPC-ACI Bridge provides two worker models:
The fixed model creates a fixed number of worker threads. If entirex.server.fixedservers=yes, the number of worker threads is specified in
entirex.server.minservers is started and the server can process this number of parallel requests.
SCALE
The scale model creates worker threads depending on the incoming load of RPC requests.
If entirex.server.fixedservers=no, the number of worker threads balances between what is specified in entirex.server.minservers
and what is specified in entirex.server.maxservers. This is done by a so-called attach thread.
At startup, the number of worker threads is the number specified in entirex.server.minservers.
A new worker thread starts if the broker has more requests than there are worker threads waiting.
If more than the number specified in entirex.server.minservers are waiting for requests, a worker thread stops if its receive call times out.
The timeout period is configured with entirex.server.waitserver.