This document covers the following topics:
The EntireX .NET Wrapper provides access to RPC servers for .NET client applications and access to .NET servers for any RPC client. The .NET Wrapper generation tools of the Workbench take as input a Software AG IDL file, which describes the interface of the RPC, and generates C# classes that implement the methods and data types of the interface.

The generated classes can be compiled with the C# compiler into a .NET assembly which can then be called from any .NET language.
The .NET Wrapper works as follows:
C# code is generated from the Software AG IDL file. Using C# is a natural choice when full-fledged .NET programming is required, since C# was designed for the .NET platform.
The .NET Wrapper runtime implements functionality that is not specific to a given IDL file (e.g., marshalling and unmarshalling of data). The generated C# code makes use of the .NET Wrapper runtime functionality. The customer interface and the .NET Wrapper runtime is "managed".NET code (C#) and makes use of advanced .NET features such as Attributes, VersionInfo, etc.
The .NET Wrapper runtime makes use of the functionality of the "unmanaged" RPC C runtime (dllimport in C#). "Managed".NET code and "unmanaged" DLL code can be combined safely.
The Software AG IDL Compiler and an appropriate template are used for the C# code generation.
In order to minimize the amount of code generated for a specific IDL, all service-type functionality required by the client interface object or the server DLL is implemented in a generic .NET Wrapper runtime SoftwareAG.EntireX.NETWrapper.Runtime.dll. The generic .NET Wrapper runtime implements service classes, i.e.:
Marshalling .NET data types to Software AG IDL data types
Unmarshalling Software AG IDL data types to .NET data types
Connecting to RPC servers via Broker
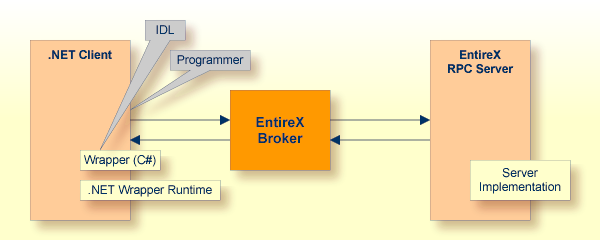
For a given IDL file, the Software AG IDL Compiler and a C# code generation template for clients are used to generate a client interface object. The source code generated by the .NET Wrapper can be compiled into a .NET assembly with the C# compiler. Application developers can use the generated client interface object assembly to write .NET applications that access RPC servers. They are not limited to C# as programming language. Any .NET programming language based on the Common Language Runtime (CLR) can make use of the client interface object assembly. Choices are C#, VisualBasic.NET or managed C++.
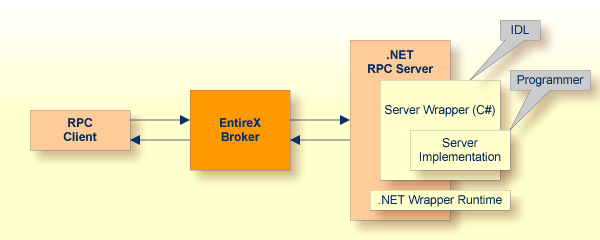
The Software AG IDL Compiler and a C# code generation template for servers are used to generate a C# code frame for a specific IDL. Application developers can use the generated frame to write their own server code for each program in the IDL. The source code can be compiled into a .NET assembly (DLL) with the C# compiler. The assembly name needs to match the library name as specified in the IDL file. At runtime, RPC clients access the .NET Server assembly via the .NET RPC Server.