EntireX Broker provides the following internal services: Command Service and Information Service, which can be used to administer and monitor brokers. Because these services are implemented internally, nothing has to be started or configured. You can use these services immediately after starting EntireX Broker. This document covers the following topics:
Queries the Broker for different types of information, generating an
output text string with basic formatting. This text output can be further
processed by script languages. ETBINFO uses data descriptions called profiles
to control the type of data that is returned for a request. ETBINFO is useful
for monitoring and administering EntireX Broker efficiently, for example how
many users can run concurrently and whether the number of specified message
containers is large enough.
Although basic formatting of the output is available, it is usually formatted by script languages or other means external to the Broker.
In a z/OS environment, run the command-line utility ETBINFO as shown below.
Note:
The service data set name and member cannot be accessed directly,
but only indirectly by its DD name in the JCL.
//ETBINFO EXEC PGM=ETBINFO,
// PARM=('ENVAR(''ETB_STUBLOG=0'')/ -p "//''EXX912.JOBS(BROKER)''" ',
// '-bbrokerid -dBROKER -xuid -ypwd')
//STEPLIB DD DISP=SHR,DSN=< EXB-load-lib >
// DD DISP=SHR,DSN=< EXX-load-lib >
// DD DISP=SHR,DSN=< WAL-load-lib >
//TRACE1 DD SYSOUT=* stublog
//SYSOUT DD SYSOUT=* stderr
//SYSPRINT DD SYSOUT=* stdout
//
The SVC number specified in the ADARUN parameter must match the SVC
number used for the target Broker ID.
The table below explains the command-line parameters. The format string and profile parameters are described in detail following the table. All entries in the Option column are case-sensitive.
| Option | Command-line Parameter | Req/ Opt |
Explanation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
-b |
brokerid |
R | Broker identifier, for example
localhost:1971:TCP.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-c |
class |
O | Class as selection criterion. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-C |
O | Create output with comma-separated values, suitable for input into a spreadsheet or other analysis tool. Any format string specified by means of format string or profile command-line parameters is ignored. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-d |
object |
R | Possible values:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-e |
recv class |
O | Receiver's class name. This selection criterion
is valid only for object PSF.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-f |
Format String | O | Format string how you expect the output. See Profile. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-g |
recv service |
O | Receiver's service name. This selection criterion
is valid only for object PSF.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-h |
help |
O | Prints help information. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-i |
convid |
O | Conversation ID as selection criterion. Only
valid for object CONVERSATION.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-I |
conv type |
O | Conversation's type. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-j |
recv server |
O | Receiver's server name. This selection criterion
is valid only for object PSF.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-k |
recv token |
O | Receiver's token. This selection criterion is
valid only for object PSF.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-l |
level |
O | The amount of information displayed:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-m |
recv userid |
O | Receiver's user ID. This selection criterion is
valid only for object PSF.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-n |
server name |
O | Server name. This selection criterion is valid
only for the objects SERVER,
SERVICE or
CONVERSATION.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-p |
pds(member) |
O | Here you can specify a PDS member that defines the layout of the output. There are
default files you can modify or you can use your own. The default files are:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-q |
puserid |
O | Physical user ID. This selection criterion is
valid only for objects CLIENT,
SERVER,
CONVERSATION,
Note: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-r |
sec |
O | Refresh information after seconds. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-s |
service |
O | Service. This selection criterion is valid only
for objects SERVER,
SERVICE or
CONVERSATION.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-t |
token |
O | This selection criterion is valid only for
objects CLIENT,
SERVER,
SERVICE or
CONVERSATION.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-u |
userid |
O | User ID. This selection criterion is only valid
for the display types CLIENT,
SERVER,
SERVICE or
CONVERSATION.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-v |
UOW status |
O | Unit of work status. This selection criterion is
valid only for object PSF.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-w |
UOW ID |
O | Unit of work ID. This selection criterion is
valid only for object PSF.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-x |
userid |
O | User ID. For security purposes. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-y |
password |
O | Password. For security purposes. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-z |
token |
O | Used with userid
to uniquely identify a caller to Command and Information Services.
|
ETBINFO supports an alternative method of passing command-line
parameters.
