Element types
The essential components of a DTD are element types. Instances of element types that occur in the DTD model hierarchy may occur in a valid XML document and are called elements.
Each element type is described by its content and its attribute types.
Three types of element types can be distinguished by their content:
Element types with text as content
Element types without content
Element types with text and/or other element types as content
To describe an element type that has only text as its content, you place an Element type object with the required name and an element of the Contents type with the #PCDATA symbol. You then draw a connection of the contains type between the element type and the content.
To describe an element type without content, you place an Element type object with the required name and an element of the Contents type with the EMPTY symbol. You then draw a connection of the contains type between the element type and the content. A typical example of an element type without content is the <img> tag in HTML. The essential benefit of empty element types is that they can have useful attributes, such as the SRC, ALIGN, ALT, and ISMAP attributes of the img tag.
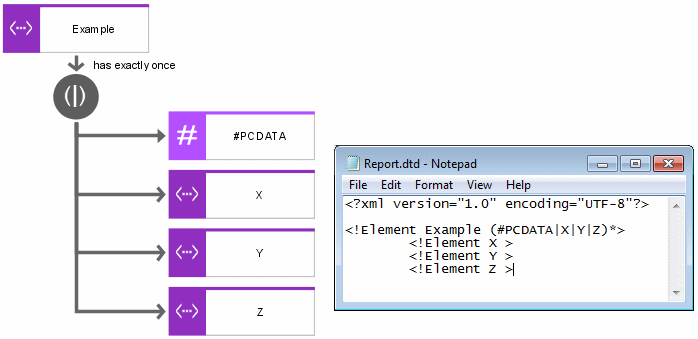
The most complex form of an element type is an element type with mixed content. In this case, text or element types can be assigned to an object of the Element type type. To describe the form in which assignments are linked to each other, rules can be used. The connections between element type and assignments describe how often an assignment may occur in the element type content.
The sequence operator and the XOR rule are available for the purpose of linking assignments.
If only one of a specified number of assignments is allowed in the content of the element type being described, the assignments must be linked to each other by an XOR rule.
If multiple assignments are allowed in the content of the element type being described, but only in a certain order, they must be linked by a sequence operator. To clearly define the required order, specify the relevant position for the assignment at the connection between the operator and the assignment.
Assignments can also be linked to the element described without using operators. In this case it is assumed that the sequence may be of any order.