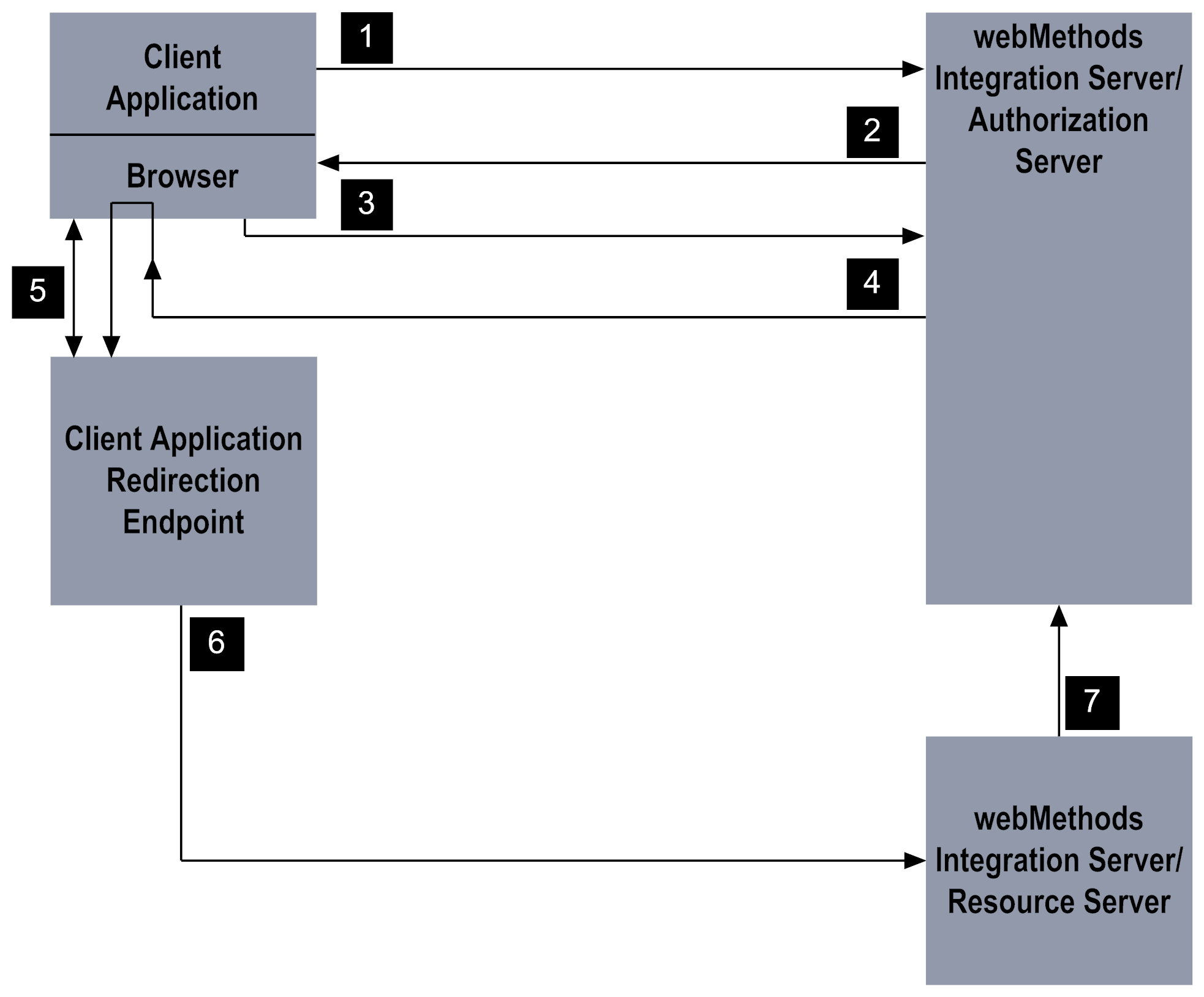

Stage | Description |
1 | The client application initiates the process by calling the pub.oauth:authorize service to request access to the resource owner’s data. |
2 | The pub.oauth:authorize service validates the request. If valid, the service responds with an HTML page that informs the owner that the client application is requesting access within a specified scope. The resource owner uses a form on the HTML page to approve or deny the request. |
3 | When the resource owner approves the request, the approval page invokes an internal service on Integration Server. If the resource owner denies the request, an error is returned. |
4 | Integration Server redirects the resource owner's browser to the client application's redirection endpoint, appending the access token as a fragment on the redirection URI. |
5 | The resource owner’s browser holds the access token in memory until the client application retrieves the access token. |
6 | The client application uses the access token to execute a service on the resource server. |
7 | The resource server checks with authorization server to make sure the requested service is within the scope for which the access token was issued and whether the client is authorized to access the folders and services in the scope. |