If the DDNAME INFFILE is allocated, using
//INFFILE DD DISP=SHR,DSN=pds(member)
and no command-line parameters are specified in the EXEC instruction,
the content of the allocated member is evaluated. See sample member below (the
apostrophes are included to show the record format (LRECL 80):
'-blocalhost:3930:TCP ' '-dBROKER '
If ETBINFO is configured using INFFILE and
a profile is specified, the syntax of the -p is
as follows:
-p//'dsname(member)' |
if a PDS member is used |
-p//'dsname' |
if a sequential data set is used |
The syntax is based on IBM conventions for
fopen.
Caution:
Make sure INFFILE does not contain
line numbers in columns 73-80. If line numbers are present, arguments are not
passed correctly.
If you do not use the profile option or a format string, your output will be an unformatted list with all columns of that display type. To display specific columns, specify a profile that includes only those columns.
The following default sample profiles include all the columns defined for each display type:
|
|
|
You can either delete the columns not required or copy the default
profile and modify the order of the columns. Ensure that the column names have
a leading "%". Column names can be written in one line or on
separate lines. The output is always written side by side. With profile parameters %DATE and %TIME you can provide a timestamp for the command-line query.
On z/OS, the profiles used to control the format of data
displayed are members of the EXB source library and are named SERVER, CLIENT,
etc. They can be saved as either sequential files or PDS members.
Profile for object SERVICE: SERVICE.
//ETBINFO EXEC PGM=ETBINFO,PARM=('/-b ETB001::NET -d SERVICE ',
// '-p "//''EXX912.JOBS(SERVICE)''" -l FULL -xUID')
The following list is displayed:
SAG ETBCIS INFO 1 0 16 86400 0 31647 0 00 00 00 00 0 0 SAG ETBCIS USER-INFO 2 0 16 86400 0 31647 0 00 00 00 00 0 0 SAG ETBCIS CMD 6 0 16 86400 0 31647 0 00 00 00 00 0 0
Your own profile: MYPROF
//ETBINFO EXEC PGM=ETBINFO,PARM=('/-b ETB001::NET -d SERVICE ',
// '-p "//''EXX912.JOBS(MYPROF)''" -xUID')
Note:
In this case, MYPROF
contains:%4.4SERVERCLASS %SERVERNAME
The following list is displayed:
ACLA ASERVER BCLA BSERVER CCLA CSERVER
You can find the sample profiles for ETBINFO in your EXB source library.
The format string, if specified, will override the use of a profile. The
format string is built like a printf() in C language.
The string must be enclosed in quotation marks. You can specify the columns by
using a "%" and the column name. The column name must contain
letters only. Numeric characters are not allowed. You can specify the length of
column output by using a format precision, as in the ANSI-C
printf() function. The column name must be followed by
a blank. For example:
etbinfo -b ETB001 -d BROKER -f "%12.12CPLATNAME %NUM-SERVER %NUM-CLIENT"
which produces the following output, for example:
MVS/SP 7.04 30 100
You can also use an arbitrary column separator, which can be any
character other than "%". You can use \n for a new
line in the output and \t for a tabulator in the format string or
profile. For example:
etbinfo -b ETB001 -d SERVER -f "UserID: %5.5USER-ID Token: %5.5TOKEN"
which produces:
UserID: HUGO Token: MYTOK UserID: EGON Token: UserID: HELMU Token: Helmu
If you want to structure your output a little more, you can operate with
the \n or \t character. For example:
etbinfo -b ETB001 -d SERVICE -f "Class:%5.5SERVER-CLASS \n\tName:%5.5SERVER-NAME \n\tService:%5.5SERVICE"
which produces:
Class:DATAB
Name:DB10
Service:Admin
Class:PRINT
Name:LPT1
Service:PRINT
...
