Shift calendar
Shift calendars can be assigned to human and technical resources to specify when a resource is available.
Organizational charts or EPCs are the appropriate models for assigning shift calendars to resources. Shift calendars can be assigned to any human or technical resource. In a hierarchy of human resources, the relevant calendar is always the one located on the lowest hierarchy level.
A shift calendar is a multi-level object model. The lowest level provides objects of the Break type. A break is the daily time interval within a shift during which no work is performed. The break is defined by its relative start and its duration. The relative start always relates to the shift to which the break is assigned. For example, if the shift begins at 8:00 a.m. and the break has a relative start of 2 hours, the break begins at 10:00 a.m.
The next hierarchy level contains objects of the Shift type. A shift is the daily time interval during which work is performed. The shift is defined by its relative shift start and its duration. A shift may have more than one break. The relative start times of breaks must lie within the shift times.
Typical examples of shifts are the early, midday, night, and day shifts. Each shift is repeated every 24 hours. A shift cycle is the weekly or multi-day time interval during which work is performed. The shift cycle thus determines the days on which a certain shift is run or is not run. The shift cycle is defined by its relative cycle start and cycle duration. The requirement that a shift cycle be continuously repeated can be defined using the Repeat in cycles attribute. In addition, the Period attribute determines how often a cycle is repeated.
Shift cycles frequently cover a period of one or two weeks. An employee can thus have an early shift one week and a midday shift the next. This sequence can be constantly repeated using shift cycles.
Example
In line with the example above, two shift cycles can be defined:

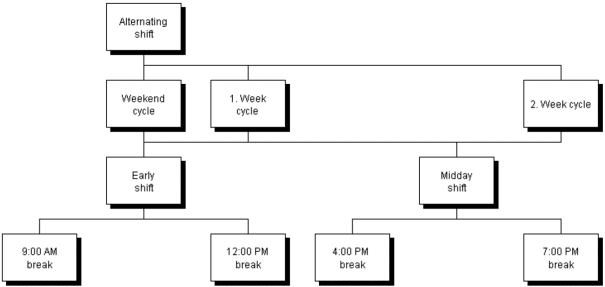
Early shift shift cycle:
Relative cycle start = 0
Cycle duration = 5 days
Repeat in cycles = yes
Period = 14 days

Midday shift shift cycle:
Relative cycle start = 7 days
Cycle duration = 5 days
Repeat in cycles = yes
Period = 14 days
The individual shifts are repeated in a 14-day rhythm, that is, the periodicity is 2 weeks. If the same employee were to work an early shift on Saturdays every four weeks, the third shift cycle could be defined as follows:

Early shift shift cycle:
Relative cycle start = 20 days
Cycle duration = 1 day
Repeat in cycles = yes
Period = 28 days
The above example is illustrated as a model below. A 1 : n allocation of shifts and shift cycles is shown.
A shift calendar is the total number of shift cycles and associated shifts describing the working hours of a resource. This description contains only the part that is repeated periodically; special rules regulating vacation, sick leave, holidays, or other days on which no work is performed are not included here.
The Shift plan object type includes the Plan start and Plan duration attributes. These attributes specify the time period during which the shift calendar is valid. Furthermore, the Repeat in cycles and Period attributes also exist for the shift calendar.