This document covers the following topics:
A synchronous request/reply call to MQ is possible. In this case, the
remote procedure call has to have both INPUT and OUTPUT parameters, or an INOUT
parameter has to be specified. The RPC Server for IBM MQ issues an MQ PUT call
with message type "Request" on the default output
queue. The Reply To Queue Name field is set to the name
of the default input queue. After the PUT call, the RPC Server for IBM MQ issues
an MQ GET on the default input queue and then it waits for the reply message
(note that for this scenario the input queue must be different from the output
queue).
The request and reply messages are correlated by the correlation ID. The reply message has to have the same correlation ID as the request message.
For Request Reply scenarios there is an implicit usage of the
correlation ID by the RPC Server for IBM MQ: MQ is
instructed to generate a correlation ID. The option
MQPMO_NEW_CORREL_ID is set internally to achieve this.
When reading the reply the option MQMO_MATCH_CORREL_ID
is specified, thus the reply message has to use the same correlation as
specified in the request message.
When the RPC Server for IBM MQ is exchanging messages via the EntireX Broker with an RPC client, the usual rules apply. By default, the message is exchanged between the RPC Server for IBM MQ and EntireX using the platform encoding of the JVM that executes the RPC Server for IBM MQ.
If the payload of the MQ message is in XML format
(property entirex.bridge.xmm has been set), the
RPC Server for IBM MQ converts the XML payload to the encoding used for the
remote procedure call. If the RPC Server for IBM MQ has to create the XML
payload, it will use UTF-8. A different encoding can be used by setting the property
entirex.bridge.xml.encoding.
If the payload of the MQ message is of type text, the translation of the MQ message payload is done by the IBM MQ Java classes. When sending a message, the RPC Server for IBM MQ converts the message to the encoding specified by the CCSID (Coded Character Set IDentification) of the queue manager. When receiving a message, the RPC Server for IBM MQ converts the message to the platform encoding of the JVM.
Note:
The default platform encoding of the JVM can be changed by setting the system property file.encoding in the startup script of the RPC Server for IBM MQ.
IBM® MQ does not have a clearly defined message layout, it is basically a stream of bytes. In general it is up to the MQ application to know the exact semantics of an MQ message. This might include application-specific headers and formatting rules. The RPC Server for IBM MQ supports a general but simplified model of message processing.
To better handle application specific message layout details a user exit
(or callback routine) can be used. The user exit is working on the IBM® MQ
Java representation of an MQ message (class com.ibm.mq.MQMessage) and can
change the MQ message. The user exit gets control:
after an MQ message has been constructed by the RPC Server for IBM MQ and before the message is put to the MQ queue,
after an MQ message has been read from an MQ queue and before it is processed by the RPC Server for IBM MQ.
The user exit can be used, for example, for an application specific
processing of the MQRFH, MQRFH2 or even custom headers.
To enable a user exit, use the property entirex.wmqbridge.userexit to specify the class name of the user
exit implementation. The class will be loaded using the standard classpath. You
can specify a separate classpath with the property
entirex.wmqbridge.userexit.classpath. Note that
for the classpath a file or HTTP URL must be specified. Your user exit class
must implement the Java interface
com.softwareag.entirex.rpcbridge.WMQBridgeExit. This Java
interface has the following methods:
/** ** This method is called after the message has been created by the WMQBridge ** and before the message is sent to an MQ queue (MQPUT). ** The Message object and/or the MessageOptions object can be changed. ** ** @param msg The MQ message object. ** @param pmo The MQPutMessageOptions object. **/ public void beforePut(com.ibm.mq.MQMessage msg, com.ibm.mq.MQPutMessageOptions pmo); /** ** This method is called before a message is retrieved from an ** MQ queue (MQGET). The MessageOptions object can be changed. ** ** @param gmo The MQGetMessageOptions object. **/ public void beforeGet(com.ibm.mq.MQGetMessageOptions gmo); /** ** This method is called after a message has been retrieved from an ** MQ queue (MQGET) and before the message will be processed by the WMQBridge. ** The Message object can be changed. ** ** @param msg The MQ message object. **/ public void afterGet(com.ibm.mq.MQMessage msg);
Calls to MQ Series are non-transactional by default. Thus the request
operates outside the normal unit-of-work protocols. When reading a message with
MQ GET, the message is deleted from the queue immediately.
If an error occurs
in the further processing of the message within the RPC Server for IBM MQ (for
example the translation to RPC or XML results in an error), the message cannot
be made available again. The same applies to sending a message, the MQ PUT
operation makes the message available immediately.
If the RPC client application uses conversational RPC, the MQ calls are
issued transactional (using the SYNCPOINT option).
A Backout Conversation will
send a backout to the queue manager, and a Commit Conversation will send a
commit to the queue manager.
To understand the level of guaranteed delivery provided by the RPC Server for IBM MQ we present the flow of control when reading a message from a queue or writing a message to a queue. Sending a message to an MQ queue:
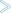 To send a message to an MQ Queue
To send a message to an MQ Queue
The RPC client application sends a send request to the RPC Server for IBM MQ.
The RPC Server for IBM MQ creates a corresponding MQ message and puts the message on the queue. If the remote procedure call is part of an RPC conversation, the message is not committed.
The RPC Server for IBM MQ returns a positive acknowledgment back to the RPC client. If something fails in step 2, an error is returned to the RPC client.
 To receive a message from an MQ Queue
To receive a message from an MQ Queue
The RPC client application sends a receive request to the RPC Server for IBM MQ.
The RPC Server for IBM MQ reads a message from the queue. If no message is available, an error is returned to the RPC client. If the remote procedure call is part of an RPC conversation, the message is not committed.
The RPC Server for IBM MQ creates a corresponding RPC reply that is sent back to the RPC client. If something fails in step 2, an error is returned to the RPC client.
If the send or receive call is part of a conversational RPC, the MQ transaction will get a commit or backout when the RPC conversation is closed, depending on the type of the endConversation call.