You can also add a timestamp to the query:
etbinfo -b ETB001 -d BROKER -f "%DATE %TIME"
which produces:
2014-08-19 10:00:00.234
For establishing an SSL connection on z/OS, IBM's Application Transparent Transport Layer Security (AT-TLS) can be used where the establishment of the SSL connection is pushed down the stack into the TCP layer.
Configure the AT-TLS rules for the policy agent (PAGENT) ![]() using an appropriate client
using an appropriate client ![]() and the z/OS Management Facility (z/OSMF)
and the z/OS Management Facility (z/OSMF) ![]() .
Together with SSL parameters (to provide certificates stored in z/OS as RACF keyrings) define AT-TLS rules, for example by
using the application
.
Together with SSL parameters (to provide certificates stored in z/OS as RACF keyrings) define AT-TLS rules, for example by
using the application ![]() job name and remote TCP port number.
If the rules match, the TCP connection is turned into an SSL connection
job name and remote TCP port number.
If the rules match, the TCP connection is turned into an SSL connection ![]() .
Refer to your IBM documentation for more information, for example the IBM Redbook Communications Server for z/OS VxRy TCP/IP Implementation Volume 4: Security and Policy-Based Networking.
.
Refer to your IBM documentation for more information, for example the IBM Redbook Communications Server for z/OS VxRy TCP/IP Implementation Volume 4: Security and Policy-Based Networking.
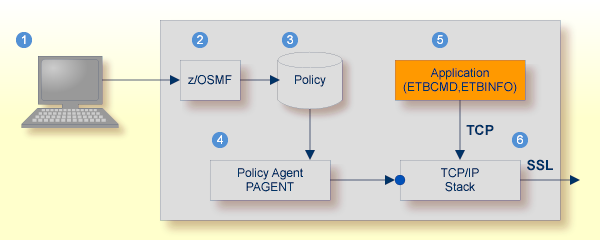
| Client to interact with z/OS Management Facility (z/OSMF). | |
| AT-TLS rules are defined with z/OSMF policy management. | |
| Policy Repository with AT-TLS rules stored as z/OS files. | |
| Policy Agent, MVS task PAGENT, provides AT-TLS rules through a policy enforcement point (PEP) to TCP/IP stack. | |
| Application using TCP connection. | |
| If AT-TLS rules match, the TCP connection is turned into an SSL connection. |
Notes:
 To set up SSL with AT-TLS
To set up SSL with AT-TLS
To operate with SSL, certificates need to be provided and maintained. Depending on the platform, Software AG provides default certificates, but we strongly recommend that you create your own. See SSL/TLS Sample Certificates Delivered with EntireX in the EntireX Security documentation.
Set up the tool for a TCP/IP connection. On mainframe platforms, use Transport-method-style Broker ID. Example:
ETB024:1699:TCP
Configure AT-TLS to turn the TCP/IP connection to an SSL connection, see above.
Make sure the broker is prepared for SSL connections as well. See Running Broker with SSL/TLS Transport under z/OS | UNIX | Windows | z/VSE.
Allows the user to take actions - for example purge a unit of work, stop a server, shut down a Broker - against EntireX Broker.
In a z/OS environment, run the ETBCMD command-line utility like
this:
//ETBCMD EXEC PGM=ETBCMD,
// PARM=('ENVAR(''ETB_STUBLOG=0'')/ -bbrokerid ',
// '-dBROKER -c... -xuid -ypwd')
//STEPLIB DD DISP=SHR,DSN=< EXB-load-lib >
// DD DISP=SHR,DSN=< EXX-load-lib >
// DD DISP=SHR,DSN=< WAL-load-lib >
//TRACE1 DD SYSOUT=* stublog
//SYSOUT DD SYSOUT=* stderr
//SYSPRINT DD SYSOUT=* stdout
//
The SVC number specified in the ADARUN parameter must match the SVC number used for the target Broker ID.
