Working with Event Rules
An event rule is a decision entity that specifies the results triggered by an event. There are two types of events:
Internal Events.
External Events.
Internal Events are triggered by other event rules and decision tables during rule execution. External events are predefined event types that were created with the webMethods Event Type Editor, see webMethods Event-Driven Architecture Help.
Important: | To work properly, internal and external event rules must be part of a rule set. |
Event Rule Structure
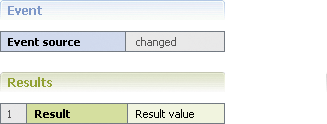
An event rule consists of an event (blue color) and one or more results (green color).
Event
The event consists of an event source that is specified by a parameter element and a type. The following types are supported:
Event | Type | Description |
Internal Event | changed | This type triggers one or more results whenever the event source changes. The change must be triggered by other event rules or decision tables. Changed type event rules have the following syntax: WHENEVER an Event Source CHANGED THEN Result. |
External Event | occurred | This type triggers one or more results whenever the external event occurres. Occurred type event rules have the following syntax: WHENEVER an Event Source OCCURRED THEN Result. |
Results
There are two types of results:
Result | Description |
Assignment Result | An assignment result is specified by a parameter element. This result type is applied, whenever you want to assign a value to a result. |
Action Result | An action result is specified by an action. This result type is applied, whenever you want to execute an action from an event rule. |
Assignment Result Values
An assignment result value can consist of:
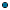
An operator and a literal value.
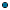
An operator and a parameter element (marked by a dotted line).
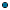
An operator and an action that delivers an output value (marked by a dotted line and () behind the action name).
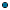
An operator and a constant (marked by a dotted line).
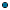
An operator and an expression.
Action Result Values
The action result value expresses the action status. There are two types:
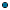
(action is enabled).
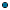
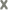
(action is disabled).
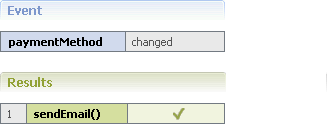
Example
The following rule can be modeled in an event rule:
Rule | WHENEVER a permitted payment method changes for a customer, THEN this customer is notified of this by email. |