Mediation and Policy Enforcement
Through service virtualization, Mediator serves as an intermediary between service consumers and service providers. This means that service requests sent from a service consumer actually go to a virtual service hosted on Mediator for processing rather than directly to the service provider. A virtual service is an enhanced copy of a service provider's Web service and acts as the consumer-facing proxy for the provider's Web service. You configure virtual services in CentraSite and deploy them to a Mediator server.
Alternatively, if you have Web services that have been externalized as APIs, the requests sent from a service consumer go to a virtualized API hosted on Mediator for processing. You virtualize an API using the CentraSite Business UI and deploy them to a Mediator server. Mediator provides virtual OData services. OData services are a special kind of virtualized APIs.
You can create policies for virtual services or virtualized APIs which provide run-time governance capabilities for them. A policy is a sequence of actions that is carried out by Mediator when a consumer requests a particular service through Mediator. The actions in a policy perform activities such as identifying/authenticating consumers, validating digital signatures, and capturing performance measurements. An action is a single task that is included in a policy and is evaluated by Mediator at run time. Actions have one or more parameters which you configure when you insert the actions into a policy. For example, an action that identifies consumers specifies one or more identifiers to identify the consumers who are trying to access the services.
Mediator provides built-in action templates. A built-in action template is a definition of an action that can be used in a policy. An action template specifies the set of parameters associated with a particular policy action. You can use these action templates to create actions for your policies.
Mediation also provides improved interoperability between consumers and providers. Since all requests from the service consumer pass through Mediator, you can configure the virtual service to make any necessary changes to the message or its protocols before engaging with the provider.
Example
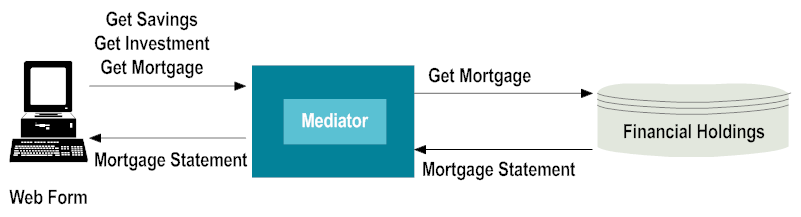
In a regular scenario, a request from a consumer application goes directly to a Web service exposed by the service provider. In a mediated system, the request goes through Mediator where policies are applied to the Web service and are enforced by Mediator.
For example, a consumer application could be a Web form filled out by a bank employee looking for all the records for a customer: savings, investment, and mortgage. The Customer Data service handles requests for such data, therefore, Mediator applies the policies to the request. The policies it enforces for the service dictate that the employee making the request is eligible to see the mortgage data, but none of the other data requested. The service retrieves the mortgage data from the Financial Holdings service provider and returns it to the consumer application.