The table below explains the command-line parameters. All entries in the Option column are case-sensitive.
| Command-line Parameter | Option | Parameter | Req/ Opt | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
brokerid |
-b |
e.g. ETB001 |
R | Broker ID. |
command |
-c |
|
R | Command to be performed. See List of Commands and Objects below. |
object type |
-d |
|
R | The object type to be operated on. See List of Commands and Objects below. Within EntireX Broker nomenclature, a participant is an application implicitly or explicitly logged on to the Broker as a specific user. A participant could act as client or server. |
-e |
errornumber |
O | Error number being trapped. | |
-E |
O | Exclude attach servers from service shutdown. | ||
help |
-h |
O | Prints help information. | |
class/server/service |
-n |
class/server/service |
O | Service triplet. |
| option | -o |
|
O | Command option. |
puserid |
-p |
puserid |
O | Physical User ID. For SERVER and PARTICIPANT objects only. This
must be a hex value.
|
seqno |
-S |
sequence number |
O | Sequence number of participant. |
token |
-t |
token |
O | Token. For PARTICIPANT object only.
|
uowid |
-u |
uowid |
O | Unit of work ID. For PSF object only. |
userid |
-U |
userid |
O | User ID. For PARTICIPANT object only.
|
secuserid |
-x |
userid |
O | User ID for security purposes. |
transportid |
-X |
Transport ID | O | One of the following:COM|NET|SSL|Snn|TCP|Tnn. See table below.
|
secpassword |
-y |
password |
O | Password for security purposes. |
This table explains the possible values for parameter transportid:
| Transport ID | Explanation |
|---|---|
COM |
all communicators |
NET |
NET transport communicator |
SSL |
all SSL communicators |
S00 |
SSL communicator 1 |
S01 |
SSL communicator 2 |
S02 |
SSL communicator 3 |
S03 |
SSL communicator 4 |
S04 |
SSL communicator 5 |
TCP |
all TCP/IP communicators |
T00 |
TCP/IP communicator 1 |
T01 |
TCP/IP communicator 2 |
T02 |
TCP/IP communicator 3 |
T03 |
TCP/IP communicator 4 |
T04 |
TCP/IP communicator 5 |
ETBCMD supports an alternative method of passing command-line
parameters.
If the DDNAME CMDFILE is allocated, using
//CMDFILE DD DISP=SHR,DSN=pds(member)
and no command-line parameters are specified in the EXEC instruction, the content of the allocated member is evaluated. See sample member below (the apostrophes are included to show the record format (LRECL 80):
'-blocalhost:3930:TCP ' '-dBROKER '
Caution:
Make sure CMDFILE does not contain
line numbers in columns 73-80. If line numbers are present, arguments are not
passed correctly.
This table lists the available commands and the objects to which they can be applied.
| Command | Object | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ALLOW-NEWUOWMSGS |
x | |||||||
CLEAR-CMDLOG-FILTER |
x | |||||||
CONNECT-PSTORE |
x | |||||||
DISABLE-ACCOUNTING |
x | |||||||
DISABLE-CMDLOG-FILTER |
x | |||||||
DISABLE-CMDLOG |
x | |||||||
DISCONNECT-PSTORE |
x | |||||||
ENABLE-ACCOUNTING |
x | |||||||
ENABLE-CMDLOG-FILTER |
x | |||||||
ENABLE-CMDLOG |
x | |||||||
FORBID-NEWUOWMSGS |
x | |||||||
PING |
x | |||||||
PRODUCE-STATISTICS |
x | |||||||
PURGE |
x | |||||||
RESET-USER |
x | |||||||
SET-CMDLOG-FILTER |
x | |||||||
SHUTDOWN |
x | x | x | x | x | |||
START |
x | |||||||
STATUS |
x | |||||||
STOP |
x | |||||||
SWITCH-CMDLOG |
x | |||||||
TRACE-OFF |
x | x | x | |||||
TRACE-ON |
x | x | x | |||||
| Example | Description |
|---|---|
etbcmd -b etb001 -h |
Displays ETBCMD help text. |
etbcmd -b etb001 -d BROKER -c
TRACE-OFF |
Turns Broker tracing off. |
etbcmd -b etb001 -d BROKER -c TRACE-ON -o
LEVEL2 |
Sets Broker trace level to 2. |
etbcmd -b etb001 -d BROKER -c
SHUTDOWN |
Performs Broker shutdown. |
etbcmd -b etb001 -d SERVICE -c SHUTDOWN -o IMMED -n
ACLASS/ASERVER/ASERVICE |
Shutdown service CLASS=ACLASS,SERVER=ASERVER,SERVICE=ASERVICE.
