The .NET RPC Server allows standard RPC clients to communicate with .NET server assemblies. It works together with the .NET Wrapper. This document covers the following topics:
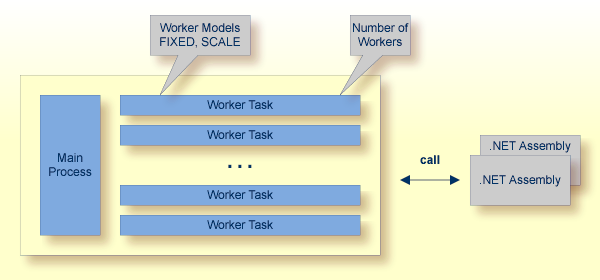
RPC requests are worked off inside the RPC server in worker tasks, which are controlled by a main task. Every RPC request occupies during its processing a worker task. If you are using RPC conversations, each RPC conversation requires its own task during the lifetime of the conversation. The .NET RPC Server provides two worker models:
FIXED
The fixed model creates a fixed number of worker tasks.
The number of worker tasks (defined with minworkers) does not increase or decrease during the lifetime of an RPC server instance.
It is configured by setting the endworkers to value "NEVER". Example:
endworkers=NEVER minworkers=4
SCALE
The scale model creates worker tasks depending on the incoming load of RPC requests.
A maximum number (maxworkers)
of the worker tasks created can be set to restrict the system load.
The minimum number (minworkers),
allows you to define a certain number of tasks - not used by the currently executing RPC request -
to wait for new RPC client requests to process.
In this way the RPC server is ready to handle many RPC client requests arriving at the same time.
It is configured by setting the endworkers
to value "TIMEOUT" or "IMMEDIATE".
With value IMMEDIATE, worker tasks shrink fast, that is, a worker task not used is stopped immediately as soon as it has finished its conversation,
except for the number of workers specified as minimum being active.
With value TIMEOUT, worker tasks shrink slowly,
that is, all worker tasks not used are stopped in the time specified by the
timeout, except for the number of workers
specified as minimum being active.
Example:
endworkers=TIMEOUT minworkers=2 maxworkers=6 timeout=60
The .NET RPC Server uses the .NET Wrapper Runtime to call the .NET Server assemblies. .NET Server assembly skeletons are generated with the .NET Wrapper.
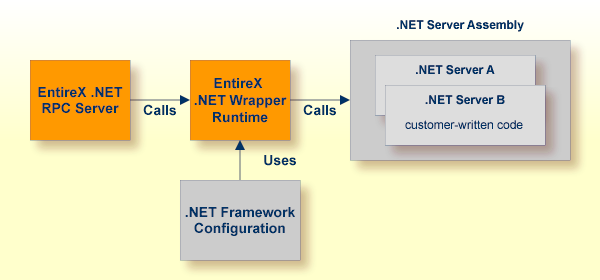
For more information on the .NET RPC Server, .NET Wrapper Runtime and .NET Framework Configuration, see Customizing the RPC Server.