Implicit IO Rules
As a shortcut to this exact but complex modeling convention the following definitions allows a modeler to create well defined data IO definitions without the need to create an extra BPMN allocation diagram:
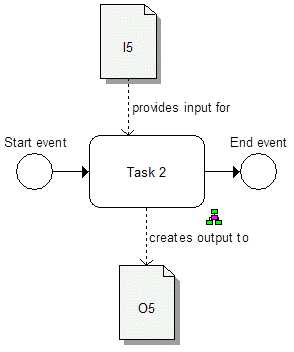
If an Artefact (I5) is connected directly towards a Task with an provides input for connection and that task is NOT connected towards an IORule object with an belongs to input set connection an implicit connection belongs to towards an invisible IORule object Implicit IO Rule is assumed.
If a Task is connected directly towards a Artefact (I6) with an provides output to connection and that Artefact is NOT connected towards an IORule object with an belongs to output set connection an implicit connection belongs to output set towards an invisible IORule object Implicit IO Rule is assumed.
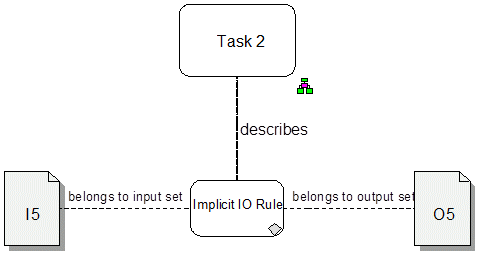
In that case, the folloging two figures represent the same IO behavior.
This diagram represents the same semantic than above (see page ), but can be modeled without an extra Allocation Diagram.
This diagram represents the same semantic as Figure above.
The Input Property Map defines which properties of the parent process are copied to which properties of the independent target sub process (before the target process is executed).
The Output Property Map defines which properties of the independent sub process are copied to which properties of the calling parent process (after the target process has been completed).
ARIS does this mapping graphically inside a BPMN Allocation Diagram which has to be assigned to the sub process symbol.