See also SHUTDOWN SERVICE for more information on
shutdown options.
|
Create list of servers and shutdown specific server in two
steps (first step uses ETBINFO). See also SHUTDOWN SERVER.
|
|
etbinfo -b etb001 -d SERVER -l FULL -f"%USER-ID
%SEQNO" |
1. Determine a list of all servers with sequence numbers. |
etbcmd -b etb001 -d SERVER -c SHUTDOWN -o IMMED
-S32 |
2. Shutdown server with sequence number 32. |
etbcmd -b etb001 -d BROKER -c
PING |
Performs an EntireX ping against the Broker. |
etbcmd -b etb001 -d PSF -c
DISCONNECT-PSTORE |
Disconnects the Broker PSTORE. |
etbcmd -b etb001 -d PSF -c
CONNECT-PSTORE |
Connects the Broker PSTORE. |
etbcmd -b etb001 -d PSF -c PURGE -u
100000000U00001A |
Purges a unit of work. |
etbcmd -b etb001 -d PSF -c
ALLOW-NEWUOWMSGS |
Allows new units of work to be stored. |
etbcmd -b etb001 -d PSF -c
FORBID-NEWUOWMSGS |
Disallows new units of work to be stored. |
For establishing an SSL connection on z/OS, IBM's Application Transparent Transport Layer Security (AT-TLS) can be used where the establishment of the SSL connection is pushed down the stack into the TCP layer.
Configure the AT-TLS rules for the policy agent (PAGENT) ![]() using an appropriate client
using an appropriate client ![]() and the z/OS Management Facility (z/OSMF)
and the z/OS Management Facility (z/OSMF) ![]() .
Together with SSL parameters (to provide certificates stored in z/OS as RACF keyrings) define AT-TLS rules, for example by
using the application
.
Together with SSL parameters (to provide certificates stored in z/OS as RACF keyrings) define AT-TLS rules, for example by
using the application ![]() job name and remote TCP port number.
If the rules match, the TCP connection is turned into an SSL connection
job name and remote TCP port number.
If the rules match, the TCP connection is turned into an SSL connection ![]() .
Refer to your IBM documentation for more information, for example the IBM Redbook Communications Server for z/OS VxRy TCP/IP Implementation Volume 4: Security and Policy-Based Networking.
.
Refer to your IBM documentation for more information, for example the IBM Redbook Communications Server for z/OS VxRy TCP/IP Implementation Volume 4: Security and Policy-Based Networking.

| Client to interact with z/OS Management Facility (z/OSMF). | |
| AT-TLS rules are defined with z/OSMF policy management. | |
| Policy Repository with AT-TLS rules stored as z/OS files. | |
| Policy Agent, MVS task PAGENT, provides AT-TLS rules through a policy enforcement point (PEP) to TCP/IP stack. | |
| Application using TCP connection. | |
| If AT-TLS rules match, the TCP connection is turned into an SSL connection. |
Notes:
 To set up SSL with AT-TLS
To set up SSL with AT-TLS
To operate with SSL, certificates need to be provided and maintained. Depending on the platform, Software AG provides default certificates, but we strongly recommend that you create your own. See SSL/TLS Sample Certificates Delivered with EntireX in the EntireX Security documentation.
Set up the tool for a TCP/IP connection. On mainframe platforms, use Transport-method-style Broker ID. Example:
ETB024:1699:TCP
Configure AT-TLS to turn the TCP/IP connection to an SSL connection, see above.
Make sure the broker is prepared for SSL connections as well. See Running Broker with SSL/TLS Transport under z/OS | UNIX | Windows | z/VSE.